Summary
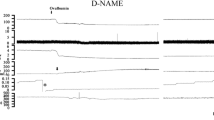
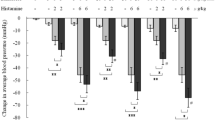
The modulating effects of exogenous and endogenous nitric oxide (NO) on the cardiac anaphylactic reaction and eicosanoid release were investigated in isolated perfused sensitized guinea-pig hearts using 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1), the active metabolite of molsidomine, as NO-donor and NG-nitro-l-arginine (NNA) as an inhibitor of NO biosynthesis. Infusion of SIN-1 (final concentrations in the perfusates 0.3 or 1.0 mmol/l) elevated coronary flow under basal conditions as well as during cardiac anaphylaxis, while NNA (0.1 mmol/l) decreased basal coronary flow and aggravated the anaphylactic coronary constriction. Both drugs did not modify the characteristic biphasic profile of the coronary constriction after antigen challenge with an initial more severe phase followed by a less pronounced long-lasting flow reduction. Neither SIN-1 nor NNA affected spontaneous heart rate. However, while NNA tended to prolong the duration of antigen-induced arrhythmias, SIN-1 (1 mmol/l) had an inhibitory effect. This protection might be related to the increased coronary flow in the presence of SIN-1. SIN-1 inhibited anaphylactic release of cysteinyl-leukotrienes (LT) and 6-keto-prostaglandin (PG) F1α, but did not influence thromboxane (TX) B2 release. On the other hand, NNA (0.1 mmol/l) inhibited anaphylactic release of TXB2, but had only marginal effects on the release of cysteinyl-LT and 6-keto-PGF1α. The results suggest that exogenous and endogenous NO functionally antagonize the effects of vasoconstrictor mediators released after antigen challenge. Additional effects of high concentrations of SIN-1 and NNA on antigen-induced eicosanoid release could modulate the vascular actions of these drugs during cardiac anaphylaxis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aehringhaus U, Peskar BA, Wittenberg HR, Wölbling RH (1983) Effect of inhibition of synthesis and receptor antagonism of SRS-A in cardiac anaphylaxis. Br J Pharmacol 80:73–80
Amezcua JL, Palmer RMJ, de Souza BM, Moncada S (1989) Nitric oxide synthesized from l-arginine regulates vascular tone in the coronary circulation of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 97:1119–1124
Anhut H, Bernauer W, Peskar BA (1977) Radioimmunological determination of thromboxane release in cardiac anaphylaxis. Eur J Pharmacol 44:85–88
Anhut H, Bernauer W, Peskar BA (1978) Pharmacological modification of thromboxane and prostaglandin release in cardiac anaphylaxis. Prostaglandins 15:889–900
Baydoun AR, Woodward B (1991) Effects of bradykinin in the rat isolated perfused heart: role of kinin receptors and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Br J Pharmacol 103:1829–1833
Bhardwaj R, Moore PK (1988) Endothelium-derived relaxing factor and the effects of acetylcholine and histamine on resistance blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol 95:835–843
Boùrgoin S, Poubelle P, Borgeat P (1987) Effet du SIN-1 sur la synthèse de leukotriènes dans les polymorphonucléaires humains. Path Biol 35:238–240
Doni MG, Whittle BJR, Palmer RMJ, Moncada S (1988) Actions of nitric oxide on the release of prostacyclin from bovine endothelial cells in culture. Eur J Pharmacol 151:19–25
Feelisch M, Noack E (1987a) Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol 139:19–30
Feelisch M, Noack E (1987b) Nitric oxide (NO) formation from nitrovasodilators occurs independently of hemoglobin or non-heme iron. Eur J Pharmacol 142:465–469
Feigl EO (1983) Coronary physiology. Physiol Rev 63:1–205
Furchgott RF, Vanhoutte PM (1989) Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J 3:2007–2018
Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV (1980) The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 288:373–376
Ishii K, Chang B, Kerwin JF, Huang Z-J, Murad F (1990) NG-nitro-l-arginine: a potent inhibitor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor formation. Eur J Pharmacol 176:219–233
Kaverina NV, Chumburidze VB (1979) Antianginal drugs. Pharmacol Ther 4:109–153
Kelm M, Schrader J (1988) Nitric oxide release from the guinea pig heart. Eur J Pharmacol 155:317–321
Lamparter B, Gross SS, Griffith OW, Levi R (1990) Endothelium-derived nitric oxide plays a role in cardiac anaphylaxis. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 305:261
Letts LG, Piper PJ (1982) The actions of leukotrienes C4 and D4 on guinea-pig isolated hearts. Br J Pharmacol 76:169–176
Levi R (1972) Effect of exogenous and immunologically released histamine on the isolated heart: a quantitative comparison. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 182:227–238
Levi R, Burker JA, Hattori Y, Hoppens CM, McManus LM, Hanahan DJ, Pickard RM (1984) Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC). A putative mediator of cardiac anaphylaxis in the guinea pig. Circ Res 54:117–124
Liebig R, Bernauer W, Peskar BA (1975) Prostaglandin, slow-reacting substance, and histamine release from anaphylactic guinea-pig hearts, and its pharmacological modification. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 289:65–76
Moore PK, al-Swayeh OA, Chong NWS, Evans RA, Gibson A (1990) l-NG-nitro arginine (l-NOARG), a novel, l-arginine reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 99:408–412
Mülsch A, Busse R (1990) NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino-(nitroamino) methyl]-l-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 341:143–147
Myers PR, Minor Jr RL, Guerra Jr R, Bates JN, Harrison DG (1990) Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature 345:161–163
Ney P, Schröder H, Schrör K (1990) Nitrovasodilator-induced inhibition of LTB4 release from human PMN may be mediated by cyclic GMP. Eicosanoids 3:243–245
Palmer RMJ, Ferrige AG, Moncada S (1987) Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 327:524–526
Palmer RMJ, Ashton DS, Moncada S (1988) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from l-arginine. Nature 333:664–666
Peskar BA, Steffens Ch, Peskar BM (1979) Radioimmunoassay of 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α in biological material. In: Albertini A, Da Prada M, Peskar BA (eds) Radioimmunoassay of drugs and hormones in cardiovascular medicine. Elsevier North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 239–250
Piper PJ, Yaacob HB, McLeod JD (1989) Interactions of leukotrienes, platelet-activating factor and thromboxane A2 in cardiac anaphylaxis. New Trends Lipid Mediators Res 3:252–256
Reden J (1990) Molsidomine. Blood Vessels 27:282–294
Simmet Th, Peskar BA (1986) Eicosanoids and the coronary circulation. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 104:1–64
Simmet Th, Luck W (1989) Clotting of whole human blood induces cysteinyl-leukotriene formation. Thromb Res 54:423–433
Simmet Th, Tippler B (1990) Cysteinyl-leukotriene production during limbic seizures triggered by kainic acid. Brain Res 515:79–86
Terashita ZI, Fukui H, Hirata M, Terao S, Ohkawa S, Nishikawa K, Kikuchi S (1981) Coronary vasoconstriction and PGI2 release by leukotrienes in isolated guinea pig hearts. Eur J Pharmacol 73:357–361
Yaacob HB, Piper PJ (1988) Inhibition of leukotriene release in anaphylactic guinea-pig hearts by a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, CGS 8515. Br J Pharmacol 95:1322–1328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to K. I. Thelen at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thelen, K.I., Dembinska-Kiéc, A., Pallapies, D. et al. Effect of 3-morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1) and NG-nitro-l-arginine (NNA) on isolated perfused anaphylactic guinea-pig hearts. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345, 93–99 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175475
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175475