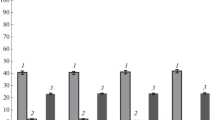
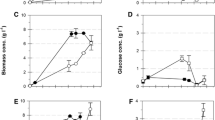
Summary
Transposon Tn 951-encoded β-galactosidase was expressed in Pseudomonas saccharophila and enabled this bacterium to grow on lactose as sole carbon source. In contrast, β-galactosidase was not expressed in Alcaligenes eutrophus even if the lacZ gene of Tn 951 was separated from the lacI gene. However, β-galactosidase was expressed in A. eutrophus, if a DNA fragment, which was suspected to harbour the promoter of the A. eutrophus poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid)-synthetic genes, was ligated to the promoter probe vector pMC1403, which employs lac Z, Y as reporter genes. Plasmid pPL76, which harboured one of the promoter-lac fusions, enabled A. eutrophus not only to express β-galactosidase but also to grow slowly on lactose (doubling time = 25–30 h). Subsequently, the promoter-lac fusion was ligated to Tn5 in pSUP5011 and was inserted into the genome of A. eutrophus H16 and of the glucose-utilizing mutant H16-G+1 by applying the suicide plasmid technique. Two recombinant strains, H16-cPL and H16-G+1-cPL, which grow with a doubling time of 16–23 h on lactose, were investigated in detail. The cells only utilized the glucose residue of lactose as a carbon source for grouth and excreted galactose into the medium. Only after the Escherichia coli gal operon had been cloned in vector pVK101 and had been mobilized to H16-cPL or H16-G+1-cPL, was lactose completely utilized; no galactose was detected in the medium and the growth yields increased twofold. Depending on the orientation of the gal operon in pVK101, the expression of galactokinase seems to be dependent either on the promoter of aminoglycoside phosphotransferase gene (kan) or on the promoter of the tetR gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtmann MA, Clak AJ (1971) Beginning in genetic analysis of conjugational transfer determined by the F factor in Escherichia coli by isolation and characterization of transfer deficient mutants. J Bacteriol 106:529–536
Baumberg S, Cornelis G, Panagiotakopoulos M, Roberts M (1980) Expression of the lactose transposon Tn 951 in Escherichia coli, Proteus and Pseudomonas. J Gen Microbiol 129:2825–2835
Bergmeyer HU, Bernt E, Schmidt F, Stork H (1974) In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1241–1246
Bowien B, Schlegel HG (1981) Physiology and biochemistry of aerobic hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria. Ann Rev Microbiol 35:405–452
Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D (1969) A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 41:459–472
Bullock WO, Fernandez JM, Short JM (1987) XL1-Blue: a high efficiency plasmid transforming rec A Escherichia coli strain with beta-galactosidase selection. Biotechniques 5:376–379
Byrom D (1987) Polymer synthesis by microorganisms: technology and economics. TIBTECH 5:246–250
Casadaban MJ, Cohen SN (1979) Lactose genes fused to exogenous promoters in one step using a Mu-lac bacteriophage: in vivo probe for transcriptional control sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4530–4533
Casadaban MJ, Chon J, Cohen SN (1980) In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active \-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol 143:971–980
Cornelis C, Debarota G, Saedler H (1978) A new transposon carrying a lactose operon. Mol Gen Genet 160:215–224
Cornelis G, Ghosal D, Saedler H (1979) Multiple integration sites for the lactose transposon Tn951 on plasmid RP1 and establishment of a coordinate system for Tn951. Mol Gen Genet 168:61–167
Ditta G, Schmidhauser T, Yakobson E, Lu P, Liang XW, Finlay DR, Guiney D, Helinski DR (1985) Plasmid related to the broad host range vector, pRK290, useful for gene cloning and for monitoring gene expression. Plasmid 13:149–153
Doi Y, Tamaki A, Kunioka M, Soga K (1987) Biosynthesis of terpolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, and 5-hydroxyvalerate in Alcaligenes eutrophus from 5-chloropentanoic and pentanoic acids. Makromol Chem Rapid Commun 8:631–635
Doudoroff M (1940) The oxidative assimilation of sugars and related substances by Pseudomonas saccharophila with a contribution to the problem of the direct respiration of di- and polysaccharides. Enzymologia 9:59–72
Doudoroff M, Stanier RY (1959) Role of poly-\-hydroxybutyric acid in the assimilation of organic carbon by bacteria. Nature 183:1440–1442
Farabaugh PJ (1978) Sequence of the lac I gene. Nature 274:765–769
Friedrich B, Hogrefe C, Schlegel HG (1981) Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 147:198–205
Fritz HJ, Bicknäse H, Gleums B, Heibach C, Rosahl S, Ehring R (1983) Characterization of two mutations in the Escherichia coli gal E gene inactivating the second galactose operator and comparative studies of repressor binding. EMBO J 2:2129–2135
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1989) The importance of PHB-synthase substrate specificity in polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis by Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 57:1–6
Heinrich MR, Howard SM (1966) Galactokinase. Methods Enzymol 9:407–408
Holmes PA (1985) Applications of PHB — a microbially produced biodegradable thermoplastic. Phys Technol 16:32–36
Holmes PA, Wright LF, Collins SH (1981) \-Hydroxybutyrate polymers. European patent application EP 052.459
Husemann M, Klintworth R, Büttcher V, Salnikow J, Weissenborn C (1988) Chromosomally and plasmid-encoded gene clusters for CO2 fixation (cfx genes) in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Mol Gen Genet 214:112–120
Kado CI, Liu ST (1981) Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol 145:1365–1373
Kandler O (1963) Carbohydrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 49:209–224
Knauf VC, Nester EW (1982) Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid 8:45–54
König C, Sammler J, Wilde E, Schlegel HG (1969) Konstitutive Glucose-6-phosphat-Dehydrogenase bei Glucose verwertenden Mutanten von einem kryptischen Wildstamm. Arch Mikrobiol 67:51–57
Kortlüke C, Hogrefe, Eberz G, Pühler A, Friedrich B (1987) Genes of lithoautotrophic metabolism are clustered on the megaplasmid pHG1 in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Mol Gen Genet 210:122–128
Kuhn M, Jendrossek, Fründ C, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus alcohol dehydrogenase gene. J Bacteriol 170:685–692
Kunioka M, Nakamura Y, Doi Y (1988) New bacterial copolyesters produced in Alcaligenes eutrophus from organic acids. Polymer Commun 29:174–176
Kurz G, Wallenfels K (1974) Lactose und andere \-d-Galactoside. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse. 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1225–1229
Lemaire HG, Müller-Hill B (1986) Nucleotide sequences of the gal E gene and the gal T gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res 14:7705–7711
Lessie TG, Phibbs PV (1984) Alternative pathways of carbohydrate utilization in pseudomonads. Ann Rev Microbiol 38:359–387
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrock J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of desoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Miller JH (1972) Assay of \-galactosidase. In: Platt T, Müller-Hill B, Miller JH Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp 319 and 353
Nano FE, Kaplan S (1982) Expression of the transposable lac operon Tn951 in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol 152:924–927
Oelmüller U, Krüger N, Steinbüchel A, Friedrich CG (1990) Isolation of prokaryotic RNA and detection of specific messenger RNA with biotinylated probes. J Microbiol Methods 11:73–81
Pedrós-Alió C, Mas J, Guerrero R (1985) The influence of poly-\-hydroxybutyrate accumulation on cell volume and bouyant density in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol 143:178–184
Perfoen M, Huybrechts R, DeLoof A (1982) Vaccuum-blotting: a new simple and efficient transfer of proteins from sodium dodecylsulfate polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose. FEBS Lett 145:369–372
Peoples OP, Sinskey AJ (1989) Fine structural analysis of the Zoogloea ramigera phbA-phbB locus encoding \-ketothiolase and acetoacetyl-CoA reductase: nucleotide sequence of phb-B. Mol Microbiol 3:359–357
Rüther U, Koenen M, Otto K, Müller-Hill B (1981) pUR322, a vector for cloning and rapid chemical sequencing of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 9:4087–4098
Schlegel HG, Gottschalk G (1965) Verwertung von Glucose durch eine Mutante von Hydrogenomonas H16. Biochem Z 341:249–259
Schlegel HG, Gottschalk G, Bartha R von (1961a) Formation and utilization of poly-\-hydroxybutyric acid by Knallgasbacteria (Hydrogenomonas). Nature 191:463–465
Schlegel HG, Kaltwasser H, Gottschalk G (1961b) Ein Submersverfahren zur Kultur wasserstoffoxydierender Bakterien: Wachstumsphysiologische Untersuchungen. Arch Mikrobiol 38:209–222
Schmidt K, Jensen SL, Schlegel HG (1963) Die Carotinoide der Thiorhodaceae. I. Okenon als Hauptcarotinoid von Chromatium okenii Perty. Arch Mikrobiol 46:117–126
Schubert P, Steinbücel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for synthesis of poly-\-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) and synthesis of PHB in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5837–5847
Simon R (1984) High frequency mobilization of Gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn 5-mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet 196:413–420
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784–791
Slater SC, Voige WH, Dennis DE (1988) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 poly-\-hydroxybutyrate biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol 170:4431–4436
Srivastava S, Urban M, Friedrich B (1982) Mutagenesis of Alcaligenes eutrophus by insertion of the drug-resistance transposon Tn5. Arch Microbiol 131:203–207
Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1989) Excretion of pyruvate by mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus, which are impaired in the accumulation of poly(\-hydroxybutyric acid) (PHB), under conditions permitting synthesis of PHB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:168–175
Steinbüchel A, Fründ C, Jendrossek D, Schlegel HG (1987) Isolation of mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus unable to derepress the fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol 148:178–186
Wilde E (1962) Untersuchungen über Wachstum und Speicherstoffsynthese von Hydrogenomonas. Arch Mikrobiol 43:109–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: A. Steinbüchel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pries, A., Steinbüchel, A. & Schlegel, H.G. Lactose- and galactose-utilizing strains of poly(hydroxyalkanoic acid)-accumulating Alcaligenes eutrophus and Pseudomonas saccharophila obtained by recombinant DNA technology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 410–417 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176656
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176656