Abstract
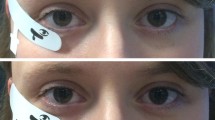
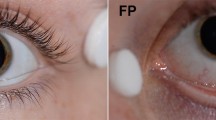
A new noncorneal electrode for clinical electroretinography was developed. It consists of a thin wire forming a loop modeled to fit into the lower conjunctival sac. Electrical contact is made with the scleral conjunctiva through an exposed portion of otherwise insulated wire. The recorded pattern electroretinograms are in the same amplitude range as if recorded by the gold foil electrode, while the flash electroretinograms with the new electrode are of about two-thirds the amplitude of corneal electrodes. The new electrode is more durable and hence less expensive than gold foil electrodes and can likewise be used without topical anesthetic. Cleaning is easy and effective. The electrode rarely causes discomfort and produces stable responses for at least 2 hours. The electrode aims to match stability of skin electrodes with sensitivity of fragile foil and fiber electrodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borda RP, Gilliam RM, Coats AC. Gold-coated Mylar™ (GCM) electrode for electroretinography. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 1977; 15: 339–43.
Arden GB, Carter RM, Hogg C, Siegel IM, Margolis S. A gold foil electrode: Extending horizons for clinical electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1979; 18: 421–6.
Dawson WW, Trick GL, Litzkow CA. Improved electrode for electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1979; 18: 988–91.
Holopigian K, Snow J, Seiple W, Siegel I. Variability of the pattern electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 1988; 70: 104–16.
Mc Allan A, Sinn J, Aylward GW. The effect of gold foil electrode position on the electroretinogram in human subjects. Vision Res 1989; 29: 1085–87.
Coupland SG, Janaky M. ERG electrode in pediatric patients: Comparison of DTL fiber, PVA-gel and non corneal skin electrodes. Doc Ophthalmol 1989; 71: 427–33.
Hawlina M, Štrucl M, Stirn-Kranjc B, Finderle Ž, Brecelj J. Pattern electroretinogram recorded by skin electrodes in early ocular hypertension and glaucoma. Doc Ophthalmol 1989; 73: 183–91.
Dawson WW, Zimmerman TJ, Houde WL. A method for more comfortable elec- troetinography. Arch Ophthalmol 1974; 91: 1–2.
Aylward GW, McClellan KA, Thomas R, Billson FA. Transient corneal changes associated with the use of gold foil electrodes. Br J Ophthalmol 1989; 73: 980–84.
Hawlina M. Pattern electroretinogram with the new ‘HK-loop’ electrode [Abstract]. Presented at the 30th symposium ISCEV, Vienna, 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawlina, M., Konec, B. New noncorneal HK-loop electrode for clinical electroretinography. Doc Ophthalmol 81, 253–259 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00156014
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00156014