Summary
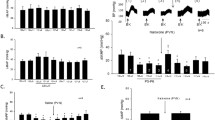
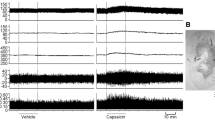
In urethane-anesthetized rats with an intact spinal cord, application of capsaicin on the outer surface of the urinary bladder produced a transient bradycardia, hypotension and negative cardiac inotropism which were neither prevented by i. v. atropine (0.5 mg/kg) nor by cervical vagotomy. In acute spinal rats (C2-C3) application of capsaicin (0.2 and 2 pg in 25 pl) on the urinary bladder induced a transient hypertension, tachycardia and positive cardiac inotropism. A second application (30 min later) induced minor cardiovascular effects, expecially with the higher dose, indicating desensitization. All cardiovascular responses to topical capsaicin were abolished by systemic capsaicin desensitization (50 mg/kg s. c., 4 days before). The excitatory cardiovascular response to capsaicin in acute spinal rats was markedly reduced by bilateral section of pelvic but not hypogastric nerves. Further, it was abolished by pretreatment with hexamethonium (20 mg/kg i.v.) or reserpine (5 mg/kg i. p., 2 days before) and reduced, at various extent for the different components, by phentolamine (0.5 mg/kg i. v.) or propranolol (1 mg/kg). In rats with pelvic and hypogastric nerves intact, section of the cord at a level (T12-L1), just above the medullary segments which receive primary afferent input from the bladder (L6-S1), abolished the excitatory cardiovascular response to application of capsaicin on the bladder. In spinal rats (C2-C3) rapid distension of the urinary bladder with saline produced transient tachycardia, hypertension and positive cardiac inotropism similar to that evoked by capsaicin. These responses were not observed in rats systemically pretreated with capsaicin. These findings indicate that certain bladder afferents which are susceptible to capsaicin desensitization in adult rats activate a spinal reflex having excitatory influence on cardiovascular function. This response is apparently mediated by spinal centers located above the site of entry of bladder pelvic afferents into the cord and most likely involves excitation of preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the spinal cord.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelli L, Conte B, Somma V, Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Geppetti P, Alessandri M, Theodorsson E, Meli A (1988) The contribution of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves to xylene-induced visceral pain in conscious, freely moving rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:545–551
Donnerer J, Lembeck F (1983) Capsaicin-induced reflex fall in rat blood pressure is mediated by afferent substance P-containing neurones via a reflex centre in the brain stem. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 324:293–295
Giuliani S, Maggi CA, Meli A(1986) Differences in cardiovascular responses to peripherally administered GABA as influenced by basal conditions and type of anaesthesia. Br J Pharmacol 88:659–670
Holzer-Petsche U, Lembeck F (1984) Systemic capsaicin treatment impairs the micturition reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 83:935–941
Jancsó G, Maggi A (1987) Distribution of capsaicin-sensitive urinary bladder afferents in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res 418:371–376
Langworthy OR (1965) Innervation of the pelvic organs of the rat. Invest Urol 2:491–511
Lembeck F, Skofltsch G (1982) Visceral pain reflex after pretreatment with capsaicin and morphine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:116–122
Longhurst JC, Ashton JH, Iwamoto GA (1980) Cardiovascular reflexes resulting from capsaicin-stimulated gastric receptors in anesthetized dogs. Circ Res 46:780–788
Longhurst JC, Kaufman MP, Ordway GA, Musch TI (1984a) Effects of bradykinin and capsaicin on endings of afferent fibers from abdominal visceral organs. Am J Physiol 247:R552-R559
Longhurst JC, Stebbins CL, Ordway GA (1984b) Chemically induced cardiovascular reflexes arising from the stomach of the cat. Am J Physiol 247:H459-H466
Mc Mahon SB (1986) Sensory-motor integration in urinary bladder function. Prog Brain Res 67:245–254
Mc Mahon SB, Morrison JFB (1982) Two groups of spinal interneurones that respond to stimulation of the abdominal viscera of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 322:21–34
Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) The role of neuropeptides in the regulation of the micturition reflex. J Anton Pharmacol 6:133–162
Maggi CA, Meli A (1988) The sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Gen Pharmacol 19:1–43
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1984) The effects of topical capsaicin on rat urinary bladder motility in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 103:41–50
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1985) Sympathetic inhibition of reflex activation of bladder motility during filling at a physiological like rate in urethane anaesthetized rats. Neuronal Urodyn 4:37–45
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986a) Somatovesical and vesicovesical excitatory reflexes in urethane anaesthetized rats. Brain Res 380:83–93
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986b) The effect of hexamethonium on the distension-induced contractile activity of the rat bladder. Evidence for the existence of a spinal ‘short loop’ vesicovesical reflex in rats. Neurourol Urodyn 5:403–410
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Geppetti P, Furio M, Frilli S, Conte B, Fanciullacci M, Giuliani S, Meli A (1987) The contribution of capsaicin-sensitive innervation to activation of the spinal vesicovesical reflex in rats: relationship between substance P levels in the urinary bladder and the sensory-efferent function of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Brain Res 415: 1–13
Maggi CA, Giuliani S, Conte B, Furio M, Santicioli P, Meli P, Gragnani L, Meli A (1988) Prostanoids modulate reflex micturition by acting through capsaicin-sensitive afferents. Eur J Pharmacol 145:105–112
Mukherjee SR (1957a) Effect of bladder distension on arterial blood pressure and renal circulation in acute spinal cats. J Physiol (Lond) 138:300–306
Mukherjee SR (1957b) Effect of bladder distension on arterial blood pressure and renal circulation: role of splanchnic and buffer nerves. J Physiol (Lond) 138:307–325
Nadelhaft I, Booth AM (1984) The location and morphology of preganglionic neurons and the distribution of visceral afferents from the rat pelvic nerve: a horseradish peroxidase study. J Comp Neurol 226:238–245
Ordway GA, Longhurst JC (1983) Cardiovascular reflexes arising from the gallbladder of the cat. Effects of capsaicin, bradykinin and distension. Circ Res 52:26–35
Ordway GA, Longhurst JC, Mitchell JH (1983) Stimulation of pancreatic afferents reflexly activates the capsaicin system in cats. Am J Physiol245:R820-R826
Purinton PT, Fletcher TF, Bradley WE (1973) Gross and light microscopy features of the pelvic plexus in the rat. Anat Rec 175:697–706
Schondorf R, Laskey W, Polosa C (1983) Upper thoracic sympathetic neuron responses to input from urinary bladder afferents. Am J Physiol 245:R311-R320
Weaver LC (1985) Organization of sympathetic responses to distension of the urinary bladder. Am J Physiol 248:R236-R240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to S. Giuliani at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giuliani, S., Alberto Maggi, C. & Meli, A. Capsaicin-sensitive afferents in the rat urinary bladder activate a spinal sympathetic cardiovascular reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338, 411–416 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172119
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172119