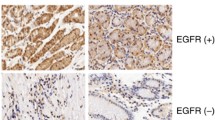
Human colon cancer (Moser) cells produce and secrete epidermal growth factor (EGF) and respond to EGF via an autocrine/paracrine mode through the cell surface EGF receptor (EGFR). In this report we show that EGF promotes the malignant behavior of the Moser cells in vitro in terms of growth in soft agarose and invasion of Matrigel-coated porous membranes. Expressing antisense EGFR RNA in the Moser cells (through transfection with an inducible antisense EGFR expression vector) downmodulated the expression of cell surface EGFR and EGFR mRNA with a concurrent inhibition of growth in soft agarose and invasion of Matrigel-coated membranes. In addition, the ability of exogenously applied EGF in promoting the malignant behavior of these cells was circumvented. We conclude that antisense EGFR RNA was a potent agent in circumventing the f malignant properties of the Moser cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross M and Dexter TM, 1991, Growth factors in development, transformation and tumorigenesis. Cell, 64, 271–80.
Kerbel RS, 1993, Growth factors as mediators of malignant tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 12, 215–17.
Donaldson RW, Nishibe S and Carpenter G, 1989, The tructure and physiology of epidermal growth factor and its receptor. In: Minter EE, Cocchi D and Locatelli V eds, Advances in Growth Hormone and Growth Factor Research, Rome: Pythagora Press; Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 165–180
Huang S, Lin P-F, Fan D, et al. 1991, Growth modulation by epidermal growth factor (EGF) in human colonic carcinoma cells: constitutive expression of the human EGF gene. J Cell Physiol, 148, 220–7.
Huang S, Trujillo J and Chakrabarty S, 1992, Proliferation of human colon cancer cells: role of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor α. Int J Cancer, 52, 978–86.
Stern DF, Hare DL, Cecchini MA and Weinberg RA, 1987, Construction of a novel oncogene based on synthetic sequences encoding epidermal growth factor. Science, 235, 321–4.
Cartlidge SA and Elder JB, 1989, Transforming growth factor α and epidermal growth factor levels in normal human gastrointestinal mucosa. Br J Cancer, 60, 657–60.
Tanaka S, Imanishi K-I and Haruma K, 1992, Immunoreactive transforming growth factor α and epidermal growth factor in colorectal adenomas and carcinomas. Oncology, 49, 381–5.
Borlinghaus P, Wieser S and Lamerz R, 1993, Epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor α, and epidermal growth factor receptor content in normal and carcinomatous gastric and colonic tissue. Clin Invest, 71, 903–7.
Karameris A, Kanavaros P, Aninos D, etal, 1993, Expression of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in gastric and colorectal carcinomas: an immunohistological study of 63 cases. Path Res Pract, 189, 133–7.
Ito M, Yoshida K, Kyo E, et al. 1990, Expression of several growth factors and their receptor genes in human colon carcinomas. Virchows Archiv B Cell Pathol, 59, 173–8.
Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick JS, et al. 1984, Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. Nature, 309, 418–23.
Huang S, Varani J and Chakrabarty S, 1994, Control of AKR fibroblast phenotype by fibronectin: regulation of cell-surface fibronectin binding receptor by fibronectin. J Cell Physiol, 161, 470–82.
Karin M, Haslinger A, Holtgreve, et al. 1984, Activation of a heterologous promoter in response to dexamethasone and cadmium by metallothionein gene 5′-flanking DNA. Cell, 36, 371–9.
Brattain MG, Levine AE, Chakrabarty S, 1984, Heterogeneity of human colon carcinoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 3, 177–91.
Chakrabarty S, Fan D and Varani J, 1990, Modulation of differentiation and proliferation in human colon carcinoma cells by transforming growth factor 1 and β2. Int J Cancer, 46, 493–9.
Dean CJ, Modjtahedi H, Eccles S, Box G and Styles J, 1994, Immunotherapy with antibodies to the EGF receptor. Int J Cancer, S8, 103–7.
Arteaga CL, Hurd SD, Dugger TC, Winnier AR and Robertson JB, 1994, Epidermal growth factor receptors in human breast carcinoma cells: a potential selective target for transforming growth factor α-Pseudomonas exotoxin 40 fusion protein. Cancer Res, 54, 4703–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakrabarty, S., Rajagopal, S. & Huang, S. Expression of antisense epidermal growth factor receptor RNA downmodulates the malignant behavior of human colon cancer cells. Clin Exp Metast 13, 191–195 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00132207
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00132207