Abstract
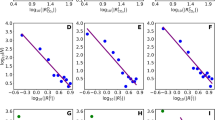
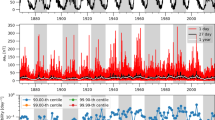
In this paper we present a general framework for forecasting the smoothed maximum level of solar activity in a given cycle, based on a simple understanding of the solar dynamo. This type of forecasting requires knowledge of the Sun's polar magnetic field strength at the preceeding activity minimum. Because direct measurements of this quantity are difficult to obtain, we evaluate the quality of a number of proxy indicators already used by other authors which are physically related to the Sun's polar field. We subject these indicators to a rigorous statistical analysis, and specify in detail the analysis technique for each indicator in order to simplify and systematize reanalysis for future use. We find that several of these proxies are in fact poorly correlated or uncorrelated with solar activity, and thus are of little value for predicting activity maxima.
We also present a scheme in which the predictions of the individual proxies are combined via an appropriately weighted mean to produce a compound prediction. We then apply the scheme to the current cycle 22, and estimate a maximum smoothed International sunspot number of 171 ± 26, which can be expressed alternatively as a smoothed 2800 MHz radio flux (F 10.7) of 211 ± 23 × (10−22 Wm−2Hz−1), or as a smoothed sunspot area of 2660 ± 430 millionths of a solar disk. Once the actual maximum for cycle 22 has been established, we will have both additional statistics for all the proxy indicators, and a clearer indication of how accurately the present scheme can predict solar activity levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altrock, R. C. (ed.): 1988, Proceedings of the Ninth Sacramento Peak Summer Symposium, National Solar Observatory, Sunspot, p. 414.
Babcock, H. W.: 1961, Astrophys. J. 133, 572.
Bao, K.: 1984, Publ. Beijing Astron. Obs. 5, 1.
Bao, K.: 1989, Publ. Beijing Astron. Obs. 12, 47.
Bevington, P. R.: 1969, Data Reduction and Final Analysis for the Physical Sciences, McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 73.
Billings, D. E.: 1966, A Guide to the Solar Corona, Academic Press, New York, p. 226.
Brown, G. M.: 1981, Solar Phys. 74, 125.
Brown, G. M.: 1986, in P. A. Simon, G. Heckman, and M. A. Shea (eds.), Solar-Terrestrial Prediction Proceedings, NOAA, Boulder, p. 1.
Brown, G. M.: 1988, Nature 333, 121.
Brown, G. M. and Williams, W. R.: 1969, Planetary Space Sci. 17, 445.
Butcher, E. C. and Brown, G. M.: 1981, Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 64, 513.
Cowling, T. G.: 1953, in G. P. Kuiper (ed.), The Sun, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, p. 575.
Foukal, P. and Lean, J.: 1988, Astrophys. J. 328, 347.
Gonzalez, G. and Schatten, K. H.: 1987, Solar Phys. 114, 189.
Hirman, J. W., Heckman, G. R., Greer, M. S., and Smith, J. B.: EOS: SPR News, 18 October, 1988.
Howard, R.: 1984, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 22, 131.
Howard, R. and LaBonte, B. J.: 1980, Astrophys. J. 239, L33.
IAU Quarterly Bulletin on Solar Activity 1–27, presently published by National Astronomical Observatory, Tokyo.
Jeffreys, W. H., Fitzpatrick, M. J., and McArthur, B. E.: 1988, GaussFit: A System for Least Squares and Robust Estimation; User's Manual, University of Texas, Austin.
Kane, R. P.: 1978, Nature 274, 139.
Kane, R. P.: 1987, Solar Phys. 108, 415.
Kane, R. P.: 1989, Solar Phys. 122, 175.
Leighton, R. B.: 1969, Astrophys. J. 156, 1.
Loucif, M. L. and Koutchmy, S.: 1989, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 77, 45.
Mayaud, P.-N.: 1972, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 6870.
CD ROM NGDC01: 1987, National Geophysical Data Center, NOAA, U.S. Dept. of Commerce.
Press, W. H., Flannery, A. P., Teukolsky, S. A., and Vetterling, W. T.: 1986, Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing, Cambridge University Press, New York, p. 487.
Rosenberg, R. L. and Coleman, P. J., Jr.: 1969, J. Geophys. Res. 74, 5611.
Schatten, K. H.: 1971, Rev. Geophys. Space Sci. 9, 773.
Schatten, K. H.: 1988a, Geophys. Res. Letters 15, 121.
Schatten, K. H.: 1988b, private communication.
Schatten, K. H.: 1990, Solar Phys. 125, 185.
Schatten, K. H. and Hedin, A. E.: 1984, Geophys. Res. Letters 1, 873.
Schatten, K. H. and Sofia, S.: 1987, Geophys. Res. Letters 14, 632.
Schatten, K. H., Scherrer, P. H., Svalgaard, L., and Wilcox, J. M.: 1978, Geophys. Res. Letters 5, 411.
Scherrer, P. H., Wilcox, J. M., Kotov, V., Severny, A. B., and Howard, R.: 1977, Solar Phys. 52, 3.
Scherrer, P. H., Wilcox, J. M., Svalgaard, L., Duvall, T. L., Jr., Dittmer, P. H., and Gustafson, E. K.: 1977, Solar Phys. 54, 353.
Sheeley, N. R. Jr.: 1964, Astrophys. J. 140, 731.
Sheeley, N. R. Jr.: 1966, Astrophys. J. 144, 728.
Sheeley, N. R. Jr.: 1976, J. Geophys. Res. 81, 3462.
Simon, P. A. and Legrand, J. P.: 1987, Astron. Astrophys. 182, 329.
Solar Geophysical Data, NOAA, U.S. Dept. of Commerce, Boulder.
Snodgrass, H. B. and Wilson, P. R.: 1987, Nature 328, 696.
Svalgaard, L.: 1972, Danish Meteorological Institute Geophysical Papers, R-29, Charlottenlund, Denmark.
Svalgaard, L.: 1972, J. Geophys. Res. 77, 4027.
Svalgaard, L.: 1977, in J. Zirker (ed.), Coronal Holes and High Speed Wind Streams, Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, p. 371.
Svalgaard, L. and Wilcox, J. M.: 1976, Nature 262, 766.
Svalgaard, L., Duvall, T. L. Jr., and Scherrer, P. H.: 1978, Solar Phys. 58, 225.
van de Hulst, H. C.: 1953, in G. P. Kuiper (ed.), The Sun, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, p. 207.
Wilson, R. M.: 1988, Geophys. Res. Letters 15, 125.
Wilson, R. M.: 1988, Solar Phys. 117, 179.
Wilson, P. R., Altrock, R. C., Harvey, K. L., Martin, S. F., and Snodgrass, H. B.: 1988, Nature 333, 748.
Wolf, R.: 1884, Astron. Mitt. Zürich, No. 61.
Yoshimura, H.: 1975, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 29, 467.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Layden, A.C., Fox, P.A., Howard, J.M. et al. Dynamo-based scheme for forecasting the magnitude of solar activity cycles. Sol Phys 132, 1–40 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00159127
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00159127