Summary
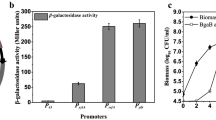
We have constructed a shuttle plasmid for Bacillus megaterium and Escherichia coli that contains the promoter and repressor gene of the B. megaterium-borne operon for xylose utilization. A polylinker downstream of the promoter allows versatile cloning of genes under its transcriptional control. We have placed gdhA (encoding glucose dehydrogenase) from B. megaterium, lacZ (encoding β-galactosidase) from E. coli, mro (encoding mutarotase) from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus, and human puk (encoding single-chain urokinase-like plasminogen activator, rscuPA) under xylose control in this vector. All four genes were between 130-fold and 350-fold inducible by 0.5% xylose in the growth medium in B. megaterium. Enzymatically active glucose dehydrogenase and mutarotase accumulated to 20% and 30% of the total soluble protein, respectively. β-Galactosidase and rscuPA were also expressed at a high level. A gel analysis of the products demonstrated their proteolytic stability in the cytoplasm, even up to 5 h after induction. The expression properties of this new host-vector system are discussed in comparison to the ones available for B. subtilis and E. coli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boylan SA, Chun KT, Edson BA, Price CW (1988) Early-blocked sporulation mutations alter expression of enzymes under carbon control in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet 212:271–280
Brürmmer W, Ebeling W (1976) Eigenschaften und Anwendung der Glukose-Dehydrogenase. Kontakte 2:3–7
Gatz C, Hillen W (1986) Acinetobacter calcoaceticus encoded mutarotase: nucleotide sequence analysis of the gene and characterization of its secretion in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 14:4309–4323
Gatz C, Altschmied J, Hillen W (1986) Cloning and expression of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus mutarotase gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 168:31–39
Geissendörfer M, Hillen W (1990) Regulated expression of heterologous genes in Bacillus subtilis using the Tn10 encoded tet regulatory elements. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:657–663
Hardy KG (1985) Bacillus cloning methods. In: Glover DM (ed) DNA cloning, a practical approach, vol 2. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 1–17
Heilmann HJ, Mägert HJ, Gassen HG (1988) Identification and isolation of glucose dehydrogenase genes of Bacillus megaterium M1286 and their expression in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 174:485–490
Hillen W, Klock G, Kaffenberger I, Wray LV Jr, Reznikoff WS (1982) Purification of the Tet repressor and the tet operator from the transposon Tn10 and characterization of their interaction. J Biol Chem 257:6605–6613
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N. Y.
Marsh JL, Erfle M, Wykes EJ (1984) The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene 32:481–485
Meinhardt F, Stahl U, Ebeling W (1989) Highly efficient expression of homologous and heterologous genes in Bacillus megaterium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:343–350
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., pp 352–355
Plough J, Kjeldgaard NO (1957) Urokinase: an activator of plasminogen from human urine. I. Isolation and properties. Biochem Biophys Acta 24:278–282
Puyet A, Sandoval H, Lopez P, Aguilar A, Martin JF, Espinosa M (1987) A simple medium for rapid regeneration of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts transformed with plasmid DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 40:1–5
Rüther U (1982) pUR allows rapid chemical sequencing of both strands of its inserts. Nucleic Acids Res 10:5765–5772
Rygus T, Scheler A, Allmansberger R, Hillen W (1991) Molecular cloning, structure, promoters, and regulatory elements for transcription of the Bacillus megaterium encoded regulon for xylose utilization. Arch Microbiol, in press
Schmucker R, Gülland U, Will M, Hillen W (1989) High level expression of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus mutarotase gene in Escherichia coli is achieved by improving the translational control sequence and removal of the signal sequence. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:509–514
Shimotsu H, Henner D (1986) Construction of a single copy integration vector and its use in analysis of regulation of the trp operon of Bacillus subtilis. Gene 43:85–94
Surek B, Wilhelm M, Hillen W (1991) Optimizing the promoter and ribosome binding sequence for expression of human single chain urokinase like plasminogen activator in Escherichia coli and stabilization of the product by avoiding the heat shock response. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:488–494
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: W. Hillen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rygus, T., Hillen, W. Inducible high-level expression of heterologous genes in Bacillus megaterium using the regulatory elements of the xylose-utilization operon. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 594–599 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169622