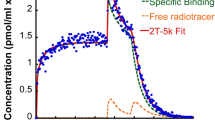
Abstract
Preliminary study of iodine-123 labeled IBF, (S)-5-iodo-7-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl] carboxamido-2, 3-dihydrobenzofuran, has demonstrated the potential of using this agent to evaluate the status of the CNS D-2 dopamine receptor in humans. To further characterize this ligand and evaluate single-photon emission tomography (SPET) quantitation, a detailed biodistribution study in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with 123I- and 125I-IBF was performed. The dual tracer was simultaneously injected for in vivo imaging, biodistribution, and ex vivo autoradiography in the same monkey. After the injection, SPET data (10 min/frame × 15) were collected with a triple-head gamma camera. Dynamic imaging data indicated that IBF localized in basal ganglia (BG) with a half life of 90-120 min. Other regions, i.e., cerebellum (CB) and cortex (CX), showed very low uptake. At 2.2 h after the injection, the monkey was sacrificed. Organ distribution data indicated that, as expected, there was a significant uptake in basal ganglia (0.029% ID/g), and the BG/CB and BG/CX ratios were 17.8 and 14.2 respectively. Lower ratios were obtained from SPET image analysis (BG/CB=3.5 at 2.5h). The eye uptake was observed with SPET, but was only quantified on autoradiograms with significant uptake (0.017% ID/g). Autoradiography of the eye demonstrated that predominant uptake was localized in the ciliary body and the choroid. The selective retention and high BG/CB ratio of 123I-IBF make it a useful agent for in vivo D-2 dopamine receptor imaging with SPET.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Köhler C, Hall H, Ögren S-O, Gawell L. Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of [3H]raclopride. Biochem Pharmacol 1985;34: 2251–2259
Köhler C, Hall H, Gawell L. Regional in vivo binding of the substituted benzamide [3H]eticlopride in the rat brain: evidence for selective labelling of dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1986;120: 217–226
Håkan H, Köhler C, Gawell L. Some in vitro receptor binding properties of H-3 eticlopride, a novel substituted benzamide, selective for dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 1985;111: 191–199
Janowsky A, de Paulis T, Clanton JA, Smith HE, Ebert MH, Kessler RM. I-125 iodopride: a specific high affinity radioligand for labeling striatal dopamine D-2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1988;150: 203–205
de Paulis T Janowsky A, Kessler R, Clanton J, Smith H. (S)-(N-[1-Ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl) methyl]-5-[I-125]iodo-2-methoxy-benzamide hydorchloride, a new selective radioligand for dopamine D-2 receptors. J Med Chem 1988;31: 2027–2033
Murphy RA, Kung IT, Kung MP, Billings JJ. Synthesis and characterization of iodobenzamide analogues: potential D-2 dopamine receptor imaging agents. J Med Chem 1990;33: 171–178
Kessler R, Ansari M, de Paulis T, Schmidt D, Clanton J, Smith H, Manning R, Gillespie D, Ebert M. High affinity dopamine D2 receptor radioligands: regional rat brain distribution of iodinated benzamides. J Nucl Med 1991;32: 1593–1600
Chumpradit S, Kung M-P, Billings J, Mach R, Kung HF. Fluorinated and iodinated dopamine agents: D2 imaging agents for PET and SPECT. J Med Chem 1993;36: 221–228
Mathis CA, Bishop JE, Gerdes JM, Whitney JM, Brennan KM, Jagust WJ. Synthesis and evaluation of high affinity, aryl-substituted [18F]fluorpropylbenzamides for dopamine D2 receptor studies. Nucl Med Biol 1992;19: 571–588
Mukherjee J, Perry B, Cooper M. Fluorinated benzamide neuroleptics-2. Synthesis and radiosynthesis of (S)-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(3-[18F]fluorpropyl )-3-substituted-2methoxybenzamides. Int J Radiat Appl Instrum [a] 1991;42: 3713–3721
Högberg T, Strom P, Hall H, Kohler C, Halldin C, Farde L. Synthesis of [I-125] [123I] and unlabelled (S3-iodo-5,6-dimethoxy-N-[1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidiny)methyl] salicylamide (NCQ298), a selective ligand for the study of dopamine D-2 receptors. Acta Pharm Nord 1990;2: 53–60
Hall H, Högberg T, Halldin C, Köhler C, Ström P, Ross S, Larsson S, Farde L. NCQ 298, a new selective iodinated salicylamide ligand for the labelling of dopamine D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 1991;103: 6–18
Martres M-P, Sales N, Bouthenet M-L, Schwartz J-C. Localization and pharmacologial characterization of D-2 dopamine receptors in rat cerebral neocortex and cerebellum using [I-125 iodosulpiride. Eur J Pharmacol 1985;118: 211–219
Neumeyer JL, Guan JH, Niznik HB. Novel photoaffinity label for the dopamine D-2 receptor: synthesis of 4-azido-5-iodo-2-methoxy-N-[1-phenylmethyl-4-piperidinyl] benzamide (Iodoazidoclebopride, IAC) and the corresponding I-125 labeled analogue. J Med Chem 1985;28: 405–407
Kung H, Guo Y-Z, Billings J, Xu X, Mach R, Blau M, Ackerhalt R. Preparation and biodistribution of [I-125]IBZM: a potential CNS D-2 dopamine receptor imaging agent. Nucl Med Biol 1988;15: 195–201
Pilowsky LS, Costa DC, Ell PJ, Murray RM, Verhoeff NP, Kerwin RW. Clozapine, single photon emission tomography, and the D-2 dopamine receptor blockade hypothesis of schizophrenia. Lancet 1992;340: 199–202
Cordes M, Henkes H, Laudahn D, Bräu H, Kramp W Girke W, Hierholzer J, Eichstädt H, Felix R. Initial experience with SPET examinations using [123I]IBZM as a D2-dopamine receptor antagonist in Parkinson's disease. Eur J Radiol 1991;12: 182–186
Costa D, Verhoeff N, Cullum I, Ell P, Syed G, Barrett J, Palazidou E, Toone B, Van Royen E, Bobeldijk M. In vivo characterization of 3-iodo-6-methoxybenzamide 123I in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 1990;16: 813–816
Schwarz J, Tatsch K, Arnold G, Gasser T, Trenkwalder C, Kirsch CM, Oertel WH. 123I-iodobenzamide-SPECT predicts dopaminergic responsiveness in patients with de novo parkinsonism. Neurology 1992;42: 556–561
Schwarz J, Tatsch K, Vogl T, Kirsch CM, Trenkwalder C, Arnold G, Gasser T, Oertel WH. Marked reduction of striatal dopamine D2 receptors as detected by 123I-IBZM-SPECT in a Wilson's disease patient with generalized dystonia. Mov Disord 1992;7: 58–61
Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Oertel W, Kirsch C-M. SPECT imaging of dopamine D2 receptors with I-123 IBZM in parkinsonian syndromes. J Nucl Med 1991;32: 1014–1015
Tatsch K, Schwarz J, Oertel WH, Kirsch CM. SPECT imaging of dopamine D2 receptors with 123,-IBZM: initial experience in controls and patients with Parkinson's syndrome and Wilson's disease. Nucl Med Commun 1991;12: 699–707
Kung M-P, Kung HF, Billings J, Yang Y, Murphy RA, Alavi A. The characterization of IBF as a new selective dopamine D-2 receptor imaging agent. J Nuct Med 1990;31: 648–654
Burgisser E. Methods for the determination of specific radioactivity of radioligands. J Receptor Res 1984;4: 357–369
Kung M-P, Liu B-L, Yang Y, Billings J, Kung HF. A kit formulation for preparation of 123I-IBZM: a new CNS D-2 dopamine receptor imaging agent. J Nuct Med 1991;32: 339–342
Billings JJ, Kung M-P, Chumpradit S, Mozley D, Alavi A, Kung HE Characterization of radioiodinated TISCH: a high-affinity and selective ligand for mapping CNS D1 dopamine receptor. J Neurochem 1992;57: 227–236
Lear JL, Plotnick J, Rumley S. Digital autoradiography: design, development, and evaluation of solid-state image analyzer. J Nucl Med 1987;28: 218–222
Gergen JA, MacLean PD. A stereotaxic atlas of the squirrel monkey's brain. Bethesda, Md.: U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, 1962.
Lindquist NG. Accumulation of drugs on melanin. Acta Radiol Suppl (Stockh) 1973;325: 1
Holman LB, Zimmerman RE, Schapiro JR, Kaplan ML, Jones AG, Hill TC. Biodistribution and dosimetry of N-isopropyl-p-[1231] iodoamphetamine in the primate. J Nucl Med 1983;24:922–941
Holman LB, Wick MM, Kaplan ML, Hill TC, Lee RL, Wu JL, Lin TH. The relationship of the eye uptake of N-isopropyl-p-[123I]-iodoamphetamine to melanin production. J Nucl Med 1984;25:315–319
Schorderet M, Nowk JZ. Retinal dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors: characterization by binding or pharmacologic studies and physiological functions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1990;10: 303–325
Rapoport SI (1976) Sites and functions of the blood-aqueous and blood-vitreous barriers of the eye. In: Rapoport SI, ed. Blood brain barrier in physiology and medicine. New York: Raven Press; 1976: 207–232
Kety SS. Regional cerebral blood flow: estimation by means of nonmetabolized tracers — an overview. Semin Nucl Med 1985;15:324–328
Snyder WS, Cook MJ, Karhausen LR, Nasset ES, Howells GP, Tipton IH. Central nervous system. In: Report of the Task Group on Reference Man. New York: Pergamon Press; 1984: 281
Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakig PS, Rakic P, Innis RB. Dopamine D-2 receptors in cerebral cortex: distribution and pharmacologic characterization with H-3 raclopride. Proc Na Acad Sci 1989;86: 6412–6416
Camps M, Kelly PH, Palacios JM. Autoradiographic localization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the brain of several mammalian species. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 1990;80: 105–127
Richfield EK, Young AB, Penney JB. Comparative distribution of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in the basal ganglia of turtles, pigeons, rats, cats, and monkeys. J Comp Neurol 1987;262:446–463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: H.F. Kung
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Billings, J.J., Guo, Y.Z., Kung, M.P. et al. Localization of IBF as a D-2 dopamine receptor imaging agent in nonhuman primates. Eur J Nucl Med 20, 1146–1153 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171012
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171012