Abstract
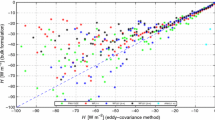
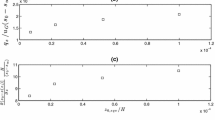
Although the bulk aerodynamic transfer coefficients for sensible (C H ) and latent (C E ) heat over snow and sea ice surfaces are necessary for accurately modeling the surface energy budget, they have been measured rarely. This paper, therefore, presents a theoretical model that predicts neutral-stability values of C H and C E as functions of the wind speed and a surface roughness parameter. The crux of the model is establishing the interfacial sublayer profiles of the scalars, temperature and water vapor, over aerodynamically smooth and rough surfaces on the basis of a surface-renewal model in which turbulent eddies continually scour the surface, transferring scalar contaminants across the interface by molecular diffusion. Matching these interfacial sublayer profiles with the semi-logarithmic inertial sublayer profiles yields the roughness lengths for temperature and water vapor. When coupled with a model for the drag coefficient over snow and sea ice based on actual measurements, these roughness lengths lead to the transfer coefficients. C E is always a few percent larger than CH. Both decrease monotonically with increasing wind speed for speeds above 1 m s−1, and both increase at all wind speeds as the surface gets rougher. Both, nevertheless, are almost always between 1.0 × 10−3 and 1.5 × 10−3.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Abramowitz, M. and Stegun, I. A. (eds.): 1965, Handbook of Mathematical Functions, Dover, New York, 1046 pp.
Andreas, E. L.: 1986, ‘A New Method of Measuring the Snow-Surface Temperature’, Cold Regions Sci. Technol. 12, 139–156.
Andreas, E. L. and Murphy, B.: 1986, ‘Bulk Transfer Coefficients for Heat and Momentum over Leads and Polynyas’, J. Phys. Oceanogr., in press.
Arya, S. P. S.: 1973, ‘Contribution of Form Drag on Pressure Ridges to the Air Stress on Arctic Ice’, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 7092–7099.
Arya, S. P. S.: 1975, ‘A Drag Partition Theory for Determining the Large-Scale Roughness Parameter and Wind Stress on Arctic Pack Ice’, J. Geophys. Res. 80, 3447–3454.
Banke, E. G., Smith, S. D., and Anderson, R. J.: 1980, ‘Drag Coefficients at AIDJEX from Sonic Anemometer Measurements’, R. S. Pritchard (ed.), in Sea Ice Processes and Models, University of Washington Press, Seattle, 430–442.
Bradley, E. F.: 1972, ‘The Influence of Thermal Stability on a Drag Coefficient Measured Close to the Ground’, Agric. Meteorol. 9, 183–190.
Brutsaert, W.: 1975a, ‘A Theory for Local Evaporation (or Heat Transfer) from Rough and Smooth Surfaces at Ground Level’, Water Resour. Res. 11, 543–550.
Brutsaert, W.: 1975b, ‘The Roughness Length for Water Vapor, Sensible Heat, and Other Scalars’, J. Atmos. Sci. 32, 2028–2031.
Businger, J. A.: 1973, ‘Turbulent Transfer in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, D. A. Haugen (ed.), in Workshop on Micrometeorology, American Meteorological Society, Boston, 67–100.
Businger, J. A., Wyngaard, J. C., Izumi, Y., and Bradley, E. F.: 1971, ‘Flux-Profile Relationships in the Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Atmos. Sci. 28, 181–189.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1966, ‘Transport of Gases to and from Grass and Grass-Like Surfaces’, Proc. Roy. Soc. London A290, 236–265.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1968, ‘Transport of Gases to and from Surfaces with Bluff and Wave-Like Roughness’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 94, 318–332.
Chamberlain, A. C.: 1983, ‘Roughness Length of Sea, Sand, and Snow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 25, 405–409.
Charnock, H.: 1955, ‘Wind Stress on Water: An Hypothesis’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 81, 639.
Colbeck, S. C.: 1976, ‘An Analysis of Water Flow in Dry Snow’, Water Resour. Res. 12, 523–527.
Colbeck, S. C. and Anderson, E. A.: 1982, ‘The Permeability of a Melting Snow Cover’, Water Resour. Res. 18, 904–908.
Danckwerts, P. V.: 1951, ‘Significance of Liquid-Film Coefficients in Gas Absorption’, Industr. Engng. Chem. 43, 1460–1467.
Danckwerts, P. V.: 1970, Gas-Liquid Reactions, McGraw-Hill, New York, 276 pp.
Deardorff, J. W.: 1968, ‘Dependence of Air-Sea Transfer Coefficients on Bulk Stability’, J. Geophys. Res. 73, 2549–2557.
Dennery, P. and Krzywicki, A.: 1967, Mathematics for Physicists, Harper and Row, New York, 384 pp.
Dipprey, D. F. and Sabersky, R. H.: 1963, ‘Heat and Momentum Transfer in Smooth and Rough Tubes at Various Prandtl Numbers’, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 6, 329–353.
Duff, G. F. D. and Naylor, D.: 1966, Differential Equations of Applied Mathematics, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 423 pp.
Dyer, A. J.: 1974, ‘A Review of Flux-Profile Relationships’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 7, 363–372.
Garratt, J. R. and Hicks, B. B.: 1973, ‘Momentum, Heat and Water Vapour Transfer to and from Natural and Artificial Surfaces’, Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 99, 680–687.
Goldstein, S., ed.: 1965, Modern Developments in Fluid Dynamics, Dover, New York, 702 pp.
Grass, A. J.: 1971, ‘Structural Features of Turbulent Flow over Smooth and Rough Boundaries’, J. Fluid Mech. 50, 233–255.
Hibler, W. D., III: 1980, ‘Modeling a Variable Thickness Sea Ice Cover’, Mon. Wea. Rev. 108, 1943–1973.
Hicks, B. B. and Martin, H. C.: 1972, ‘Atmospheric Turbulent Fluxes over Snow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 2, 496–502.
Hill, R. J.: 1978, ‘Spectra of Fluctuations in Refractivity, Temperature, Humidity, and the Temperature-Humidity Cospectrum in the Inertial and Dissipation Ranges’, Radio Sci. 13, 953–961.
Kestin, J. and Persen, L. N.: 1962, ‘The Transfer of Heat across a Turbulent Boundary Layer at Very High Prandtl Numbers’, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 5, 355–371.
Khundzhua, G. G. and Andreyev, Ye. G.: 1974, ‘An Experimental Study of Heat Exchange between the Ocean and the Atmosphere in Small-Scale Interaction’, Izv., Atmos. Oceanic Phys. 10, 685–687.
Kim, H. T., Kline, S. J., and Reynolds, W. C.: 1971, ‘The Production of Turbulence near a Smooth Wall in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’, J. Fluid Mech. 50, 133–160.
Kind, R. J.: 1976, ‘A Critical Examination of the Requirements for Model Simulation of Wind-Induced Erosion/Deposition Phenomena such as Drifting Snow’, Atmos. Environ. 10, 219–227.
Kondo, J.: 1975, ‘Air-Sea Bulk Transfer Coefficients in Diabatic Conditions’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 9, 91–112.
Kondo, J. and Yamazawa, H.: 1986, ‘Bulk Transfer Coefficient over a Snow Surface’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 34, 125–135.
Large, W. G. and Pond, S.: 1982, ‘Sensible and Latent Heat Flux Measurements over the Ocean’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 12, 464–482.
Leavitt, E., Bell, D., Clarke, M., Anderson, R., and Paulson, C: 1977, ‘Computation of Air Stress and Sensible Heat Fluxes from Surface Layer Profile Data, AIDJEX, 1975’, AIDJEX Bull. 36, 157–174.
Lettau, H. H.: 1979, ‘Wind and Temperature Profile Prediction for Diabatic Surface Layers including Strong Inversion Cases’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 17, 443–464.
Liu, W. T. and Businger, J. A.: 1975, ‘Temperature Profile in the Molecular Sublayer near the Interface of a Fluid in Turbulent Motion’, Geophys. Res. Letters 2, 403–404.
Liu, W. T., Katsaros, K. B., and Businger, J. A.: 1979, ‘Bulk Parameterization of Air-Sea Exchanges of Heat and Water Vapor including the Molecular Constraints at the Interface’, J. Atmos. Sci. 36, 1722–1735.
Mangarella, P. A., Chambers, A. J., Street, R. L., and Hsu, E. Y.: 1973, ‘Laboratory Studies of Evaporation and Energy Transfer Through a Wavy Air-Water Interface’, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 3, 93–101.
Maykut, G. A.: 1978, ‘Energy Exchange over Young Sea Ice in the Central Arctic’, J. Geophys. Res. 83, 3646–3658.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M.: 1971, Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence, Vol. 1, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass., 769 pp.
Owen, P. R. and Thomson, W. R.: 1963, ‘Heat Transfer across Rough Surfaces’, J. Fluid Mech. 15, 321–334.
Parkinson, C. L. and Washington, W. M.: 1979, ‘A Large-Scale Numerical Model of Sea Ice’, J. Geophys. Res. 84, 311–337.
Paulson, C. A.: 1970, ‘The Mathematical Representation of Wind Speed and Temperature Profiles in the Unstable Atmospheric Surface Layer’, J. Appl. Meteorol. 9, 857–861.
Pruppacher, H. R. and Klett, J. D.: 1978, Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation, D. Reidel, Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, 714 pp.
Schlichting, H.: 1968, Boundary-Layer Theory, 6th ed., J. Kestin (trans.), McGraw-Hill, New York, 748 pp.
Schmidt, R. A.: 1982, ‘Vertical Profiles of Wind Speed, Snow Concentration, and Humidity in Blowing Snow’, Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 23, 223–246.
Shirasawa, K.: 1981, ‘Studies on Wind Stress on Sea Ice’, Low Temp. Sci. A40, 101–118.
Tennekes, H. and Lumley, J. L.: 1972, A First Course in Turbulence, MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass., 300 pp.
Thorpe, M. R., Banke, E. G., and Smith, S. D.: 1973, ‘Eddy Correlation Measurements of Evaporation and Sensible Heat Flux over Arctic Sea Ice’, J. Geophys. Res. 78, 3573–3584.
Untersteiner, N. and Badgley, F. I.: 1965, ‘The Roughness Parameter of Sea Ice’, J. Geophys. Res. 70, 4573–4577.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreas, E.L. A theory for the scalar roughness and the scalar transfer coefficients over snow and sea ice. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 38, 159–184 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121562
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121562