Abstract
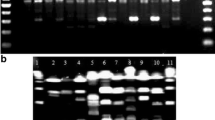
Genetic differences between a collection of aeromonads were studied in two laboratories by analysis of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). A single randomly designed primer, generated reproducible profiles of genomic DNA in both laboratories for Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida, although the profiles differed between laboratories. Analysis of atypical strains of A. salmonicida and isolates of the A. hydrophila group produced scattered profiles in both laboratories. The uniform fingerprints produced for A. salmonicida subspecies salmonicida indicate genomic homogeneity. The scattered RAPD profiles of the motile aeromonads demonstrate the genomic diversity of this group. A group of unspeciated motile aeromonads gave uniform fingerprints, suggesting the possibility of a genomically homogeneous species. Although the RAPD technique is susceptible to the effects of minor technical variations, this study has demonstrated that where there is DNA similarity, it can be recognized, and where there is diversity, differentiation can be made. RAPD promises to be useful in epidemiological studies for rapid identification of bacteria where a source of reference DNA is available and may be useful in preliminary investigations of relatedness within groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd, E.F., Hiney, M.P., Peden, J.F. and Smith, P.R. (1994) Assessment of genetic diversity among Aeromonas salmonicida isolates by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Journal of Fish Diseases 17, 97–98.
Ellsworth, D.L., Rittenhouse, K.D. and Honeycutt, R.L. (1993) Artifactual variation in randomly amplified polymorphic DNA banding patterns. Biotechniques 14, 214–217.
Farber, J.M. and Addison, C.J. (1994) RAPD typing for distinguishing species and strains in the genus Listeria. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 77, 242–250.
Fekete, A., Bantle, J.A., Halling, S.M. and Stich, R.W. (1992) Amplification fragment length polymorphism in Brucella strains by use of polymerase chain reaction with arbitrary primers. Journal of Bacteriology 174, 7778–7783.
Fukatsu, T. and Ishikawa, H. (1994) Differentiation of aphid clones by arbitrarily primed PCR (AP-PCR). Molecular-Ecology 3, 187–192.
Joseph, S.W. and Carnahan, A. (1994) The isolation, identification and systematics of the motile Aeromonas species. Annual Review of Fish Diseases 4, 315–343.
Kuijper, E.J., Steigerwalt, A.G., Schoenmaker, B.S.C.I.M., Peters, M.F., Zanen, H.C. and Brenner, D.J. (1989) Phenotypic characteristics and DNA relatedness in human fecal isolates of Aeromonas species. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 27, 132–138.
McCourt, R.M., Helfgott, D.M. and Hoshaw, R.W (1992) Using random primed polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fragments to detect polyploid species complexes in Spirogyra. Journal of Phycology 283, 7.
MacInnes, J.I., Trust, T.J. and Crosa, J.H. (1979) Deoxyribonucleic acid relationships among members of the genus Aeromonas 25, 570–586.
Mazurier, S., van de Giessen, A., Heuvelman, K. and Wernars, K. (1992) RAPD analysis of Campylobacter isolates: DNA fingerprinting without the need to purify DNA. Letters in Applied Microbiology 14, 260–262.
Meunier, J.R. and Grimont, P.A.D. (1993) Factors affecting reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting. Res. Microbiol 144, 373–379.
Micheli, M.R., Bova, R., Pascale, E. and D'Ambrosio, E. (1994) Reproducible DNA fingerprinting with the random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) method. Nucleic Acids Research 22, 1921–1922.
Miyata, M., Aoki, T., Inglis, V., Yoshida, T. and Endo, M. (1995) RAPD analysis of Aeromonas salmonicida and Aeromonas hydrophila. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 79 (2), 131–185.
Muralidharan, K. and Wakeland, E.K. (1993) Concentration of primer and template qualitatively affects products in random-amplified polymorphic DNA PCR. Biotechniques 14, 362–364.
Neiderhauser, C., Hofelein, C., Allman, M., Burkhalter, P., Luthy, J. and Candrian, U. (1994) Random amplification of polymorphic bacterial DNA: evaluation of 11 oligonucleotides and application to food contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes. Journal of Applied Bacteriology 77, 574–582.
Nielsen, B., Olsen, J.E. and Larsen, J.L. (1994) Ribotyping of Aeromonas salmonicida subspecies salmonicida. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 18, 155–158.
Penner, G.A., Bush, A., Wise, R., Kim, W., Domier, L., Kasha, K., Laroche, A., Scoles, G., Molnar, S.J. and Fedak, G. (1993) Reproducibility of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis among laboratories. PCR Methods and Applications 2, 341–345.
Popoff, M., Coynault, C., Kiredjian, M. and Lemelin, M. (1981) Polynucleotide sequence relatedness among motile Aeromonas species. Current Microbiology 5, 109–114.
Schierwater, B. and Ender, A. (1993) Different thermostable DNA polymerases may amplify different RAPD products. Nucleic Acids Research 21, 4647–4648.
Schmidt, T.M., Pace, B. and Pace, N.R. (1991) Detection of DNA contamination in Taq polymerase. Biotechniques 11, 176–177.
Stephan, R., Schraft, H. and Untermann, F. (1993) Characterisation of Bacillus licheniformis with the RAPD technique (randomly amplified polymorphic DNA). Letters in Applied Microbiology 18, 260–263.
Towner, K.J. and Cockayne, A. (1993) Molecular Methods for Microbial Identification and Typing. Chapman and Hall: Cambridge.
Williams, J.G.K., Kubelik, A.R., Livak, K.J., Rafalski, J.A. and Tingey, S.V. (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Research 18, 6531–6535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inglis, V., Colquhoun, D., Pearson, M.D. et al. Analysis of DNA relationships among Aeromonas species by RAPD (randomly amplified polymorphic DNA) typing. Aquacult Int 4, 43–53 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175220