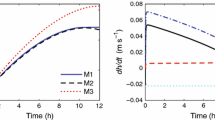
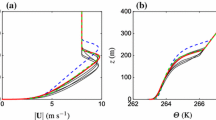
Abstract
A simple formulation of the boundary layer is developed for use in large-scale models and other situations where simplicity is required. The formulation is suited for use in models where some resolution is possible within the boundary layer, but where the resolution is insufficient for resolving the detailed boundary-layer structure and overlying capping inversion. Surface fluxes are represented in terms of similarity theory while turbulent diffusivities above the surface layer are formulated in terms of bulk similarity considerations and matching conditions at the top of the surface layer. The boundary-layer depth is expressed in terms of a bulk Richardson number which is modified to include the influence of thermals. Attention is devoted to the interrelationship between predicted boundary-layer growth, the turbulent diffusivity profile, ‘countergradient’ heat flux and truncation errors.
The model predicts growth of the convectively mixed layer reasonably well and is well-behaved in cases of weak surface heat flux and transitions between stable and unstable cases. The evolution of the modelled boundary layer is studied for different ratios of surface evaporation to potential evaporation. Typical variations of surface evaporation result in a much greater variation in boundary-layer depth than that caused by the choice of the boundary-layer depth formulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
André, J. C., De Moor, G., Lacerrère, P., Therry, G., and Vachat, R.: 1978, ‘Modelling the 24 Hour Evolution of the Mean and Turbulent Structures of the Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 35, 1861–1883.
André, J. C. and Mahrt, L.: 1982, ‘The Nocturnal Surface Inversion and Influence of Clear-Air Radiative Cooling’, J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 864–878.
Anthes, R. A., Kuo, Y.-H., Benjamin, S. G., and Li, Y.-F.: 1982, ‘The Evolution of the Mesoscale Environment of Severe Local Storms: Preliminary Modeling Results’, J. Cli. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 1187–1213.
Binkowski, F. S.: 1983, ‘A Simple Model for the Diurnal Variation of the Mixing Depth and Transport Flow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 27, 217–236.
Brost, R. A. and Wyngaard, J. C.: 1978, ‘A Model Study of the Stably Stratified Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 8, 1427–1440.
Busch, N. E., Chang, S. W., and Anthes, R. A.: 1976, ‘A Multi-Level Model of the Planetary Boundary Layer Suitable for Use with Mesoscale Dynamical Models’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 15, 909–919.
Businger, J. A., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Bradley, E. F.: 1971, ‘Flux-Profile Relationships in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 181–189.
Chang, S. W.: 1979, ‘An Efficient Parameterization of Convective and Nonconvective Planetary Boundary Layers for Use in Numerical Models’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 18, 1205–1215.
Chang, S. W.: 1981, ‘Test of a Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterization Based on a Generalized Similarity Theory in Tropical Cyclone Models’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 109, 843–853.
Clarke, R. H.: 1970, ‘Recommended Methods for the Treatment of the Boundary Layer in Numerical Models of the Atmosphere’, Austr. Meteorol. Mag. 18, 51–73.
Clarke, R. H., Dyer, A. J., Brook, R. R., Reid, D. C., and Troup, A. J.: 1971, ‘The Wangara Experiment: Boundary Layer Data’, Tech. Paper No. 19, Div. Met. Phys., CSIRO, Australia.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1966, ‘The Counter Gradient Heat Flux in the Lower Atmosphere and in the Laboratory’, J. Atmos. Sci. 23, 503–506.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1972, ‘Parameterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer for Use in General Circulation Models’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 100, 93–106.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1973, ‘The Use of Subgrid Transport Equations in a Three-Dimensional Model of Atmospheric Turbulence’, J. Fluids Engr. 95, 429–438.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1974, ‘Three-Dimensional Study of the Height and Mean Structure of the Planetary Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 15, 1241–1251.
Højstrup, J.: 1982, ‘Velocity Spectra in the Unstable Planetary Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 2239–2248.
Holton, J. R., Wallace, J. M., and Joung, J. A.: 1971, ‘On Boundary Layer Dynamics and the ITCZ’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 275–280.
Holtslag, A. A. M. and Van Ulden, A. P.: 1983, ‘A Simple Scheme for Daytime Estimates of Surface Fluxes from Routine Weather Data’, J. Cli. Appl. Meteorol. 22, 517–529.
Holzworth, G. C.: 1964, ‘Estimates of Mean Maximum Mixing Depths in the Contiguous United States’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 92, 235–242.
Louis, J.-F.: 1979, ‘A Parametric Model of Vertical Eddy Fluxes in the Atmosphere’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 187–202.
Mahrt, L.: 1981, ‘Modelling the Depth of the Stable Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 21, 3–19.
Mahrt, L. and Ek, M.: 1984, ‘The Influence of Atmospheric Stability on Potential Evaporation’, J. Cli. Appl. Meteorol. 23, 222–234.
Mahrt, L., Heald, R. C., Lenschow, D. H., Stankov, B. B., and Troen I.: 1979, ‘An Observational Study of the Structure of the Nocturnal Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 247–264.
Mailhôt, J., and Benoit, R.: 1982, ‘A Finite-Element Model of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Suitable for Use with Numerical Weather Prediction Models’, J. Atmos. Sci. 39, 2249–2266.
Manins, P. C.: 1982, ‘The Daytime Planetary Boundary Layer: A New Interpretation of Wangara Data’, Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 108, 689–705.
McCumber, M. C. and Pielke, R. A.: 1981, ‘Simulation of the Effects of Surface Fluxes of Heat and Moisture in a Mesoscale Numerical Model Soil Layer’, J. Geophy. Res. 86, 9929–9938.
Monteith, J. L.: 1981, ‘Presidential Address: Evaporation and Surface Temperature’, Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 107, 1–24.
Pan, H.-L. and Mahrt, L.: 1986, ‘Interaction Between Soil Hydrology and Boundary-Layer Development’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol., submitted.
Pielke, R. A. and Mahrer, Y.: 1975, ‘Technique to Represent the Heated Boundary Layer in Mesoscale Models with Coarse Vertical Resolution’, J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 2288–2309.
Priestley, C. H. B. and Swinbank, W. C.: 1947, ‘Vertical Transport of Heat by Turbulence in the Atmosphere’, Proc. R. Soc. A189, 543–561.
Smeda, M. S.: 1979, ‘A Bulk Model for the Atmospheric Planetary Boundary Layer’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 14, 411–428.
Tennekes, H.: 1973, ‘A Model for the Dynamics of the Inversion above a Convective Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 30, 558–567.
Therry, G. and Lacarrère, P.: 1983, ‘Improving the eddy kinetic energy model for planetary boundary layer description’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 63–88.
Wyngaard, J. C. and Brost, R. A.: 1984, ‘Top-Down and Bottom-Up Diffusion in the Convective Boundary Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 41, 102–112.
Yamada, T. and Mellor, G.: 1975, ‘A Simulation of the Wangara Atmospheric Boundary Layer Data’, J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 2309–2329.
Yu, T.-W.: 1977, ‘A Comparative Study on Parameterization of Vertical Turbulent Exchange Processes’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 105, 57–66.
Zhang, D. and Anthes, R. A.: 1982, ‘A High-Resolution Model of the Planetary Boundary Layer — Sensitivity Tests and Comparisons with SESAME-70 Data’, J. Appl. Meteorol., 1594–1609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Troen, I.B., Mahrt, L. A simple model of the atmospheric boundary layer; sensitivity to surface evaporation. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 37, 129–148 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122760
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00122760