Summary
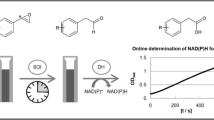
A new alcohol dehydrogenase catalysing the enantioselective reduction of acetophenone to R(+)-phenylethanol was found in a strain of Lactobacillus kefir. A 70-fold enrichment of the enzyme with an overall yield of 76% was obtained in two steps. The addition of Mg2+ ions was found to be necessary to prevent rapid deactivation. The enzyme depends essentially on NADPH and was inactive when supplied with NADH as the coenzyme. Important enzymological data of the dehydrogenase are: K m (acetophenone) 0.6 mM, K m (NADPH) 0.14 mM, and a pH optimum for acetophenone reduction at 7.0. Addition of EDTA leads to complete deactivation of the enzyme activity. Added iodoacetamide or p-hydroxymercuribenzoate cause only slight inhibition, revealing that the active centre of the enzyme contains no essential SH-group. Besides acetophenone several other aromatic and long-chain aliphatic secondary ketones are substrates for this enzyme. Batch production of phenylethanol was examined using three different methods for the regeneration of NADPH: glucose/glucose dehydrogenase, glucose-6-phosphate/glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and isopropanol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Hughes MN, Poole RK (1989) Metals and micro-organisms. Chapman and Hall, London
Hummel W (1990) Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of optically pure R(+)-phenylethanol. Biotechnol Lett 12:403–408
Hummel W, Kula M-R (1989a) Simple method for small-scale disruption of bacteria and yeasts. J Microbiol Methods 9:201–209
Hummel W, Kula M-R (1989b) Dehydrogenases for the synthesis of chiral compounds. Eur J Biochem 184:1–13
Hummel W, Schütte H, Kula M-R (1985) d-2-Hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus casei. A new enzyme suitable for stereospecific reduction of 2-ketocarboxylic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21:7–15
Hummel W, Schütte H, Kula M-R (1988) d(−)-Mandelic acid dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus curvatus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:433–439
Jones JB (1986) Enzymes in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 42:3351–3403
Keinan E, Seth KK, Lamed R (1987) Synthetic applications of alcohol-dehydrogenase from Thermoanaerobium brockii. Ann N Y Acad Sci 501:130–149
Prelog V (1984) Specification of the stereospecificity of some oxidoreductases by diamond lattice sections. Pure Appl Chem 9:119–130
Schütte H, Hummel W, Kula M-R (1984) l-2-Hydroxyisocaproate dehydrogenase — a new enzyme from Lactobacillus confusus for the stereospecific reduction of 2-ketocarboxylic acids. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:167–176
Seebach D, Zuger MF, Giovannini F, Sonnleitner B, Fiechter A (1984) Preparative microbial reduction of ß-oxoesters with Thermoanaerobium brockii. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 23:151–152
Sieh CJ, Chen C-S (1984) Microbial asymmetric catalysis — enantioselective reduction of ketones. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 23:570–578
Wandrey C (1986) Synthesis of l-amino acids by isolated enzymes and microorganisms. In: Schneider MP (ed) Enzymes as catalysts in organic synthesis. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrecht, pp 263–284
Wong C-H, Drueckhammer DG (1985) Enzymatic synthesis of chiral hydroxy compounds using immobilized glucose dehydrogenase from Bacillus cereus for NAD(P)H regeneration. Bio/Technology 3:649–651
Wong C-H, Whitesides GM (1981) Enzyme-catalyzed organic synthesis: NAD(P)H cofactor regeneration by using glucose-6-phosphate and the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides. J Am Chem Soc 103:4890–4899
Wong C-H, Drueckhammer DG, Sweers HM (1985) Enzymatic vs. fermentative synthesis: thermostable glucose dehydrogenase catalyzed regeneration of NAD(P)H for use in enzymatic synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 107:4028–4031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hummel, W. Reduction of acetophenone to R(+)-phenylethanol by a new alcohol dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus kefir . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34, 15–19 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170916
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170916