Summary
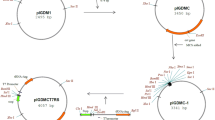
A cloning vector system was constructed on the basis of the pBR322 derivative pEG1 by introducing the whole parB locus of plasmid R1 cloned behind the promoter of the alkaline phosphatase gene (phoA) of Escherichia coli. The parB locus in combination with the phoA promoter ensures both (i) plasmid stabilization due to the post-segregational killing of plasmid-free cells during growth and (ii) killing of the cells induced by the potential environmental signal phosphate limitation. This vector, therefore, appears to be a model system for increasing the stability of recombinant plasmids and for decreasing the potential risks in the application of recombinant bacteria in industrial fermentations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bej AK, Perlin MH, Atlas RM (1989) “Suicide” systems for the containment of genetically engineered microorganisms: model conditional lethal systems for E. coli and Pseudomonas using hok. In: Molecular genetics of bacteria and phages. Procaryotic genetic regulation. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., p 157
Borriss R, Bäumlein H, Hofemeister J (1985) Expression in E. coli of a cloned β-glucanase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:63–71
Gerdes K (1988) The parB (hok/sok) locus of plasmid R1: a general purpose plasmid stabilization system. Bio/Technology 6:1402–1405
Gerdes K, Thisted T, Martinussen J (1990) Mechanism of post-segregational killing by the hok/sok system of plasmid R1: sok antisense RNA regulates formation of a hok mRNA species correlated with killing of plasmid-free cells. Mol Microbiol 4:1807–1818
Hecker M, Riethdorf S, Bauer C, Schroeter A, Borriss R (1988) Expression of a cloned β-glucanase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in an Escherichia coli relA strain after plasmid amplification. Mol Gen Genet 215:181–183
Hofmann KH, Schweder T, Reinhardt U, Hecker M (1991) Stability of plasmid pBR322 in Escherichia coli NF161 (relA+) and NF162 (relA) grown in a methionine limited chemostat. Acta Biotechnol 11:403–406
Holzhauer M (1988) Biochemische Labormethoden. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Imanaka T (1986) Application of recombinant DNA technology to the production of useful biomaterials. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 33:1–27
Knudsen SM, Karlström OH (1991) Development of efficient suicide mechanism for biological containment of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:85–92
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Mitchell JJ, Lucas-Lenhard JM (1980) The effect of alcohols on guanosine-5-diphosphate-3-diphosphate metabolism in stringent and relaxed Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 255:6307–6313
Molin S, Klemm P, Poulsen LK, Biehl H, Gerdes K, Andersson P (1987) Conditional suicide system for containment of bacteria and plasmids. Bio/Technology 5:1315–1317
Noack D, Roth M, Geuther R, Müller G, Undisz K, Hoffmeier C, Gaspar S (1991) Maintenance and genetic stability of vector plasmids pBR322 and pBR325 in Escherichia coli K12 strains grown in a chemostat. Mol Gen Genet 184:121–124
Schendel FJ, Baude EJ, Flickinger MC (1989) Determination of protein expression and plasmid copy number from cloned genes in Escherichia coli by flow injection analysis using an enzyme indicator vector. Biotechnol Bioeng 34:1023–1036
Wanner BL (1987) Bacterial alkaline phosphatase gene regulation and the phosphate response in Escherichia coli. In: Torriani-Gorini A, Rothman FG, Silver S, Wright A, Yagil E (eds) Phosphate metabolism and cellular regulation in microorganisms. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., pp 12–19
Yisraeli JK, Melton DA (1988) Synthesis of long, capped transcripts in vitro by SP6 and T7 RNA F polymerases. Methods Enzymol 180:42–50
Zabriskie DW, Arcuri EJ (1986) Factors influencing productivity of fermentations employing recombinant microorganisms. Enzyme Microb Technol 8:705–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: T. Schweder
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schweder, T., Schmidt, I., Herrmann, H. et al. An expression vector system providing plasmid stability and conditional suicide of plasmid-containing cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 91–93 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169425
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169425