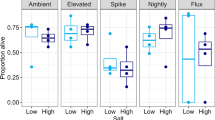
A large number of studies conclusively demonstrate that low pH conditions have important ecological effects on amphibian communities. These effects vary developmentally and depend on complex interactions with other physical, chemical, and biological parameters. Acid sensitivity varies widely within and among species of amphibians. In spite of the importance of acidity to their reproductive success and the presence of many acidic amphibian habitats, there is, at present, little direct evidence that acid precipitation has produced widespread declines in amphibian populations. However, the potential role of sublethal effects of acidity on amphibian declines has not been studied thoroughly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers, P.H. and Prouty, R.M. (1987) Survival of Spotted Salamander eggs in temporary woodland ponds of coastal Maryland. Environ. Pollut. 46, 45–61.
Andren, C., Henrikson, L., Olsson, M. and Nilson, G. (1988) Effects of pH and aluminum on embryonic and early larval stages of Swedish Brown Frogs Rana arvalis, R. temporaria, and R. dalmatina. Holart. Ecol. 11, 127–35.
Andren, C., Marden, M. and Nilson, G. (1989) Tolerance to low pH in a population of Moor Frogs, Rana arvalis, from an acid and a neutral environment: a possible case of rapid evolutionary response to acidification. Oikos 56, 215–23.
Aston, R.J., Beattie, R.C. and Milner, A.G.P. (1987) Characteristics of spawning sites of the Common Frog (Rana temporaria) with particular reference of acidity. J. Zool., Lond. 213. 233–42.
Barinaga, M. (1990) Where have all the froggies gone? Science 247, 1033–4.
Beattie, R.C., Aston, R.J. and Milner, A.G.P. (1991) A field study of fertilization and embryonic development in the Common Frog (Rana temporaria) with particular reference to acidity and temperature. J. Appl. Ecol. 28, 346–57.
Beattie, R.C., Aston, R.J. and Milner, A.G.P. (1992) Embryonic and larval survival of the Common Frog (Rana temporaria L.) in acidic and limed ponds. Herpetol. J. 26, 356–60.
Beebee, T.J. (1986) Acid tolerance of Natterjack Toad (Bufo calamita) development, Herpetol. J. 1, 78–81.
Beebee, T.J.C., Flower, R.J., Stevenson, A.C., Patrick, S.T., Appleby, P.G., Fletcher, C., Marsh, C., Natkanski, J., Rippey, B. and Battarbee, R.W. (1990) Decline of Natterjack Toad in Britain: palaeoecological, documentary and experimental evidence for breeding site acidification. Biol. Conserv. 53, 1–20.
Beebee, T.J.C. and Griffin, J.R. (1977) A preliminary investigation into Natterjack Toad (Bufo calamita) breeding site characteristics in Great Britain. J. Zool. Lond. 181, 341–50.
Berven, K.A. (1982) The genetic basis of altitudinal variation in the Wood Frog, Rana sylvatica. I. An experimental analysis of life history traits. Evolution 36, 962–83.
Berven, K.A. and Gill, D.E. (1983) Interpreting geographic variation in life history traits. Am. Zool. 23, 85–97.
Blem, C.R. and Blem, L.B. (1989) Tolerance of acidity in a Virginia population of the Spotted Salamander, Ambystoma maculatum (Amphibia: Ambystomatidae). Brimleyana 15, 37–45.
Blem, C.R. and Blem, L.B. (1991) Cation concentration and acidity in breeding ponds of the Spotted Salamander, Ambystoma maculatum (Shaw) (Amphibia: Ambystomatidae), in Virginia. Brimleyana 17, 67–76.
Bradford, D.F. (1991) Mass mortality and extinction in a high-elevation population of Rana muscosa. J. Herpetol. 25, 174–7.
Bradford, D.F., Swanson, C. and Gordon, M.S. (1992) Effects of low pH and aluminum on two declining species of amphibians in the Sierra Nevada, California. J. Herpetol., in press.
Brodie, E.D.Jr. and Formanowicz, D.R.Jr. (1983) Prey size preference of predators: differential vulnerability of larval amphibians. Herpetologica 39, 67–75.
Burton, T.M. and Likens, G.E. (1975) Salamander populations and biomass in the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest, New Hampshire. Copeia 541–6.
Clark, K.L. (1986a) Distributions of anuran populations in central Ontario relative to habitat acidity. Water Air Soil Pollut. 30, 727–34.
Clark, K.L. (1986b) Responses of Spotted Salamander, Ambystoma maculatum, populations in central Ontario to habitat acidity. Can. Field Nat. 100, 463–9.
Clark, K.L. and Hall, R.J. (1985) Effects of elevated hydrogen ion and aluminum concentration on the survival of amphibian embryos and larvae. Can. J. Zool. 63, 116–23.
Clark, K.L. and LaZerte, B.D. (1987) Intraspecific variation in hydrogen ion and aluminium toxicity in Bufo americanus and Ambystoma maculatum. Can. J. Fisheries Aquatic Sci. 44, 1622–8.
Cook, R.P. (1983) Effects of acid precipitation on embryonic mortality of Ambystoma salamanders in the Connecticut Valley of Massachusetts. Biol. Conserv. 27, 77–88.
Cooke, A.S. and Frazer, J.F.D. (1976) Characteristics of newt breeding sites. J. Zool. Lond. 178, 223–36.
Conant, R. (1975) A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern North America, 2nd Edition. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Corn, P.S. and Vertucci, F.A. (1992) Descriptive risk assessment of the effects of acidic deposition on Rocky Mountain amphibians. J. Herpetol., 23, 361–9.
Corn, P.S., Stolzenburg, W. and Bury, R.B. (1989) Acid precipitation studies in Colorado and Wyoming: interim report of surveys of montane amphibians and water chemistry. US Fish Wildlife Service Biol. Rep. 80(40.26).
Cummins, C.P. (1986) Effects of aluminium and low pH on growth and development in Rana temporaria tadpoles. Oecologia 69, 248–52.
Cummins, C.P. (1988) Effect of calcium on survival of Rana temporaria embryos at low pH. Funct. Ecol. 2, 297–302.
Cummins, C.P. (1989) Interaction between the effects of pH and density on growth and development in Rana temporaria L. tadpoles. Funct. Ecol. 3, 45–52.
Dale, J.M., Freedman, B. and Kerekes, J. (1985a) Acidity and associated water chemistry of amphibian habitats in Nova Scotia. Can. J. Zool. 63, 97–105.
Dale, J.M., Freedman, B. and Kerekes, J. (1985b) Experimental studies of the effects of acidity and associated water chemistry on amphibians. Proc. Nova Scotia Inst. Sci. 35, 35–54.
Dickman, M. (1968) The effect of grazing by tadpoles on the structure of a periphyton community. Ecology 49, 1188–90.
Dunson, W.A. and Connell, J. (1982) Specific inhibition of hatching in amphibian embryos by low pH. J. Herpetol. 16, 314–15.
Freda, J. (1986) The influence of acidic pond water on amphibians: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 30, 439–50.
Freda, J. (1991) The effect of aluminum and other metals on amphibians. Environ. Pollut. 71, 305–28.
Freda, J., Cavdek, V. and McDonald, D.G. (1989) Role of organic complexation in the toxicity of aluminum to Rana pipiens embryos and Bufo americanus tadpoles. Can. J. Fisheries Aquatic Sci. 47, 217–24.
Freda, J. and Dunson, W.A. (1984) Sodium balance of amphibian larvae exposed to low environmental pH. Physiol. Zool. 57, 435–43.
Freda, J. and Dunson, W.A. (1985a) The effect of acidic precipitation on amphibians breeding in temporary ponds of Pennsylvania. US Fish Wildlife Service Biol. Rep. 80(40.22).
Freda, J. and Dunson, W.A. (1985b) Field and laboratory studies of ion balance and growth rates of ranid tadpoles chronically exposed to low pH. Copeia 415–23.
Freda, J. and Dunson, W.A. (1985c) The influence of external cation concentration on the hatching of amphibian embryos in water of low pH. Can. J. Zool. 63. 2649–56.
Freda, J. and Dunson, W.A. (1986) Effects of low pH and other chemical variables on the local distribution of amphibians. Copeia 454–66.
Freda, J. and McDonald, D.G. (1989) Effects of aluminum on the Leopard Frog Rana pipiens: life stage comparisons and aluminum uptake. Can. J. Fisheries Aquatic Sci. 47, 210–16.
Freda, J., Sadinski, W.J. and Dunson, W.A. (1991) Long term monitoring of amphibian populations with respect to the effects of acidic deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut. 55, 445–62.
Frisbie, M.P. and Wyman, R.L. (1991) The effects of soil pH on sodium balance in the Redbacked Salamander, Plethodon cinereus and 3 other terrestrial salamanders. Physiol. Zool. 64, 1050–68.
Gascon, C. and Planas, D. (1986) Spring pond water chemistry and the reproduction of the Wood Frog, Rana sylvatica. Can. J. Zool. 64, 543–50.
Gascon, C., Planas, D. and Moreau, G. (1987) The interaction of pH, calcium and aluminium concentrations on the survival and development of Wood Frog (Rana sylvatica) eggs and tadpoles. Ann. R. Zool. Soc. Belg. 117, 189–99.
Gorman, E., Eisenreich, S.J., Ford, J. and Santelmann, M.V. (1985) Chemistry of bog waters. In Stumm, W. (ed) Chemical Processes in Lakes. New York: Wiley.
Gosner, K.L. and Black, I.H. (1957) The effects of acidity on the development and hatching of New Jersey frogs. Ecology 38, 256–62.
Hagström, T. (1981) Reproductive strategy and success of amphibians in water acidified by atmospheric pollution. Proc. Eur. Herpetol. Symp. C.W.L.P. Oxford, 1980, pp. 55–57.
Harte, J. and Hoffman, E. (1989) Possible effects of acidic deposition on a Rocky Mountain population of the Tiger Salamander Ambystoma tigrinum. Conserv. Biol. 3, 149–58.
Henrikson, B. (1990) Predation on amphibian eggs and tadpoles by common predators in acidified lakes. Holart. Ecol. 13, 201–6.
Huckabee, J.W., Goodyear, C.P. and Jones, R.D. (1975) Acid rock in the Great Smokies: unanticipated impact on aquatic biota of road construction in regions of sulfide mineralization. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 104, 677–84.
Karns, D.R. (1983) Toxic bog water in northern Minnesota peatlands: ecological and evolutionary consequences for breeding amphibians. PhD Dissertation, University of Minnesota.
Karns, D.R. (1992) Effects of acidic bog habitats on amphibian reproduction in a northern Minnesota Peatland. J. Herpetol., 26, 401–12.
Leuven, R.S.W., denHartog, C., Christiaans, M.M.C. and Heijligers, W.H.C. (1986) Effects of water acidification on the distribution patterns and the reproductive success of amphibians. Experientia 42, 495–503.
Ling, R.W., VanAmberg, J.P. and Werner, J.K. (1986) Pond acidity and its relationship to larval development of Ambystoma maculatum and Rana sylvatica in upper Michigan. J. Herpetol. 20, 230–6.
Mushinsky, H.R. and Brodie, E.D.Jr. (1975) Selection of substrate pH by salamanders. Am. Midland Nat. 93, 440–3.
Padhye, A.D. and Ghate, H.V. (1988) Effect of altered pH on embryos and tadpoles of the frog Microhyla ornata. Herpetol. J. 1, 276–9.
Pierce, B.A. (1991) Additional studies of acid sensitivity of eggs and larvae of two potholedwelling amphibians from Utah. Final Report to the Air Quality Division, National Park Service, US Department of the Interior.
Pierce, B.A., Hoskins, J.B. and Epstein, E. (1984) Acid tolerance in Connecticut Wood Frogs (Rana sylvatica). J. Herpetol. 18, 159–67.
Pierce, B.A. and Harvey, J.M. (1987) Geographic variation in acid tolerance of Wood Frogs. Copeia 1987, 94–103.
Pierce, B.A. and Montgomery, J. (1989) Effects of short-term acidification on growth rates of tadpoles. J. Herpetol. 23, 97–102.
Pierce, B.A. and Sikand, N. (1985) Intrapopulation variation in acid tolerance of Connecticut Wood Frogs: genetic and maternal effects. Can. J. Zool. 63, 1647–51.
Pierce, B.A. and Wooten, D.K. (1992a) Genetic variation in tolerance of amphibians to low pH. J. Herpetol., 26, 422–9.
Pierce, B.A. and Wooten, D.K. (1992b) Acid tolerance of Ambystoma texanum from central Texas. J. Herpetol. 26, 230–2.
Portnoy, J. (1990) Breeding biology of the Spotted Salamander Ambystoma maculatum (Shaw) in acidic temporary ponds on Cape Cod, USA. Biol. Conserv. 53, 61–5.
Pough, F.H. (1976) Acid precipitation and embryonic mortality of Spotted Salamanders Ambystoma maculatum. Science 192, 68–72.
Pough, F.H. and Wilson, R.E. (1977) Acid precipitation and reproductive success of Ambystoma salamanders. Water Air Soil Pollut. 7, 531–44.
Punzo, F. (1983) Effects of environmental pH and temperature on embryonic survival capacity and metabolic rates in the Smallmouth Salamander, Ambystoma texanum. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 31, 467–73.
Sadinski, W.J. and Dunson, W.A. (1992) A multilevel study of low pH on amphibians of temporary ponds. J. Herpetal 26, 413–22.
Schlichter, L. (1981) Low pH affects the fertilization and development of Rana pipiens eggs. Can. J. Zool. 59, 1693–9.
Seale, D.B. (1980) Influence of amphibian larvae on primary production, nutrient flux, and competition in a pond ecosystem. Ecology 61, 1531–50.
Smith, D.C. (1987) Adult recruitment in chorus frogs: effects of size and date at metamorphosis. Ecology 68, 344–50.
Strijbosch, H. (1979) Habitat selection of amphibians during their aquatic phase. Oikos 33, 363–72.
Tome, M.A. and Pough, F.H. (1982) Responses of amphibians to acid precipitation. In Haines, T.A. and Johnson, R.E. (eds) Acid Rain/Fisheries, pp. 245–54. Bethesda, MD: American Fisheries Society.
Travis, J. (1980) Phenotypic variation and the outcome of interspecific competition in hylid tadpoles. Evolution 34, 40–50.
Tyler-Jones, R., Beattie, R.C. and Aston, R.J. (1989) The effects of acid water and aluminium on the embryonic development of the Common Frog, Rana temporaria. J. Zool. Lond. 219, 355–72.
Urch, U.A. and Hedrick, J.L. (1981) Isolation and characterization of the hatching enzyme of the amphibian Xenopus laevis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 206, 424–31.
Vernberg, F.J. (1955) Correlation of physiological and behavioral indexes of activity in the study of Plethodon cinereus (Green) and Plethodon glutinosus (Green). Am. Midland Nat. 54, 382–93.
Vitt, L.J., Caldwell, J.P. Wilbur, H.M. and Smith, D.C. (1990) Amphibians as harbingers of decay. BioScience 40, 418.
Wake, D.B. (1991) Declining amphibian populations. Science 253, 860.
Warner, S.C., Dunson, W.A. and Travis, J. (1991) Interaction of pH, density, and priority effects on the survivorship and growth of 2 species of hylid tadpoles. Oecologia 88, 331–9.
Wilbur, H.M. and Collins, J.P. (1973) Ecological aspects of amphibian metamorphosis. Science 182, 1305–14.
Wooten, D.K. (1992) The effect of low pH and genetics on growth of Pseudacris streckeri larvae. M.S. Thesis, Baylor University.
Wyman, R.L. (1988) Soil acidity and moisture and the distribution of amphibians in five forests of southcentral New York. Copeia 394–9.
Wyman, R.L. and Hawksley-Lescault, D.S. (1987) Soil acidity affects distribution, behavior, and physiology of the salamander Plethodon cinereus. Ecology 68, 1819–27.
Wyman, R.L. and Jancola, J. (1992) Degree and scale of terrestrial acidification and amphibian community structure. J. Herpetol., 26, 392–401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierce, B.A. The effects of acid precipitation on amphibians. Ecotoxicology 2, 65–77 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058215
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058215