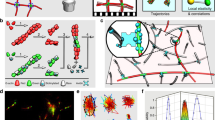
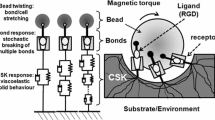
Abstract
An improved magnetic bead microrheometer based on phase contrast microscopy allowing high resolution measurements of local deformations within macromolecular networks is applied to study local viscoelastic properties of cross-linked actin networks. By embedding non-magnetic colloidal beads as probes into the networks, the spatial variation of the strain field within cross-linked actin networks can be mapped. Moreover, the Poisson ratio and shear modulus can be measured locally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darnell J, Lodish H, Baltimore D (1990) Molecular cell biology. Scientific American Books, New York
Door R, Frösch D, Martin R (1991) Estimation of section thickness and quantification of iron standards with EELS. J Microsc 162: 15–22
Elias HG (1971) Makromoleküle. Struktur, Eigenschaften, Synthesen, Stoffe. Hüthig & Wepf, Basel
Evans E, Ritchie K, Merkel R (1995) Sensitive force technique to probe molecular adhesion and structural linkages at biological interfaces. Biophys J 68: 2580–2587
Finer JT, Simmons RM, Spudich JA (1994) Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps. Nature 368: 113–119
Ishijima A, Doi T, Sakurada K, Yanagida T (1991) Sub-piconewton force fluctuations of actomyosin in vitro. Nature 352:301–306 Kuo SC, Sheetz MP (1992) Optical tweezers in cell biology. TIBS 2: 116–118
Landau LD, Lifshitz EM (1959) Course of theoretical physics, Vol 6. Fluid mechanics. Pergamon Press, London
Landau LD, Lifshitz EM (1959) Course of theoretical physics, Vol 7. Theory of elasticity. Pergamon Press, London
Müller O (1991) Entwicklung eines Rheometers zur Untersuchung viskoelastischer Eigenschaften membranassoziierter Aktinnetzwerke im verdünnten and halbverdünnten Bereich. Doctoral thesis, TU München
Müller O, Gaub HE, Bärmann M, Sackmann E (1991) Viscoelastic moduli of sterically and chemically cross-linked actin networks in the dilute to semi-dilute regime: measurements by an oscillating disk rheometer. Macromolecules 24: 3111–3120
Piekenbrock T, Sackmann E (1992) Quasielastic light scattering study of thermal excitations of F-actin solutions and of growth kinetics of actin filaments. Biopolymers 32: 1471–1489
Ruddies R, Goldmann WH, Isenberg G, Sackmann E (1992) The viscoelastic moduli of actin/filamin solutions: A micro-rheologic study. Biochem Soc Trans 21: 37S
Ruddie R, Goldmann WH, Isenberg G, Sackmann E (1993) The viscoelasticity of entangled actin networks: the influence of defects and modulation by talin and vinculin. Eur Biophys J 22: 309–321
Sackmann E (1994) Intra- and extracellular macromolecular networks: physics and biological function. Macromol Chem Phys 195: 7–28
Schindl M, Wallraff E, Deubzer B, Witke W, Gerisch G, Sackmann E (1995) Cell-substrate interactions and locomotion of dictyostelium wild-type and mutants defective in three cytoskeletal proteins: a study using quantitative reflection interference contrast microscopy. Biophys J 68: 1177–1190
Schleicher M, Gerisch G, Isenberg G (1984) New actin-binding proteins from dyctostelium discoideum. EMBO (Eur Mol Biol Organ) J 3: 2095–2100
Schmidt C (1988) Struktur und Dynamik polymerer Aktinnetzwerke und ihre Wechselwirkung mit Modellmembranen. Doctoral thesis, TU München
Stossel TP (1994) The machinery of cell crawling. Sci Amer 271 (3): 54–55, 58–63
Svoboda K, Schmidt CF, Schnapp BJ, Block SM (1993) Direct observation of kinesin stepping by optical trapping interferometry. Nature 365: 721–727
Wachsstock DH, Schwarz WH, Pollard TD (1993) Affinity of α-actinin for actin determines the structure and mechanical properties of actin filament gels. Biophys 165: 205–214
Wang N, Butler JP, Ingber DE (1993) Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science 260: 1124–1127
Zaner KS, Valberg PA (1989) Viscoelasticity of F-actin measured with magnetic microparticles. J Cell Biol 109: 2233–2243
Ziemann F, Rädler J, Sackmann E (1994) Local measurements of viscoelastic moduli of entangled actin networks using an oscillating magnetic bead microrheometer. Biophys 166: 2210–2216
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, F.G., Ziemann, F. & Sackmann, E. Shear field mapping in actin networks by using magnetic tweezers. Eur Biophys J 24, 348–353 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180376
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180376