Abstract
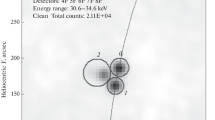
Stereoscopic observations of high energy (≳ 100 keV) photon emission from five solar flares have been made with the X-ray spectrometers aboard the ISEE-3 (International Sun Earth Explorer-3) and PVO (Pioneer Venus Orbiter) spacecraft. The observed altitude structure of the photon source and its dependence on the photon energy and time during a flare are compared with the predictions of thermal and non-thermal models of the hard X-ray source. In the case of the impulsive source, it is found that (1) the thermal model with adiabatic compression and expansion of a magnetically-confined plasma and the thin target (non-thermal) model are not consistent with the observations; (2) the thick target (non-thermal) model and the dissipative thermal model are partially in agreement with the observations; (3) the emission probably originates in many individual non-thermal sources distributed in altitude, the lower altitude sources being brighter than those at higher altitude. In the case of the gradual source, it is found that (1) models with purely coronal sources are not consistent with the observations; (2) a partial precipitation model with trapped as well as precipitating electrons is consistent with the observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, J. C.: 1971, Solar Phys. 18, 489.
Brown, J. C., and Hayward, J.: 1981, Solar Phys. 73, 121.
Brown, J. C., and Hoyng, P.: 1975, Astrophys. J. 200, 734.
Brown, J. C., and McClymont, A. N.: 1975, Solar Phys. 41, 135.
Brown, J. C., Melrose, D. B. and Spicer, D. S.: 1979, Astrophys. J. 228, 592.
Crannell, C. J., Frost, K., Mätzler, C., Ohki, K., and Saba, J.: 1978, Astrophys. J. 223, 620.
Datlowe, D. W., and Lin, R. P.: 1973, Solar Phys. 32, 459.
Emslie, A. G.: 1980, Stanford University Institute of Plasma Research Report No. 822.
Hudson, H. S.: 1972, Solar Phys. 24, 414.
Kane, S. R.: 1974, in G. Newkirk (ed.), ‘Coronal Disturbances’, IAU Symp. 57, 105.
Kane, S. R.: 1981, Astrophys. Sp. Sci. 75, 163.
Kane, S. R., Anderson, K. A., Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. W., and Laros, J.: 1979, Astrophys. J. Lett. 233, L151.
Kane, S. R., Anderson, K. A., Evans, W. D., Klebesadel, R. W., and Laros, J.: 1980, Astrophys. J. Lett. 239, L85.
Kane, S. R., Fenimore, E. E., Klebesadel, R. W., and Laros, J.: 1982, Astrophys. J. Lett. 254, L53.
Melrose, D. B., and Brown, J. C.: 1976, Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 176, 15.
Ramaty, R: 1973, in R. Ramaty and R. G. Stone (eds.), High Energy Phenomena on the Sun, NASA SP-342, p. 188.
Stewart, R. T., and Nelson, G. J.: 1980, Proc. Astron. Soc. Australia 3, 380.
Takakura, T.: 1974, in S. R. Kane (ed.), ‘Solar Gamma-, X-, and EUV Radiation’, IAU Symp. 68, 299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kane, S.R. Spatial structure of high energy photon sources in solar flares. Sol Phys 86, 355–365 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157209
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157209