Abstract
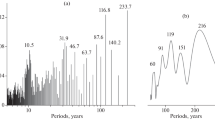
The sunspot record for the time interval 1749–1977 can be represented conveniently by an harmonic model comprising a relatively large number of lines. Solar activity can otherwise be considered as a sequence of partly overlapping events, triggered periodically at intervals of the order of 11 years. Each individual cycle is approximated by a function of the Maxwell distribution type; the resulting impulse model consists of the superposition of the independent pulses. Application of these two models for the prediction of annual values of the Wolf sunspot numbers leads to controversial results. Mathematical modelling of the sunspot time series does not give an unambiguous result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard, Y.: 1974, Nonlinear Parameter Estimation, Academic Press, N.Y.
Blackman, R. B. and Tukey, J. W.: 1959, The Measurement of Power Spectra, Dover, N.Y.
Brown, G. M.: 1974, Nature 251, 592.
Chen, W. Y. and Stegen, G. R.: 1974, J. Geophys. Res. 79, 20, 3019.
Cohen, T. J. and Lintz, P. R.: 1974, Nature 250, 398.
Cole, T. W.: 1973, Solar Phys. 30, 103.
Currie, R. G.: 1973, Astrophys. Space Sci. 20, 509.
Dodson, H. W. and Hedeman, E. R.: 1972, in E. R. Dyer (ed.), Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Part I, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 151.
Gleissberg, W.: 1952, Die Häufigkeit der Sonnenflecken, Akademie-Verlag, Berlin.
Harwood, J. M. and Malin, S. R. C.: 1977, Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 50, 605.
Hill, J. R.: 1977, Nature 266, 151.
Kane, R. P.: 1978, Nature 274, 139.
McNish, A. G. and Lincoln, J. V.: 1949, Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 30, 673.
Mörth, H. T. and Schlamminger, L.: 1979, in B. M. McCorman and T. A. Seliga (eds.), Solar-Terrestrial Influences on Weather and Climates, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 193.
Ramaswany, G.: 1977, Nature 265, 713.
Schatten, K. H., Scherrer, P. H., Svalgaard, L., and Wilcox, J. M.: 1978, Geophys. Res. Letters 5, 411.
Smythe, C. M. and Eddy, J. A.: 1977, Nature 266, 1977.
Sneyers, R.: 1976, J. Appl. Met. 15, 387.
Ulrych, T. J. and Clayton, R. W.: 1976, Phys. Earth. Planet. Interiors 12, 188.
Wolff, C. L.: 1976, Astrophys. J. 205, 612.
Zhukov, L. V. and Muzalevskii, Yu. S.: 1969, Astron. Zh. 46, 600 (English transl. in Soviet Astron.-AJ 13, 473).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Meyer, F. Mathematical modelling of the sunspot cycle. Sol Phys 70, 259–272 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151333
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151333