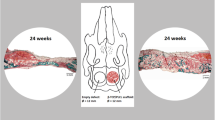
This study was undertaken to assess the osteoinductive effect addition of demineralized bone matrix (DBM) gel has, on the behaviour of osteoconductive bone-bonding PEO/PBT copolymer (PolyactiveR) implants. Cranial defects in rats were filled with these composites to study bone formation in comparison with several controls after 2 and 8 weeks survival time. Osteogenesis was qualitatively evaluated by using light- and transmission electron microscopy as well as backscatter electron imaging. Quantification of the amount of bone ingrowth was performed by using a computerized image analysis system. Initially, rapid calcification was observed in the polymer and DBM, followed by formation of new trabecular bone around the demineralized bone fragments. Bone ingrowth in implants consisting of plain copolymer was less than expected based on previous research, but the addition of demineralized bone matrix gel resulted in a significantly greater amount of new bone formation in the defects. We concluded that the application of DBM-gel to PolyactiveR implants had a beneficial effect on the amount of new bone formation in this material. This procedure combines the osteoinductive potential of DBM with the mechanical and bone-bonding properties of a copolymer, thus opening the way to the development of a line of osteoactive composite implants with good surgical handling properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. F. MUSCHLER and J. M. LANE, in “Bone graft substitutes” (W.B. Saunders, New York, 1992) p. 375.
E. M. YOUNGER and M. W. CHAPMAN, J. Orthop. Trauma 3 (1989) 192.
A. KENLEY, K. YIM, J. ABRAMS, E. RON, T. TUREK, L. J. MARDEN and J. O. HOLLINGER, Pharmaceutical Res. 10 (1993) 1393.
C. J. DAMIEN and J. R. PARSONS, J. Appl. Biomater. 2 (1991) 187.
C. A. EAST and W. F. LARRABEE, J. Long-term effects Med. Implants 1 (1991) 53.
M. JARCHO, Clin. Orthop. 157 (1981) 259.
T. KOKUBO, in “Bone-bonding biomaterials”, edited by P. DUCHENNE, T. KOKUBO and C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK (Reed Healthcare communications, Leiderdorp, 1992) p. 31.
J. M. TOTH, K. L. LYNCH and D. A. HACKBARTH, in “Bioceramics”, Vol. 6, edited by P. DUCHENNE and D. CHRISTIANSEN (Butterworth-Heineman Ltd., Philadelphia, 1993) p. 9.
K. de GROOT, C. de PUTTER, P. A. E. SILLEVIS SMIT, A. A. DRIESSEN, Sci. Ceram. (1981) 33.
M. R. URIST, Science 150 (1965) 893.
M. R. URIST and B. S. STRATES, J. Dent. Res. 50 (1971) 1392.
M. R. URIST, K. SATO, A. G. BROWNELL et al., Proc. Soc. Exp. Bid. Med. 173 (1983) 194.
M. WOZNEY, Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1 (1981) 267.
K. ELIMA, Ann. Med. 25 (1993) 395.
D. BAKKER, C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, S. C. HESSELING, H. K. KOERTEN, W. KUYPERS and J. J. GROTE, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24 (1990) 489.
C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, D. BAKKER, H. LEENDERS, J. van den BRINK, S. C. HESSELING, Y. P. BOVELL, A. M. RADDER, R. J. B. SAKKERS, M. L. GAILLARD, P. H. HEINZE and G. J. BEUMER, in “Bone-bonding biomaterials”, edited by P. DUCHENNE, T. KOKUBO and C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK (Reed Healthcare Communications, Leiderdorp, 1992) p. 13.
C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, J. van den BRINK, H. LEENDERS and D. BAKKER, Cells Mater. 3 (1993) 23.
A. M. RADDER, H. LEENDERS and C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 28 (1994) 141.
N. SENN, Amer. J. Med. Sci. 98 (1889) 219.
J. B. MULLIKEN, J. GLOWACKI, L. B. KABAN, J. FOLKMAN and J. E. MURRAY, Ann. Surg. 194 (1981) 366.
A. B. PREWETT, J. R. PARSONS, C. J. DAMIEN and L. W. MEEKS, in “Bone-bonding biomaterials”, edited by P. DUCHENNE, T. KOKUBO and C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK (Reed Healthcare Communications, Leiderdorp, 1992) p. 139.
J. W. HAGEN, J. M. SEMMELINK, C. P. A. T. KLEIN, B. PRAHL-ANDERSEN and E. H. BURGER, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26 (1992) 897.
K. YAMASHITA and T. TAKAGI, Arch. Histol. Cytol. 55 (1992) 31.
A. M. RADDER and C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. (in press).
C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, D. BAKKER, S. C. HESSELING and H. K. KOERTEN, Biomaterials 12 (1991) 87.
S. K. BULSTRA, M. M. W. F. DREES, R. KUYPER, C. A. van BLITTERSWIJK, G. HEIDENDAL and A. J. van der LINDEN (submitted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
ENT-department, University Hospital Leiden
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Haastert, R.M., Grote, J.J., Van Blitterswijk, C.A. et al. Osteoinduction within PEO/PBT copolymer implants in cranial defects using demineralized bone matrix. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 5, 764–769 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120373