Abstract
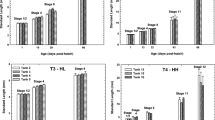
The effects of temperature and salinity on yolk utilization and growth of larval striped bass (Morone soxatilis) from Canadian maritime stocks were studied to determine optimal rearing conditions. Larval length increased during yolk utilization and maximum length (Lmax) was attained at about 70 degree-days post-hatch. Dry weight declined during yolk utilization, whereas, larval wet weight was relatively constant and only declined when yolk was depleted. Temperature and salinity significantly affected the Lmax. Temperatures exceeding 18 ‡C resulted in lower Lmax. Higher Lmax values were attained at 5 % than at 1 or 10 %. Time to reach Lmax was longer at 5 and 10 % than at 1 % for any experimental temperature. Time to reach Lmax was 3 days post-hatch longer than times to maximum embryo dry weight. The Q10 of yolk utilization was 1.71, 1.53 and 2.52 at 1, 5 and 10 %, respectively. Times to terminal yolk utilization were about 1.2 d shorter than times to Lmax. Morphological changes during yolk utilization indicated rapid development of locomotory and predatory capabilities. These and other developmental strategies were compared to those of salmonids. Rearing striped bass larvae at 14 \-16‡C and 5 % throughout yolk utilization should result in longer larvae at initial first feeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, A.B. (1964) Some observations on factors associated with survival of striped bass eggs and larvae. California Fish and Game 50, 100–113.
Doroshev, S.I. (1970) Biological features of the eggs, larvae and young of the striped bass (Roccus saxatilis, Walbaum) in connection with the problem of its acclimatization in the USSR. Journal of Ichthyology 10, 235–248.
Eldridge, M.B., Joseph, J.D., Taberski, K.M. and Seaborn, G.T. (1983) Lipid and fatty acid composition of the endogenous energy sources of striped bass (Morone saxatilis) eggs. Lipids 18, 510–513.
Eldridge, M.B., Whipple, J.A. and Bowers, H.J. (1982) Bioenergetics and growth of striped bass, Morone saxatilis, embryos and larvae. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries Bulletin 80, 461–474.
Hall, L.W., Jr. (1991) A synthesis of water quality and contaminants data on early life stages of striped bass, Morone saxatilis. Reviews in Aquatic Sciences 4, 261–268.
Hansen, T. (1985) Artificial hatching substrate: effect on yolk absorption, mortality and growth during first-feeding of sea trout (Salmo trutta). Aquaculture 46, 275–285.
Hansen, T. and Møller, D. (1985) Yolk absorption, yolk sac constrictions, mortality and growth during first feeding of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) incubated on Astroturf. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42, 1073–1078.
Heming, T.A. (1982) Effects of temperature on utilization of yolk by chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) eggs and alevins. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 39, 184–190.
Hughes, J.T., Shleser, R.A. and Tchobanoglow, G. (1974) A rearing tank for lobster larvae and other aquatic species. Progressive Fish Culturist 36, 129–132.
Lal, K., Lasker, R. and Kuljis, A. (1977) Acclimation and rearing of striped bass larvae in seawater. California Fish and Game 63, 210–218.
Melvin, G.D. (1991) A review of striped bass (Morone saxatilis) population biology in eastern Canada. In: Proceedings of a Workshop on Biology and Culture of Striped Bass (Morone saxatilis) (ed R.H. Peterson). Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 1832, 1–12.
Morgan, R.P., II, Rasindr, V.d. and Copp, R.L. (1981) Temperature and salinity effects on development of striped bass eggs and larvae. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 110, 95–99.
Peterson, R.H. (1991) Consideration for design of culture facilities for early stages of striped bass (Morone saxatilis). Bulletin of the Aquaculture Association of Canada 91–3, 86–88.
Peterson, R.H. and Martin-Robichaud, D.J. (1995) Yolk utilization by Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) alevins, interaction of temperature with substrate. Aquacultural Engineering 14, 85–99.
Rees, R.A. and Harreil, R.M. (1990) Artificial spawning and fry production of striped bass and hybrids. In: Culture and Propagation of Striped Bass and its Hybrids (eds R.M. Harrell, J.H. Kerby and R.V. Minton). American Fisheries Society Publication, Bethesda, Maryland pp. 43–72.
Rogers, B.A. and Westin, D.T. (1981) Laboratory studies on effects of temperature and delayed initial feeding on development of striped bass larvae. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 100, 100–110.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J. (1981) Biology. W.H. Freeman and Co., New York 859 p.
Tsai, C-F. (1991) Prey density requirements of the striped bass, Morone saxatilis (Walbaum), larvae. Estuaries 14, 207–211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peterson, R.H., Martin-Robichaud, D.J. & Berge, O. Influence of temperature and salinity on length and yolk utilization of striped bass larvae. Aquacult Int 4, 89–103 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140591
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140591