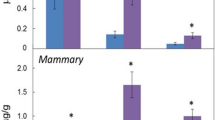
Diets rich in linoleic acid (LA) stimulate the metastasis of MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells from the mammary fat pads of nude mice. This omega-6 fatty acid is metabolized to various cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase products, several of which have been previously associated with tumor cell invasion and metastasis. We now report that MDA-MB-435 cells secreted increased levels of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) and 15-HETE when cultured in the presence of 2.7 µm (0.75 µg/ml) LA; 5-HETE secretion was unchanged. The 12-lipoxygenase inhibitor esculetin (20 µM) completely blocked the LA-stimulated 12-HETE secretion. Linoleic acid also increased MDA-MB-435 cell invasion in an in vitro assay; this stimulation was abolished by 20 µM esculetin, but was unaffected by piroxicam, a selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor. The effect of LA on invasion was replicated by 0.1 µM 12-HETE, but not by 5-HETE or PGE2; 15-HETE was stimulatory only at a concentration of 1.0 µm. Zymographic and Northern blot analyses showed that these events are accompanied by the induction of 92 kDa isoform type IV collagenase (metalloproteinase-9) enzymic activity and mRNA expression by exogenous LA and 12-HETE, and their suppression by the 12-lipoxygenase inhibitor. These results suggest that the effects of dietary LA on breast cancer cell metastasis in the nude mouse model are due, at least in part, to enhanced 12-HETE biosynthesis, with an associated increase in proteolytic enzyme activity and tumor cell invasiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nomura, AMY, Le Marchand, L, Kolonel, LN and Hankin, JH, 1991, The effect of dietary fat on breast cancer survival among Caucasian and Japanese women in Hawaii. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 18, 5135–5141.
Rohan, TE, Hiller, JE and McMichael, AJ, 1993, Dietary factors and survival from breast cancer. Nutr Cancer, 20, 167–77.
Rose, DP, Hatala, MA, Connolly, JM and Rayburn, J, 1993, Effect of diets containing different levels of linoleic acid on human breast cancer growth and lung metastasis in nude mice. Cancer Res, 53, 4686–90.
Chen, YQ, Liu, B, Tang, DG and Honn, KV, 1992, Fatty acid modulation of tumor cell-platelet-vessel wall interaction. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 11, 389–409.
Connolly, JM and Rose, DP, 1993, Effects of fatty acids on invasion through reconstituted basement membrane (“Matrigel”) by a human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Lett, 75, 137–42.
Liu, X-H and Rose, DP, 1994, Stimulation of type IV collagenase expression by linoleic acid in a metastatic human breast cancer cell line. Cancer Lett, 76, 71–7.
Neichi, T, Koshihara, Y and Muroto, S-I, 1983, Inhibitory effects of esculetin on 5-lipoxygenase and leukotriene biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta, 753, 130–2.
Carty, TJ, Stevens, JS, Lombardino, JG, Parry, MJ and Randall, MJ, 1980, Piroxicam, a structurally novel anti-inflammatory compound. Mode of prostaglandin synthesis inhibition. Prostaglandins, 19, 671–82.
Rose, DP and Connolly, JM, 1990, Effects of fatty acids and inhibitors of eicosanoid synthesis on the growth of a human breast cancer cell line in culture. Cancer Res, 50,7139–44.
Rose, DP, Connolly, JM and Liu, X-H, 1994, Dietary fatty acids and human breast cancer cell growth, invasion, and metastasis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 364,83–91.
Yamagata, S, Ito, Y, Tanaka, R and Shimizu, S, 1988, Gelatinases of metastatic cell lines of murine colonic carcinoma as detected by substrate gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 151, 158–62.
Ballin, M, Gomez, DE, Sinha, CC and Thorgeirsson, UP, 1988, ras oncogene mediated induction of a 93 kDa metalloproteinase: strong correlation with the malignant phenotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 154, 832–8.
Timár, J, Silletti, S, Bazaz, R, Raz, A and Honn, KV, 1993, Regulation of melanoma cell motility by the lipoxygenase metabolite 12(S)-HETE. Int J Cancer, 55, 1003–10.
Honn, KV, Timár, J, Rozhin, J, et al. 1994, A lipoxygenase metabolite, 12(S)-HETE, stimulates protein kinase C-mediated release of cathepsin B from malignant cells. Exp Cell Res, 214, 120–30.
Sloan, BF, Dunn, JR and Honn, KV, 1981, Lysosomal cathepsin B: correlation with metastatic potential. Science, 212, 1151–3.
Scaddan, PB and Dufresne, MJ, 1995, Characterization of cysteine proteases and their endogenous inhibitors in MCF-7 and adriamycin-resistant MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Invasion Metastasis, 13, 301–13.
Liu, B, Maher, RJ, Hannun, YA, Porter, AT and Honn, KV, 1994, 12(S)-HETE enhancement of prostate tumor cell invasion: seléctive role of PKCα. J Natl Cancer Inst, 86,1145–51.
Meschter, CL, Connolly, JM and Rose, DP, 1992, Influence of regional location of the inoculation site, and dietary fat on the pathology of MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cell-derived tumors grown in nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis, 10, 167–73.
Rose, DP, Connolly, JM and Liu, X-H, 1994, Effects of linoleic acid on the growth and metastasis of two human breast cancer cell lines in nude mice, and the invasive capacity of these cell lines in vitro. Cancer Res, 54, 6557–62.
Rose, DP and Connolly, JM, 1993, Effects of omega-3 fatty acids on human breast cancer growth and metastases in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst, 85,1743–7.
Rose, DP, Connolly, JM, Rayburn, J and Coleman, M, 1995, Influence of eicosapentaenoic or docosahexaenoic acid-containing diets on the growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells in nude mice. J Natl Cancer Inst, 87, 587–92.
Liu, X-H and Rose, DP, 1995, Suppression of type IV collagenase in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells by eicosapentaenoic acid in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett, 92, 21–6.
Fulton, AM, Zhang, S-Z and Chong, YC, 1991, Role of the prostaglandin E2 receptor in mammary tumor metastasis. Cancer Res, 51, 2047–50.
Fulton, AMand Heppner, GH, 1985, Relationships of prostaglandin E and natural killer sensitivity to metastatic potential in murine mammary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res, 45, 4779–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XH., Connolly, J.M. & Rose, D.P. Eicosanoids as mediators of linoleic acid-stimulated invasion and type IV collagenase production by a metastatic human breast cancer cell line. Clin Exp Metast 14, 145–152 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121211
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121211