Summary
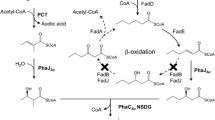
Recombinant strains of Pseudomonas oleovorans, which harbour the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-biosynthetic genes of Alcaligenes eutrophus, accumulated poly(hydroxyalkanoates), composed of 3-hydroxybutyrate(3HB), 3-hydroxyhexanoate (3HHx) and 3-hydroxyactanoate (3HO), up to 70% of the cell dry weight if the cells were cultivated with sodium octanoate as the carbon source. Physiological and chemical analysis revealed multiple evidence that this polymer is a blend of the homopolyester poly(3HB) and of the copolyester poly(3HHx-co-3HO) rather than a random or a block copolyester of 3HB, 3HHx and 3HO. The molar ratio between poly(3HHx-co-3HO) and poly(3HB) varied drastically during the process of fermentation. Whereas synthesis of poly(3HHx-co-3HO) started immediately after ammonium was exhausted in the medium, synthesis of poly(3HB) occurred only after a lag-phase. From freeze-dried cells poly(3HHx-co-3HO) was much more readily extracted with chloroform than was poly(3HB). The blend was fractionated into petrol-ether-insoluble poly(3HB) and petrol-ether-soluble poly(3HHx-co-3HO). The molecular weight values of these polyesters measured by gel permeation chromatography were 2.96 × 106 and 0.35 × 106 and were similar of those polymers accumulated by A. eutrophus or by wild-type P. oleovorans, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballistreri A, Garozzo D, Giuffrida M, Impallomeni G, Montaudo G (1989) Sequencing bacterial poly(β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate) by partial methanolysis, high-performance liquid chromatography fractionation, and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry analysis. Macromolecules 22:2107–2111
Bradel R, Kleinke A, Reichert KH (1989) Molecular weight of bacterially produced poly-d(−)-3-hydroxybutyrate. In: Behrens D, Driesel A.J (eds) DECHEMA Biotechnology Conferences, vol 3, pp 207–209, Frankfurt
Brandl H, Gross RA, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1988) Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates) for potential applications as biodegradable polyesters. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1977–1982
Byrom D (1987) Polymer synthesis by microorganisms: technology and economics. TIBTECH 5:246–250
Doi Y, Tamaki A, Kunioka M, SogaK (1987) Biosynthesis of terpolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate from 5-chlorpentanoic and pentanoic acids. Makromol Chem Rapid Commun 8:631–635
doi Y, Tamaki A, Kunioka M, soga K (1988) Production of copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate from butyric and pentanoic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:330–334
Gross RA, DeMello C, Lenz RW, Brandl H, Fuller RC (1989) Biosynthesis and characterization of poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates) produced by Pseudomonas oleovorans. Macromolecules 22:1106–1115
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Chu L, Dawes EA (1988a) Characterization of two 3-ketothiolases possessing duffering substrate specificities in the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:259–264
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Chu L, Dawes EA (1988b) The role of NADH- and NADHP-linked acetoacetyl-CoA reductases in the poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:259–264
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1989a) A survey of the accumulation of novel polyhydroxyalkanoates by bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 11:471–476
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1989b) The importance of PHB-synthase substrate specificity in polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis by Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 57:1–6
Helleur RJ (1988) Pyrolysis-gas chromatography for the rapid characterization of bacterial poly(β-hydroxybutyrate-co-β-hydroxyvalerate). Polymer Preprints 29:609–610
Holmes PA (1985) Applications of PHB — a microbially produced biodegradable thermoplastic. Phys Technol 16:32–36
Holmes PA, Wright LF, collins SH (1981) β-Hydroxybutyrate polymers. European Patent Application EP 052.459
Huisman GW, Leeuw O de, Eggink G, Witholt B (1989) Synthesis of poly-3-hydroxyalkanoates is a common feature of fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1949–1954
Kunioka M, Nakamura Y, Doi Y (1988) New bacterial copolyesters produced in Alcaligenes eutrophus from organic acids. Polymer Commun 29:174–176
Kunioka M, Tamaki A, Doi Y (1989) Crystalline and thermal properties of bacterial copolyesters: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 22:694–697
Lageveen RG, Huisman GW, Preusting H, Ketelaar P, Eggink G, Witholt B (1988) Formation of polyesters by Pseudomonas oleovorans: effect of substrates on the formation and composition of poly(R)-3-hydroxyalkanoates and poly-(R)-3-hydroxyalkenoates. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2924–2930
Peoples OP, Sinskey AJ (1989) Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Identification and characterization of the PHB polymerase gene (phbC). J Biol Chem 264:15298–15303
Schlegel HG, Kaltwasser H, Gottschalk G (1961) Ein Submersverfahren zur Kultur wasserstoffoxidierender Bakterien: wachstumsphysiologische Untersuchungen. Arch Mikrobiol 38:209–222
Schubert P, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for synthesis of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) and synthesis of PHB in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5837–5847
Slater SC, Voige WH, Dennis DE (1988) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 poly-β-hydroxybutyrate biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol 170:4431–4436
Smet MJ de, Eggink G, Witholt B, Kingma J, Wynberg H (1983) Characterization of intracellular inclusions formed by Pseudomonas oleovorans during growth on octane. J Bacteriol 154:870–878
Steinbüchel A (1989) Poly(hydroxyfettsäuren) — Speicherstoffe von Bakterien: Biosynthese und Genetik. Forum Mikrobiol 12:190–198
Steinbüchel A, Schubert P (1989) Expression of the Alcaligenes eutrophus poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid)-synthetic pathway in Pseudomonas sp. Arch Microbiol 153:101–104
Stickland HL (1951) The determination of small quantities of bacteria by means of the Biuret reaction. J Gen Microbiol 5:698–703
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: A. Steinbüchel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Timm, A., Byrom, D. & Steinbüchel, A. Formation of blends of various poly(3-hydroxyalkanoic acids) by a recombinant strain of Pseudomonas oleovorans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33, 296–301 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164525
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164525