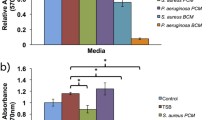
Wound infections retard healing rates and can lengthen the time a patient is required to spend in hospital. Obviously it is desirable to minimize or remove pathogenic organisms to allow wound healing to progress optimally. At present there are a large range of topical applications available in the form of antibiotics or antiseptics, but the toxic effects of these agents may outweight the benefits. In this study two conventional antiseptic agents were examined together with a range of phosphate-based glasses which were designed to release metal ions into an aqueous environment. As a control a series of standard metal ion solutions were prepared and examined in the same test system. The metal ions examined are considered important in the wound healing environment either for their potential bacteriostatic effects or indeed their potential for increasing cellular activity. This part of the study examined the effects of these agents on mammalian cells in vitro, using a standard MTT assay to assess the cytotoxicity or activity of cultured mouse fibroblasts. It was found that chlorhexidene, a commonly used antiseptic agent, was toxic at low levels. The controlled release glasses, in most cases, increased the rate of cell activity before reaching toxic levels. This effect was also found with the standard metal solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
A. BARTON and M. BARTON, “The Management and Prevention of Pressure Sores” (Faber and Faber, London, 1981).
D. J. LEAPER and R. A. SIMPSON, J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2 (1986) 135.
W. LINEWEAVER et al., Arch. Surg. 20 (1985) 267.
S. F. BLOOMFIELD and T. J. SIZER, Pharm J. 235 (1985) 153.
R. A. KOZAL et al., Arch. Surg. 123 (1988) 420.
M. K. DASGUPTA, Adv. Perit. Dial. 10 (1994) 195.
J. BURNIE, T. GILCHRIST, C. F. DRAKE et al., Biomaterials 2 (1984) 244.
H. WAN, R. WILLIAMS, P. DOHERTY and D. F. WILLIAMS, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 5 (1994) 154.
J. PYLE et al., J. Appl. Bacteriol. 72 (1992) 71.
S. S. BRENNAN et al., J. Hosp. Infect. 8 (1986) 263.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheridan, R., Doherty, P.J., Gilchrist, T. et al. The effect of antibacterial agents on the behaviour of cultured mammalian fibroblasts. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 6, 853–856 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00134331
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00134331