Abstract
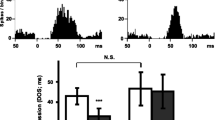
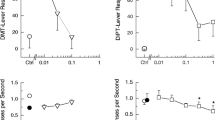
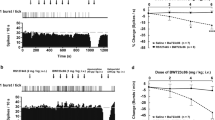
In the present study, in vivo extracellular unitary recordings, in vitro [3H]5-HT uptake and [3H]cyanoimipramine binding assays were used to assess the effect of acute and prolonged administration of the putative antidepressant tianeptine, on the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) transporter. Microiontophoretic application of tianeptine onto dorsal hippocampus CA3 pyramidal neurons, as well as its intravenous administration (2 mg/kg), increased their firing frequency. Following intracerebroventricular administration of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine, the activation induced by the microiontophoretic application of tianeptine remained unchanged, thus suggesting that the 5-HT carrier is not involved in this effect. Furthermore, in spite of its activating effect on CA3 pyramidal neuron firing frequency, the intravenous administration of tianeptine did not alter the time of recovery of these neurons from microiontophoretic applications of 5-HT, an index of 5-HT uptake activity. In keeping with this observation, the acute administration of tianeptine did not change the effectiveness of the 5-HT reuptake blocker paroxetine (1 mg/kg, i.v.) in prolonging the suppressant effect of microiontophoretically-applied 5-HT. However, in rats that had received tianeptine for 14 days (20 mg/kg/day, s.c.), the recovery time from the suppressant effect of microiontophoretic applications of 5-HT was reduced by 40% and the effectiveness of paroxetine (1 mg/kg, i.v.) was decreased. These effects were no longer observed following a 48 h washout period. In a second series of experiments, the ability of tianeptine to interfere with the uptake blocking capacity of paroxetine was assessed in vitro, using hippocampal slices obtained from rats that had been treated with tianeptine for 14 days (20 mg/kg/day, s.c.; by minipump). The effectiveness of paroxetine to block [3H]5-HT uptake was unchanged in slices obtained from rats still bearing the osmotic minipump at the time of the sacrifice, as well as from those which had undergone a 48 h washout period. To assess whether prolonged administration of tianeptine would induce adaptive changes on 5-HT uptake sites, [3H]cyanoimipramine-binding parameters were measured following a 48 h washout period. Affinity values remained unchanged while density values were significantly increased in cortex (+22%) but not in hippocampus (+12%). It is concluded that, i) the activation of CA3 pyramidal neurons observed following acute tianeptine administration cannot be attributed to its 5-HT uptake enhancing properties and ii) the prolonged administration of tianeptine induces adaptive changes on cortical but not on hippocampal 5-HT transporters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassant M, Lee H, Jazat F, Lamour Y (1991) Comparative study of tianeptine and other antidepressants on the activity of medial septal neurons in rats anesthesized by urethane. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:568–573
Bertorelli R, Amoroso D, Girotti P, Consolo S (1992) Effect of tianeptine on the central cholinergic system: involvement of serotonin. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:276–281
Björklund A, Baumgarten HG, Rensch A (1975) 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine: Improvement of its selectivity for serotonin neurons in the CNS by pretreatment with desipramine. J Neurochem 24:833–835
Blier P, de Montigny C (1994) Current advances in the treatment of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:220–266
Blier P, Mongeau R, Weiss M, de Montigny C (1993) Modulation of serotonin neurotransmission by presynaptic alpha-2-adrenergic receptors: a target for antidepressant pharmacotherapy. Int Acad Biomed Drug Res 5:74–82
Chaput Y, Lesieur P, de Montigny C (1990) Effects of short-term serotonin depletion on the efficacy of serotonin neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. Synapse 6:328–337
Datla K, Curzon G (1993) Behavioural and neurochemical evidence for the decrease of brain extracellular 5-HT by the antidepressant drug tianeptine. Neuropharmacology 9:839–845
de Simoni M, de Luigi A, Clavenna A, Manfridi A (1992) In vivo studies on the enhancement of serotonin uptake by tianeptine. Brain Res 574:93–97
de Souza EB, Kuyatt BL (1987) Autoradiographic localization of [3H]paroxetine-labelled serotonin uptake sites in rat brain. Synapse 1:488–496
Dewar K, Reader T, Grondin L, Descarries L (1991) [3H]Paroxetine binding and serotonin content of rat and rabbit cortical areas, hippocampus, neostriatum, ventral mesencephalic tegmentum, and midbrain raphe nuclei region. Synapse 9:14–26
Dresse A, Scuvée-Moreau J (1988) Electrophysiological effects of tianeptine on rat locus coeruleus, raphe dorsalis and hippocampus activity. Clin Neuropharmacol [Suppl 2]:S51–S58
Dumbrille-Ross A, Tang S (1983) Binding of [3H]Ro-112465: Possible identification of a subclass of [3H]imipramine binding sites. Mol Pharmacol 23:607–613
Fattaccini C, Bolaños-Jimenez F, Gozlan H, Hamon M (1990) Tianeptine stimulates uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine in vivo in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 29:1–8
Frankfurt M, McKittrick CR, McEwen BS (dy1993) Changes in serotonin receptor subtypes induced by short and long-term antidepressant treatment. Neurosciences (abstract no. 564.2)
Hrdina P, Foy B, Helmer A, Summers R (1990) Antidepressant binding sites in brain: Autoradiographic comparison of [3H]imipramine localization and relationship to serotonin transporter. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:410–418
Kandel E, Spencer W (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol 24:243–259
Kato G, Weitsch F (1988) Neurochemical profile of tianeptine, a new antidepressant drug. Clin Neuropharmacol [Suppl 2]: S43-S50
Kovachich G, Aronson C, Brunswick D, Frazer A (1988) Quantitative autoradiography of serotonin uptake sites in rat brain using [3H]cyanoimipramine. Brain Res 454:78–88
Langer S, Moret C, Raisman R, Dubocovich M, Briley M (1980) High affinity [3H]imipramine binding in rat hypothalamus: Association with uptake of serotonin but not of norepinephrine. Science 210:1133–1135
Lesch K, Aulakh C, Wolozin B, Tolliver T, Hill J, Murphy D (1993) Regional brain expression of serotonin transporter mRNA and its regulation by reuptake inhibiting antidepressants. Mol Brain Res 17:31–35
Letteron P, Descatoire V, Tinel M, Maurel P, Lebbe G, Loeper J, Larrey O, Freneaux E, Pessayre D (1989) Metabolic activation of the antidepressant tianeptine. I. Cytochrome P-450-mediated in vitro covalent binding. Biochem Pharmacol 38:3241–3246
Mennini T, Garattini S (1991) Neurobiologie de la tianeptine. Presse Medicale 37:1823–1827
Mennini T, Mocaer E, Garattini S (1987) Tianeptine a selective enhancer of serotonin uptake in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:478–482
Ortiz J, Mocaer E, Artigas F (1991) Effects of the antidepressant drug tianeptine on plasma and platelet serotonin concentrations in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 199:335–339
Piñeyro G, Blier P, Dennis T, de Montigny C (1994) Desensitization of the neuronal 5-HT carrier following its long-term blockade. J Neurosci 14:3036–3047
Ranck J (1975) Behavioral correlates and firing repertoires of neurons in the dorsal hippocampal formation of unrestrained rats. In: Isaacson I, Robert L (eds) The hippocampus. Plenum, New York, p 207
Reith M, Sershen H, Allen D, Lajtha A (1983) High and low affinity binding of [3H]imipramine in mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 102:389–395
Royer R, Albin H, Barrucand D, Salvadori-Failler, Kammoun A (1988) Pharmacokinetic and metabolic parameters of tianeptine in healthy volunteers and in populations with risk factors. Clin Neuropharmacol [Suppl 2]:590–896
Watanabe Y, Sakai R, McEwen B, Mendelson S (1993) Stress and antidepressant effects on hippocampal and cortical 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors and transport sites for serotonin. Brain Res 615:87–94
Whitton P, Sarna G, O'Connell M, Curzon G (1991) The effect of the novel antidepressant tianeptine on the concentration of 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat hippocampal dialysates in vivo. Neuropharmacology 30:1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased 10 May 1994
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piñeyro, G., Deveault, L., Blier, P. et al. Effect of acute and prolonged tianeptine administration on the 5-HT transporter: electrophysiological, biochemical and radioligand binding studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 351, 111–118 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169324
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169324