Abstract
Three different restriction enzymes (PstI, EcoRI, SspI) were used to analyze the total genomic DNA fingerprints of 52 Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) isolates collected between 1982 and 1992 from patients and carriers in central-northern Italy. The same isolates were also characterized by biotyping and antimicrobial agent susceptibility typing. In addition, 13 Hib reference strains from Sweden and the Netherlands were subjected to DNA fingerprinting and compared to Italian isolates.
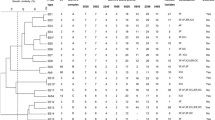
Both genotypic and phenotypic analysis revealed low variability among the Italian study isolates. Most were biotype I and all study isolates but one were susceptible to ampicillin, chloramphenicol, rifampin, third-generation cephalosporins and cotrimoxazole. Among the 52 Italian isolates, 3 distinct DNA patterns were identified, and 88.5% of study strains belonged to the same DNA group. There was sharing of the predominant DNA profile among isolates cultured in different years from different geographical areas and different invasive, respiratory and surface infections. However, another DNA pattern was only found in carrier isolates and in one surface infection isolate.
Comparison by DNA fingerprinting showed that the majority of Italian isolates were closely related to most of the analyzed Swedish and Dutch reference strains, previously shown by other techniques to be predominant in those areas. This finding provides additional support for the hypothesis that there may be a dominant European Hib clone.
The results show that DNA fingerprinting is a reliable method for Hib characterization and may be a useful additional epidemiological tool for this microorganism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barenkamp S.J., Munson R.S. Jr and Granoff D.M. (1981): Subtyping isolates of Haemophilus influenzae type b by outer-membrane protein profiles - Journal of Infectious Diseases 143: 668–676.
Bruce K.D. and Jordens J.Z. (1991): Characterization of non-capsulate Haemophilus influenzae by whole-cell polypeptide profiles, restriction endonuclease analysis, and rRNA gene restriction patterns -Journal of Clinical Microbiology 29: 291–296.
Elliot J.A., Pigott N., Cochi S.L. and Facklam R.R. (1990): Major subtypes of invasive Haemophilus influenzae from 1983 to 1985 in Atlanta, Ga - Journal of Clinical Microbiology 28: 833–836.
Granoff D.M., Pandey J.P., Boies E., Squires J., Munson Jr R.S. and Suarez B. (1984): Response to immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide — pertussis vaccine and risk of Haemophilus meningitis in children with Km(1) immunoglobulin allotype - Journal of Clinical Investigation 74: 1708–1714.
Granoff D.M., Sheetz K., Pandey J.P., Nahm M.H., Rambeck J.H., Jacobs J.L., Musser J., Selander R.K., Kabeer M., Murphy T.V. and Osterholm M.T. (1989): Host and bacterial factors associated with Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in Minnesota children vaccinated with type b polysaccharide vaccine - Journal of Infectious Diseases 159: 908–916.
Granoff D.M., Suarez B.K., Pandey J.P. and Shackelford P.G. (1988): Genes associated with the G2m(23) immunoglobulin allotype regulate the IgG subclass responses to Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide vaccine - Journal of Infectious Diseases 157: 1142–1149.
Hampton C.M., Barenkamp S.J. and Granoff D.M. (1983): Comparison of outer membrane protein subtypes of Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates from healthy children in the general population and from diseased patients - Journal of Clinical Microbiology 18: 596–600.
Kayser F.H., Morenzoni G. and Santanam P. (1990): The second European collaborative study on the frequency of antimicrobial resistance in Haemophilus influenzae - Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9: 810–817.
Loos B.G., Bernstein J.M., Dryja D.M., Murphy T.F. and Dickinson D.P. (1989): Determination of the epidemiology and transmission of non-typable Haemophilus influenzae in children with otitis media by comparison of total genomic DNA restriction fingerprints - Infection and Immunity 57: 2751–2757.
Mandelman P.M., Wiley E.A., Stull T.L., Clausen C., Chaffin D.O. and Onay O. (1990): Problems with current recommendations for susceptibility testing of Haemophilus influenzae - Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy 34: 1480–1484.
Moeser P.J., Costello P.B., Gillikin S. and Murphy T.F. (1991): Haemophilus infuenzae polyarthritis in an adult: an analysis of serotype b strains - Reviews of Infectious Diseases 13: 61–63.
Murphy T.F., Dudas K.C., Mylotte J.M. and Apicella M.A. (1983): A subtyping system for non-typable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins - Journal of Infectious Diseases 147: 838–846.
Musser J.M., Barenkamp S.J., Granoff D.M. and Selander R.K. (1986): Genetic relationships of serologically non-typable and serotype b strains of Haemophilus infuenzae - Infection and Immunity 52: 183–191.
Musser J.M., Kroll J.S., Granoff D.M., et al. (1990): Global genetic structure and molecular epidemiology of encapsulated Haemophilus infuenzae - Reviews of Infectious Diseases 12: 75–111.
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (1990): Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests, 4th ed. Approved standard M2-A4- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Villanova, Pa.
Paterson A.J., Macsween K.F. and Pennington T.H. (1987): Haemophilus influenzae subtyping by SDS-PAGE of whole-cell polypeptides - Epidem. Inf. 99: 179–189.
Pennington T.H. and Freebairn E.M. (1989): Subtyping of Haemophilus influenzae type b strains from Europe and North America by SDS-PAGE of whole-cell polypeptides: the geographical distribution of subtypes - Epidem. Inf. 102: 11–19.
Petersen G.M., Silimperi D.R., Rotter J.I., Terasaki P.I., Schanfield M.S., Park M.S. and Ward J.I. (1987): Genetic factors in Haemophilus influenzae type b disease susceptibility and antibody acquisition -Journal of Pediatrics 110: 228–233.
Porras O., Caugant D.A., Gray B., Lagergard T., Levin B.R. and Svanborg-Eden C. (1986): Difference in structure between type b and nontypable Haemophilus influenzae populations - Infection and Immunity 53: 79–89.
Poulsen K., Hjorth J.P. and Kilian M. (1988): Limited diversity of the immunoglobulin A1 protease gene (Iga) among Haemophilus influenzae serotype b strains - Infection and Immunity 56: 987–992.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F. and Maniatis T. (1989): Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd editions -Edited by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., U.S.A.
Slack M.P.E. (1990): Haemophilus. In: Topley & Wilson's: Principles of Bacteriology, Virology and Immunity. Parker M.T., Duerden B.J. (eds.) — vol. 2, p. 355–382, 8th Ed., London.
Takala A.K., Eskola J., Bol P., Van Alphen L., Palmgren J. and Mäkelä P.H. (1987): Haemophilus influenzae type b strains of outer membrane subtypes 1 and 1c cause different types of invasive disease -Lancet ii: 647–649.
Van Alphen L., Bol P. and Geelen-Van Der Broek L. (1991): Differences in subtype distribution of Haemophilus infuenzae type b from carriers in the general population and patients with meningitis -Journal of Medical Microbiology 34: 313–316.
Van Alphen L., Geelen L., Jonsdottir K., Talaka A.K., Käyhty H. and Zanen H.C. (1987): Distinct geographic distribution of subtypes of Haemophilus infuenzae type b in Western Europe - Journal of Infectious Diseases 156: 216–218.
Van Alphen L., Riemens T., Poolman J., Hopman C. and Zanen H.C. (1983): Homogeneity of cell envelope protein subtypes, lipopolysaccharide serotypes, and biotypes among Haemophilus influenzae type b from patients with meningitis in the Netherlands - Journal of Infectious Diseases 148: 75–81.
Van Ham S.M., Mooi F.R., Sindhunata M.G., Maris W.R. and Van Alphen L. (1989): Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of Haemophilus influenzae fimbrial genes establishes adherence to oropharyngeal epithelial cells - EMBO J. 11: 3535–3540.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mencarelli, M., Marsili, C., Zanchi, A. et al. Genomic DNA fingerprints and phenotypic characteristics of serotype B Haemophilus influenzae isolates from Italy. Eur J Epidemiol 9, 353–360 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157390
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157390