Abstract
Pyrheliometry, definition of the radiation scale in the International System of Units and monitoring the variability of solar total irradiance have been a focus of research at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory since the mid 1960's. A series of automated, electrically self-calibrating, cavity pyrheliometers known as Active Cavity Radiometers (ACR's) was developed as part of this program. A series of ground based experiments in 1968–69 led to the discovery of a systematic error in the International Pyrheliometric Scale. ACR's were among the instruments used to define the World Radiometric Reference in 1975.
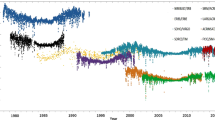
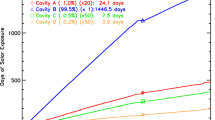
ACR flight experiments have been conducted to determine the 1 AU total solar irradiance and monitor its variability in time. A 1969 balloon experiment yielded a 1366 W m-2 result. The value from a 1976 sounding rocket experiment was 1368.1 W m-2. The results for two additional rocket experiments in 1978 and 80, revised in accordance with recent calibrations of ACR response to elevated pressures during these flights are: 1367.6 and 1367.8 W m-2, respectively. An ACR experiment (ACRIM) on the Solar Maximum Mission satellite has shown continuous variability of the total solar flux below the ±0.05% level and two large, temporary decreases of 0.1–0.2% lasting more than a week. The mean 1 AU total flux for ACRIM's first five months' observations was 1367.7 W m-2. Inflight comparison of ACR rocket and satellite measurements in May, 1980 demonstrated agreement to within ±0.05%. The 1 AU total solar irradiance results from ACR rocket and satellite experiments between 1976 and 1980 differ from their mean of 1367.8 W m-2 by no more than ±0.02%. The less precise 1969 balloon result is 0.1% lower. Although no observations were made from 1970–75, if solar behaviour in those five years was similar to that observed since 1976 then the upper limits of long term solar total irradiance variability are ±0.2% for the 1969–1980 period and ±0.1% between 1976 and 1980, based on the set of ACR observations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brusa, R. W. and Fröhlich, C.: 1975, Scientific Discussions of IPC IV, WRC Publ. No. 534, WRC, Davos, Switzerland.
Crommelynck, D.: 1981, Solar Phys. 74, 509 (this volume).
Duncan, C. H., Harrison, R. G., Kendall, J. H., Willson, R. C., Hickey, J. E., and Thekaekara, M. P.: 1977, J. Appl. Opt. 16, 2690.
Duncan, C. H. et al.: 1980, ‘1980 Rocket Measurements of the Solar Constant’, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, Maryland, in press.
Fröhlich, C.: 1977, in O. R. White (ed.), The Solar Output and Its Variation, University of Colorado Press, Boulder, Colo.
Fröhlich, C. and Brusa, R.: 1981, Solar Phys. 74, 209 (this volume).
Hickey, J. R. et al.: 1976, ‘Extra-Terrestrial Solar Irradiance Measurements from the Nimbus 6 Satellite’, Proc. Joint Conference on Sharing the Sun, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
Hickey, J. R., Stowe, L. L., Jacobowitz, H.; Pellegrino, P., Masckoff, R. H., House, F., and Vonder Haar, T. H.: 1980, Science 208, 281.
Kendall, J. M. Sr. and Berdahl, C. M.: 1969, J. Appl Opt. 9, 1082.
Kendall, J. M. Sr., Haley, F., and Plamondon, J.: 1965, Cavity Type Absolute Total Radiation Radiometer, Proc. Instr. Soc. Am., Oct. 4–7, Los Angeles, Calif.
Plamondon, J. A.: 1969, JPL Space Programs Summary, 37—59, Vol. III, p. 162, Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif.
Plamondon, J. A. and Kendall, J. M. Sr.: 1965, JPL Space Prog. Summary, 37–35, Vol. IV, Jet Propulsion Lab, Pasadena, Calif.
Willson, R. C.: 1969, JPL Tech. Rept. 32–1365, Jet Propulsion Lab, Calif.
Willson, R. C.: 1971, J. Geophys. Res. 76, 4325.
Willson, R. C.: 1972, Nature 239, 208.
Willson, R. C.: 1973, J. Appl. Opt. 12, 810.
Willson, R. C.: 1973, Solar Energy 14, 203.
Willson, R. C.: 1978, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 4003.
Willson, R. C.: 1979, J. Appl. Optics 18, 179.
Willson, R. C.: 1980, ‘Results of the Active Cavity Radiometer Experiment on the Solar Maximum Mission’, Workshop on Solar Variability, NASA-GSFC, Greenbelt, Maryland.
Willson, R. C. and Hickey, J.R.: 1977, The Solar Output and Its Variation, University of Colorado Press, Boulder, Colo., p. 111.
Willson, R. C. and Hudson, H. S.: 1980a, Adv. Space. Res. 1, 285.
Willson, R. C. and Hudson, H. S.: 1980b, ‘Variations of Solar Irradiance’, accepted for publication by the Astrophys. J. Letters.
Willson, R. C., Duncan, C. H., and Geist, J.: 1980a, Science 207.
Willson, R. C. et al.: 1980b, Science 211, 700.
Zelewski, E., Geist, J., and Willson, R. C.: 1979, Proc. Soc. Phot. Opt. Instr. 196, 152.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Proceedings of the 14th ESLAB Symposium on Physics of Solar Variations, 16–19 September 1980, Scheveningen, The Netherlands.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willson, R.C. Solar total irradiance observations by Active Cavity Radiometers. Sol Phys 74, 217–229 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151292
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151292