Abstract
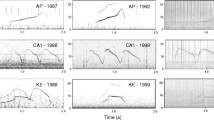
To examine whether context-specific information is superimposed upon the individual cues present in the whistling of the bottlenosed dolphin, Tursiops truncatus, parameter variations within the two most frequently emitted whistle types of a captive individual were investigated in three different behavioural contexts. The study concentrated on comparing signal features of spontaneously occurring vocalizations in two possible phases following the performance of a trained discrimination task and those occurring during isolation. Phases of the discrimination task differed according to whether the animal showed “correct” (reward given) or “incorrect” performance (no reward). Signature whistles were most common in isolation, but also represented just over half of the whistles following a choice task. Of 14 signature whistle frequency and time parameters measured 9 differed significantly between isolation and at least one of the phases following a choice task (Table 1). Three parameters also varied according to whether performance was correct or incorrect. In contrast, only one out of four parameters (start frequency) measured from the second most frequent whistle type varied significantly between contexts (isolation vs. phase following correct choice). The results indicate that not only identity but also context-related information is available in the whistles of a bottlenosed dolphin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Au WWL, Pawloski DA (1992) Cylinder wall thickness difference discrimination by an echolocating Atlantic bottlenose dolphin. J Comp Physiol A 170: 41–47
Bastian J (1967) The transmission of arbitrary environmental information between bottlenose dolphins. In: Busnel RG (ed) Animal sonar systems, vol II. Laboratoire de Physiologie Acoustique, Jouy-en-Josas, pp 803–873
Beach FA, Herman LM (1972) Preliminary studies of auditory problem-solving and intertask transfer by the bottlenosed dolphin. Psychol Rec 22: 49–62
Beeman K (1989) ‘SIGNAL’ Software Manual. Engineering Design, Belmont
Bullock TH, Ridgway SH (1972) Evoked potentials in the central auditory system of alert porpoises to their own and artificial sounds. J Neurobiol 3: 79–99
Caldwell MC, Caldwell DK (1965) Individualized whistle contours in bottlenosed dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Nature 207: 434–435
Caldwell MC, Caldwell DK (1968) Vocalization of naive captive dolphins in small groups. Science 159: 1121–1123
Caldwell MC, Caldwell DK, Turner RH (1970) Statistical analysis of the signature whistle of an Atlantic bottlenosed dolphin with correlations between vocal changes and levels of arousal. Technical Report No. 8. Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History Foundation, Los Angeles
Caldwell MC, Caldwell DK, Tyack PL (1990) A review of the signature-whistle-hypothesis for the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin. In: Leatherwood S, Reeves RR (eds) The bottlenose dolphin. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 199–234
Cross EM, Chaffin WW (1982) Use of the binomial theorem in interpreting results of multiple tests of significance. Educ Psychol Meas 42: 25–34
Ford JKB (1989) Acoustic behaviour of resident killer whales (Orcinus orca) off Vancouver Island, British Columbia. Can J Zool 67: 727–745
Herman LM, Arbeit WR (1972) Frequency difference limens in the bottlenose dolphin: 1–70 KCs. J Aud Res 12: 109–120
Herman LM, Tavolga WN (1980) The communication systems of cetaceans. In: Herman LM (ed) Cetacean behavior: mechanisms and functions. Wiley, New York, pp 149–209
Jacobs DW (1972) Auditory frequency discrimination in the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus Montague: a preliminary report. J Acoust Soc Am 52: 696–698
Janik VM (1992) Zum Einsatz von Pfifftypen und Pfifftypvariationen beim Großen Tümmler, Tursiops truncatus, in visuellen Diskriminationstests. Diploma Thesis, Freie Universität Berlin
Janik VM, Todt D (1992) Context related parameter variations of signature whistles in the bottlenosed dolphin. In: Elsner N, Richter DW (eds) Rhythmogenesis in neurons and networks: proceedings of the 20th Göttingen neurobiology conference. Thieme, Stuttgart, p 245
Jürgens U (1979) Vocalization as an emotional indicator: a neuroethological study in the squirrel monkey. Behavior 69: 88–117
Kramer M, Schmidhammer J (1992) The chi-squared statistic in ethology: use and misuse. Anim Behav 44: 833–841
Lang TG, Smith HAP (1965) Communication between dolphins in separate tanks by way of an acoustic link. Science 150: 1839–1843
Marler P, Evans CS, Hauser MD (1992) Animal signals: motivational, referential, or both? In: Papousek H, Jürgens U, Papousek M (eds) Nonverbal vocal communication: comparative and developmental approaches. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 66–86
Moore PWB (1988) Dolphin echolocation and audition. In: Nachtigall PE, Moore PWB (eds) Animal sonar: processes and performance. Plenum, New York, pp 161–168
Moore PWB, Pawloski DA (1990) Investigations on the control of echolocation pulses in the dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). In: Thomas J, Kastelein RA (eds) Sensory abilities of cetaceans. Plenum, New York, pp 305–316
Morton ES (1982) Grading, discretness, redundancy, and motivation-structural rules. In: Kroodsma DE, Miller EH, Ouellet H (eds) Acoustic communication in birds, vol 1: production, perception, and design features of sounds. Academic Press, New York, pp 183–212
Popper AN (1980) Sound emission and detection by delphinids. In: Herman LM (ed) Cetacean behavior: mechanisms and functions. Wiley, New York, pp 1–52
Ralston JV, Herman LM (1989) Dolphin auditory perception. In: Dooling RJ, Hulse SH (eds) The comparative psychology of audition: perceiving complex sounds. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, pp 295–328
Richards DG, Wolz JP, Herman LM (1984) Vocal mimicry of computer-generated sounds and vocal labelling of objects by a bottlenosed dolphin, Tursiops truncatus. J Comp Psychol 87: 10–28
Sayigh LS, Tyack PL, Wells RS, Scott MD (1990) Signature whistles of free-ranging bottlenose dolphins Tursiops truncatus: stability and mother-offspring comparisons. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 26: 247–260
Siegel S, Castellan NJ Jr (1988) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences, second edition. McGraw-Hill, New York
Taruski AG (1979) The whistle repertoire of the North Atlantic pilot whale (Globicephala melaena) and its relationship to behavior and environment. In: Winn HE, Olla BL (eds) Behavior of marine animals, vol 3, Cetaceans. Plenum, New York, pp 345–368
Thompson RKR, Herman LM (1975) Underwater frequency discrimination in the bottlenosed dolphin (1–140 KHz). J Acoust Soc Am 57: 943–948
Tyack P (1986) Whistle repertoires of two bottlenosed dolphins, Tursiops truncatus: mimicry of signature whistles? Behav Ecol Sociobiol 18: 251–257
Yunker MP, Herman LM (1974) Discrimination of auditory temporal differences in the bottlenosed dolphin and by the human. J Acoust Soc Am 56: 1870–1875
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janik, V.M., Todt, D. & Dehnhardt, G. Signature whistle variations in a bottlenosed dolphin, Tursiops truncatus . Behav Ecol Sociobiol 35, 243–248 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00170704