Abstract
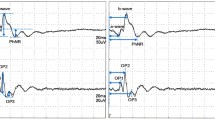
The direct current electroretinogram (ERG) and the standing potential (SP) were recorded from both eyes of 14 albino rabbits during intraocular perfusion of one of the eyes, which was vitrectomized, with a recently developed eye irrigation solution (PHS) produced by Pharmacia Ophthalmics. PHS was then replaced by a test solution containing melatonin dissolved in PHS (0.002 μM-200 μM). The fluids were subsequently alternated (PHS - melatonin - PHS). During uniocular irrigation with melatonin the mean c-wave amplitude and SP level of the intact control eye were increased (c-wave + 24%, p < 0.01; SP + 0.65 mV, p < 0.05) compared with the values during the initial perfusion with PHS. In contrast, the c-wave amplitude of the irrigated eye was markedly decreased in many rabbits during perfusion with melatonin compared with the initial PHS, but the mean reduction was small and not statistically significant. The mean SP level was reduced (-1.54 mV, p < 0.001). This difference between the eyes probably depends on the route by which melatonin reaches the retinal pigment ephithelium and thus whether it primarily affects the apical (as in the irrigated eye) or the basal (as in the control eye) pigment epithelial membrane. A peak in the e-wave amplitude was observed in both eyes during uniocular irrigation with melatonin when compared with the amplitude measured during the initial perfusion with PHS (irrigated eye: + 27%, p < 0.001; control eye + 18%, p < 0.002).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besharse JC, Dunis DA (1983) Methoxyindoles and photoreceptor metabolism. Science 219: 1341–1343
Bubenik GA, Brown GM, Uhlir I, Grota LJ (1974) Immunohistological localization of N-acetylindole-alkylamines in pineal gland, retina and cerebellum. Brain Res 81: 233–242
Dawis SM, Niemeyer G (1985) Biogenic monoamines affect a slow light-evoked electrical response of the retinal pigment epithelium. Soc Neurosci Abstr 11
Dawis SM, Niemeyer G (1986) Dopamine influences the light peak in the perfused mammalian eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 27: 330–335
Dick E, Miller RF (1978) Light-evoked potassium activity in mudpuppy retina: its relationship to the b-wave of the electroretinogram. Brain Res 154: 388–394
Dubocovich ML (1983) Melatonin is a potent modulator of dopamine release in the retina. Nature (Lond) 306: 782–784
Elenius V (1958) Recovery in the dark of the rabbit's electroretinogram in relation to intensity, duration and colour of light-adaption. Acta Physiol Scand 44, suppl 150, 57 pp
Faber DS (1969) Analysis of the slow transretinal potentials in response to light. Ph.D. Thesis. State University of New York at Buffalo
Gouras P (1969) Clinical electro-oculography. In: The Retina, (ed) Straatsma BR. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press pp 565–581
Griff ER, Steinberg RH (1982) Origin of the light peak: in vitro study of Gekko gekko. J Physiol (Lond) 331: 637–652
Hamm HE, Menaker M (1980) Retinal rhythms in chicks: Circadian variation in melatonin and serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 4998–5002
Kolder H (1959) Spontane und experimentelle Änderungen des Bestandpotentials des menschlichen Auges. Pflügers Arch Ges Physiol 268: 258–272
Kris C (1958) Corneo-fundal potential variations during light and dark adaptation. Nature (Lond) 182: 1027–1028
Linsenmeier RA, Steinberg RH (1982) Origin and sensitivity of the light peak of the intact cat eye. J Physiol (Lond) 331: 653–673
Michaelson IC (1954) Retinal circulation in man and animals. Springfield: Charles C. Thomas
Miller RF, Dowling JE (1970) Intracellular responses of the Müller (glial) cells of the mudpuppy retina: their relation to b-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol 33: 323–341
Miller SS, Steinberg RH (1977) Passive ionic properties of frog retinal pigment epithelium. J Membr Physiol 36: 337–372
Newman EA (1979) B-wave currents in the frog retina. Vision Res 19: 227–234
Newman EA (1980) Current source-density analysis of the b-wave of frog retina. J Neurophysiol 43: 1355–1366
Nilsson SEG, Skoog K-O (1975) Covariation of the simultaneously recorded c-wave and standing potential of the human eye. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 53: 721–730
Noell WK (1953) Studies on the electrophysiology and the metabolism of the retina. US Air Force, SAM Project 21–1201–0004. Randolph Field, Texas
Oakley B II (1977) Potassium and the photoreceptor-dependent pigment epithelial hyperpolarization. J Gen Physiol 70: 405–425
Oakley B II, Green DG (1976) Correlation of light-induced changes in retinal extracellular potassium concentration with c-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol 39: 1117–1133
Oakley B II, Steinberg RH, Miller SS, Nilsson SEG (1977) The in vitro frog pigment epithelial hyperpolarization in response to light. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 16: 771–774
Pang SF, Yu HS, Suen HC, Brown GM (1980) Melatonin in the retina of rats: a diurnal rhythm. J Endocrinol 87: 89–93
Pierce ME, Besharse JC (1985) Circadian regulation of retinomotor movements. I. Interaction of melatonin and dopamine in the control of cone length. J Gen Physiol 86: 671–689
Shimazaki H, Oakley B II (1985) Effects of cesium upon Müller cell membrane responses, [K+]0, and the electroretinogram. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26 (ARVO suppl): 112
Skoog K-O (1975) The directly recorded standing potential of the human eye. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 53: 120–132
Skoog K-O, Nilsson SEG (1974) The c-wave of the human d.c.-registered ERG. I. A quantitative study of the relationship between c-wave amplitude and stimulus intensity. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 52: 759–773
Steinberg RH, Miller S (1973) Aspects of electrolyte transport in frog pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 16: 365–372
Steinberg RH, Niemeyer G (1981) Light peak of cat DC electroretinogram: not generated by a change in [K+]0. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 20: 414–418
Steinberg RH, Schmidt R, Brown KT (1970) Intracellular responses to light from cat pigment epithelium: origin of the electroretinogram c-wave. Nature (Lond) 227: 728–730
Textorius O, Nilsson SEG, Skoog KO (1978) Studies on acute and late stages of experimental central retinal artery occlusion in the Cynomolgus monkey. I. Intensity-amplitude relations of the d.c. recorded ERG with special reference to the c-wave. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 56: 648–664
Textorius O, Nilsson SEG, Andersson BE (1986) Effects of intraocular perfusion with two alternating irrigation solutions on the simultaneously recorded electroretinogram of albino rabbits. Doc Ophthalmol 63: 349–358
Textorius O, Welinder E, Nilsson SEG (1985) Combined effects of DL-α-aminoadipic acid with sodium iodate, ethyl alcohol, or light stimulation on the ERG c-wave and on the standing potential of albino rabbit eyes. Doc Ophthalmol 60: 393–400
Vivien-Roels B, Pévet P, Dubois MP, Arendt J, Brown GM (1981) Immunohistochemical evidence for the presence of melatonin in the pineal gland, the retina and the Harderian gland. Cell Tissue Res 217: 105–115
Wiechmann AF, Bok D, Horwitz J (1985) Localization of hydroxy-indole-0-methyltransferase in the mammalian pineal gland and retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 26: 253–265
Witkovsky P, Dudek FE, Ripps H (1975) Slow PIII component of the carp electroretinogram. J Gen Physiol 65: 119–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Textorius, O., Nilsson, S.E.G. Effects of intraocular irrigation with melatonin on the c-wave of the direct current electroretinogram and on the standing potential of the eye in albino rabbits. Doc Ophthalmol 65, 97–111 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00162725
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00162725