Abstract
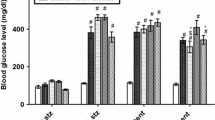
The changes in the pharmacological responses to cesium were examined in streptozotocin(STZ)-induced diabetic mice. An acute administration of cesium chloride (10 mEqCs+/kg IP) to non-diabetic control mice elicited increased salivation and inhibition of respiration followed by death in about half of the animals examined. These effects of cesium were diminished in STZ-diabetic mice. LD50 for acute cesium was higher in STZ-diabetic mice (14.3 mEq/kg) than non-diabetic buffer controls (11.7 mEq/kg); however, subchronic administration of cesium did not decrease the LD50 in STZ-diabetic mice. The sleeping time induced by pentobarbital was reduced in STZ-diabetic mice and the reduction of the pentobarbital-induced hypnosis was reversed by subchronic cesium pretreatment but not by acute cesium administration. Methamphetamine-induced mortality was increased in STZ-diabetic mice and acute administration of cesium decreased the toxicity in both control and diabetic mice. Inhibition of locomotor activity elicited by acute single injection of cesium chloride was observed in both STZ-diabetic and non-diabetic mice. These results indicate that responses to cesium as well as centrally-acting drugs are affected differentially in STZ-diabetic mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bose R, Pinsky C (1984) Central depressant action of cesium in mice. Psychopharmacology 84:80–84
Chance MRA (1946) Aggregation as a factor influencing the toxicity of sympathomimetic amines in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 87:214–219
Cochran KW, Doull J, Mazur M, DuBois KP (1950) Acute toxicity of zirconium, columbium, strontium, lanthanum, cesium, tantalum and yttrium. Arch Indust Hyg Occup Med 1:637–650
Dixon WJ (1965) The up-and-down method for small samples. J Am Statist Assoc 60:967–978
Eichelman B, Thoa NB, Perez-Cruet J (1973) Alkali metal cations: Effects on aggression and adrenal enzymes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1:121–123
Fujii E, Nomoto T, Tsukahara F, Aoki K, Tanaka R, Fujii A, Furiya Y, Maetani H (1983) Antinociceptive potency of morphine in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. J Tokyo Wom Med Coll 53:1039–1045 (Abstract in English)
Fujii E, Tsukahara F, Nomoto T (1984) Influences of drugs in streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic mice (III): Alterations in the sensitivity to ketamine anesthesia and antinociceptive potency of thalamonal. Jpn J Pharmacol [Suppl] 36:334p
Jenner FA, Judd A, Parker J (1975) The effects of lithium, rubidium and cesium on the response of rats to tranylcypromine and alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine given separately or in combination. Br J Pharmacol 54:233–234
Jones GR, Lazarus JH, Davies CJ, Greenwood RH (1983) The effect of short term lithium carbonate in Type II diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res 15:422–424
Johnson FN (1972) Effects of alkali metal chlorides on activity in rats. Nature 238:333–334
Kuntscherová J, Vlk J (1970) Influence of alloxan diabetes on acetylcholine synthesis in tissue of the albino rat. Physiol Bohemoslov 19:431–434
Lasagna L, McCann WP (1957) Effect of tranquilizing drugs on amphetamine toxicity in aggregated mice. Science 125:1241–1242
Messiha FS (1976) Distribution and retention of exogenously administered alkali metal ions in the mouse brain. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 219:87–96
Messiha FS (1978a) Anti-depressant action of caesium chloride and its modification of chlorpromazine toxicity in mice. Br J Pharmacol 64:9–12
Messiha FS (1978b) Cesium and rubidium salts: Effects on voluntary intake of ethanol by the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 9:647–651
Niedermeier W, Griggs JH (1971) Trace metal composition of synovial fluid and blood serum of patients with rhematoid arthritis. J Chronic Dis 23:527–536
Pinsky C, Bose R, Dua A. K, Bigornia L (1980) Interdisciplinary studies on brain level determination and behavioral effects of Cesium (Cs). Pharmacologist 22:158
Pinsky C, Bose R, Taylor JR, McKee JSC, Lapointe C, Birchall J (1981) Cesium in mammals: Acute toxicity, organ changes and tissue accumulation. J Environ Sci Health(A) 5:549–567
Rastogi RB, Singhal RL, Lapierre YD (1980) Effects of rubidium and cesium on central catecholamines and locomotor behavior in rats. J Neurochem 34:1764–1767
Richmond CR (1980) Retension and excretion of radionuclides of the alkali metals by five mammalian species. Health Phys 38:1111–1153
Saran AS (1982) Antidiabetic effects of lithium. J Clin Psychiatry 43:383–384
Tsukahara F, Fujii E, Nomoto T (1983) Influences of drugs in streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic mice (I): Alterations in the sensitivity to the pentobarbital hypnosis and hypothermia. Jpn J Pharmacol [Suppl] 33:246p
Zdankiewicz DD, Fasching JL (1976) Analysis of whole blood by neutron activation: A search for a biochemical indicator of neoplasia. Clin Chem 22:1361–1365
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, E., Nomoto, T. Central action of cesium chloride in streptozotocin-diabetic mice. Psychopharmacology 93, 173–177 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179929
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00179929