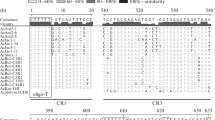
Summary
The intergenic spacer (IGS) of a 10-kbp repeat (clone pRZ7D) of the nuclear 18S, 5.8S, and 25S ribosomal RNA genes ofCucurbita pepo (zucchini) was sequenced and compared to the IGS sequences of two other Cucurbitaceae.Cucurbita maxima (squash), andCucumis sativus (cucumber). The nucleotide sequence and the structural organization of the IGS ofC. pepo andC. maxima are rather similar (between 75 and 100% sequence similarity depending on the region compared). The IGS are mainly composed of three different repeated elements interspersed into unique sequences: GC-rich clusters, a 422-bp AT-rich element including the transcription initiation site (TIS) for RNA polymerase I, and 260-bp repeats in the 5′ external transcribed spacer (D repeats). The TIS is duplicated in the 10-kbp repeat class ofC. pepo, as it is also described for the 11.5-kbp rDNA repeat ofC. maxima. The IGS ofCucumis sativus is also composed of different repeated elements; however, obvious sequence identity to theCucurbita species only occurs around the TIS and the preceding AT-rich region. GC-rich clusters with different primary sequences are present in the IGS of all three plants. Remarkably, the repeated elements in the 5′ETS accumulate TpG and TpNpG motifs, whereas CpG and CpNpG motifs less frequently occur. This accumulation might be caused by the transition of methylated cytosines (inmCpG ormCpNpG motifs) into thymidine via deamination in a previously GC-rich ancestor. The following singular region exhibits 50% G + C inC. pepo, 53% G + C inC. maxima, and 63% G + C inC. sativus. A model for a common ancestor of the 3′IGS for these Cucurbitaceae is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IGS:
-
(intergenic spacer)
- ITS:
-
(internal transcribed spacer)
- ETS:
-
(external transcribed spacer)
- NTS:
-
(nontranscribed spacer)
- rDNA:
-
(ribosomal DNA)
- rRNA:
-
(ribosomal RNA)
- TIS:
-
(transcription initiation site)
- TTS:
-
(transcription termination site)
References
Aissani B, Bernardi G (1991) CpG islands, genes and isochores in the genomes of vertebrates. Gene 106:185–195
Appels R, Moran LB, Gustafson JP (1986) The structure of DNA from rye (Secale cereale) NOR R1 locus and its behaviour in wheat backgrounds. Can J Genet Cytol 28:673–685
Barker RF, Harberd NP, Jarvis MG, Flavell RB (1988) Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. J Mol Biol 201:1–17
Bennet RI, Smith AG (1991) The complete nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer region of an rDNA operon fromBrassica oleracea and its comparison with other crucifers. Plant Mol Biol 16:1095–1098
Coulondre C, Miller JH, Farabaugh PJ, Gilbert W (1978) Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots inEscherichia coli. Nature 274:775–778
Delcasso-Tremousaygue D, Grellet F, Panabieres F, Ananiev ED, Delseny M (1988) Structural and transcriptional characterization of the external spacer of a ribosomal RNA nuclear gene from a higher plant. Eur J Biochem 172:767–776
De Winter RFJ, Moss T (1987) A complex array of sequences enhances ribosomal transcription inXenopus laevis. J Mol Biol 196:813–827
Dover GA (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families: how biological novelties arise, spread and are assimilated. Trends Genet 2:159–165
Flavell RB, O'Dell M, Thompson WT, Vincentz M, Sardana R, Barker RF (1986) The differential expression of ribosomal RNA genes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B314:385–397
Ganal M, Hemleben V (1986) Comparison of the ribosomal RNA genes in four closely relatedCucurbitaceae. Plant Syst Evol 154:63–77
Ganal M, Torres R, Hemleben V (1988) Complex structure of the ribosomal DNA spacer ofCucumis sativus (cucumber). Mol Gen Genet 212:548–554
Gerstner J, Schiebel K, v. Waldburg G, Hemleben V (1988) Complex organization of the length heterogeneous 5′ extemal spacer of mung bean (Vigna radiata) ribosomal DNA. Genome 30:723–733
Gründler P, Unfried I, Pointner R, Schweizer D (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the 25S-18S ribosomal gene spacer fromArabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 17:6395–6396
Gründler P, Unfried I, Pascher K, Schweizer D (1991) rDNA intergenic region fromArabidopsis thaliana. Structural analysis, intraspecific variation and functional implications. J Mol Biol 221:1209–1222
Gruenbaum J, Naveh-Many T, Cedar H, Razin A (1981) Sequence specificity of methylation in higher plant DNA. Nature 292:860–862
Grummt I, Kuhn A, Bartsch I, Rosenbauer H (1986) A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell 47:901–911
Hemleben V, Leweke B, Roth A, Stadler J (1982) Organization of highly repetitive satellite DNA of two Cucurbitaceae species (Cucumis melo andCucumis sativus). Nucleic Acids Res 10:631–644
Hemleben V, Ganal M, Gerstner J, Schiebel K, Torres RA (1988) Organization and length heterogeneity of plant ribosomal RNA genes. In: Kahl G (ed) The architecture of eukaryotic genes. VHC, Weinheim, pp 371–383
Hemleben V, Zentgraf U, King K, Borisjuk N, Schweizer G (1992) Middle repetitive and highly repetitive sequences detect polymorphisms in plants. In: DNA-polymorphisms in eucaryotic genomes. BTF, Vol. 5, Hüthig, Heidelberg
Ingle J, Timmis J, Sinclair J (1975) The relationship between satellite desoxyribonucleic acid, ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene redundancy, and genomic size in plants. Plant Physiol 55:496–501
Kato A, Nakajima T, Yamashita J, Yakura K, Tanifuji S (1990) The structure of the large spacer region of the rDNA inVicia faba andPisum sativum. Plant Mol Biol 14:983–993
Kavanagh T, Timmis J (1986) Heterogeneity in cucumber ribosomal DNA. Theor Appl Genet 72:337–345
Kelly RJ, Siegel A (1989) TheCucurbita maxima ribosomal DNA intergenic spacer has a complex structure. Gene 80: 239–248
Kelly RJ, Johnson RD, Siegel A (1990) Heterogeneity and organization of the ribosomal RNA genes ofCucurbita maxima. Plant Mol Biol 14:927–933
Labhart P, Reeder R (1984) Enhancer-like properties of the 60/81 bp elements in the ribosomal spacer ofXenopus laevis. Cell 37:285–289
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Moss T (1983) A transcriptional function for the repetitive ribosomal spacer inXenopus laevis. Nature 302:223–228
Myers EW, Miller W (1988) Optimal alignment in linear space. CABIOS 4:11–17
Pustell JM, Katafos FC (1984) A convenient and adaptable package of computer programs for DNA and protein sequence management, analysis and homology determination. Nucleic Acids Res 12:643–655
Rathgeber J, Capesius I (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer and the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from mustard (Sinapis alba). Nucleic Acids Res 18:1288
Reeder RH (1984) Enhancers and ribosomal gene spacers. Cell 38:349–351
Reeder RH (1990) rRNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Trends Genet 6:390–395
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1987) Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. Plant Mol Biol 9:509–520
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson A (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Schiebel K, v Waldburg G, Gerstner J, Hemleben V (1989) Termination of transcription of ribosomal RNA genes of mung bean occurs within a 175 by repetitive element of the spacer region. Mol Gen Genet 218:302–307
Schmitz ML, Maier UG, Brown JWS, Feix G (1989) Specific binding of nuclear proteins to the promotor region of a maize nuclear rRNA gene unit. J Biol Chem 264:1467–1472
Scott N, Kavanagh T, Timmis J (1984) Methylation of rRNA genes in some higher plants. Plant Sci Lett 35:213–217
Siegel A, Kolacz K (1983) Heterogeneity of the pumpkin ribosomal DNA. Plant Physiol 72:166–171
Sollner-Webb B, Tower J (1986) Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Ann Rev Biochem 55:801–830
Taylor JH (1984) DNA methylation and cellular differentiation. Springer-Verlag, Wien-New York
Torres RA, Zentgraf U, Hemleben V (1989) Species and genus specificity of the intergenic spacer (IGS) in the ribosomal RNA genes ofCucurbitaceae. Z Naturforsch 44c:1029–1034
Torres RA, Ganal M, Hemleben V (1990) GC balance in the internal transcribed spacers ITS 1 and ITS 2 of nuclear ribosomal genes. J Mol Evol 30:170–181
Torres RA and Hemleben V (1991) Use of ribosomal DNA spacer probes to distinguish cultivars ofCucurbita pepo L. and other Cucurbitaceae. Euphytica 53:11–17
Whitaker TW, Bemis WP (1976) Cucurbits. In: Simmonds NW (ed) Evolution of crop plants. Longman, London, pp 64–69
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of M13 mp18 and pUC 19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Zentgraf U, Ganal M, Hemleben V (1990) Length heterogeneity of the rRNA precursor in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Mol Biol 15:465–474
Zentgraf U, Hemleben V (1992) Complex formation of nuclear proteins with the RNA polymerase I promoter and repeated elements in the external transcribed spacer ofCucumis sativus ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 20:3685–3691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: V. Hemleben
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, K., Torres, R.A., Zentgraf, U. et al. Molecular evolution of the intergenic spacer in the nuclear ribosomal RNA genes of Cucurbitaceae. J Mol Evol 36, 144–152 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166250
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166250