Abstract
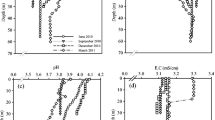
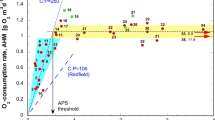
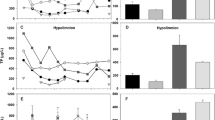
Onondaga Lake is a hypereutrophic, industrially polluted lake located in Syracuse, NY. High hypolimnetic concentrations of H2S that develop after anoxia restrict the accumulation of total Fe2+ due to the formation of FeS, and may limit Fe-PO4 interactions. High water column concentrations of Ca2+ and high rates of CaCO3 deposition occur due to inputs of Ca2+ from an adjacent soda ash manufacturing facility. Patterns of P concentration and other water chemistry parameters in the lower waters, and results from chemical equilibrium calculations, suggest that Ca-PO4 minerals may regulate the supply of P from sediments to the water column in Onondaga Lake. These findings have important management implications for Onondaga Lake. First, declines in water column Ca2+ concentrations due to reductions in industrial CaCl2 input may result in conditions of undersaturation with respect to Ca-PO4 mineral solubility and increases in the release of P from sediments to the water column. Second, introduction of O2 from hypolimnetic oxygenation, as a lake remediation initiative, may enhance P supply from sediments, because of increased solubility of Ca-PO4 minerals at lower pH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlgren, I., 1977. Role of sediments in the process of recovery of a eutrophic lake. In H. L. Gotterman (ed.), Interactions between sediments and fresh water. Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, 372–377.
Anderson, J. M., 1975. Influence of pH on release of phosphorus from lake sediments. Arch. Hydrobiol. 76: 411–419.
APHA (American Public Health Association), 1985. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 16th Edition. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, 1268 pp.
Auer, M. T., N. A. Johnson, M. R. Penn & S. W. Effler, 1993. Measurement and verification of rates of sediment phosphorus release for a hypereutrophic urban lake. In P. C. M. Boers, T. E. Cappenberg & W. van Raaphorst (eds), Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on Phosphorus in Sediments. Developments in Hydrobiology 84. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 301–309. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 253.
Auer, M. T., M. L. Storey, S. W. Effler, N. A. Auer & P. Sze, 1990. Zooplankton impacts on chlorophyll and transparency in Onondaga Lake, New York, USA. In R. D. Gulati, E. H. R. R. Lammens, M.-L. Meijer & E. van Donk (eds), Fluxes between Trophic Levels and through the Water-Sediment Interface. Developments in Hydrobiology 61. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 603–617. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 200/201.
Baccini, P., 1985. Phosphate interactions at the sediment-water interface. In W. Stumm (ed.), Chemical processes in lakes. Wiley-Interscience, New York: 189–205.
Ball, J. W., D. K. Nordstorm & E. A. Jenne, 1980. Additional and revised thermodynamic data for WATEQ-2 computerized model for trace and major element speciation and mineral equilibrium of natural waters, U.S., Geol. Surv. Water Resource Investigations, Menlo Park, California.
Böstrom, B., J. M. Andersen, S. Flerscher & M. Jansson, 1988. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment-water interface. In G. Persson & M. Jansson (eds), Phosphorus in Freshwater Ecosystems. Developments in Hydrobiology 48. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 229–244. Reprinted from Hydrobiologia 170.
Caraco, N. F., J. J. Cole & G. E. Likens, 1989. Evidence for sulfate-controlled P release from sediments of aquatic systems. Nature (London) 341: 316–318.
Caraco, N. F., J. J. Cole & G. E. Likens, 1991. A cross-system study of phosphorus release from Lake sediments. In J. Cole, G. Lovett and S. Findlay (eds), Comparative analyses of ecosystems: Patterns, mechanisms, and theories. Springer-Verlag, New York: 241–258.
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Perterson & P. R. Newroth, 1986. Lake and reservoir restoration. Butterworth, Boston.
Devan, S. P. & S. W. Effler, 1984. History of phosphorus loading to Onondaga Lake. J. Envir. Eng. Div., ASCE 110: 93–109.
Effler, S. W. & C. T. Driscoll, 1985. Calcium chemistry and deposition in ionically enriched Onondaga Lake, New York. Envir. Sci. Technol. 19: 716–720.
Effler, S. W., G. P. Hassett, M. T. Auer & N. Johnson, 1988. Depletion of epilimnetic oxygen and accumulation of hydrogen sulfide in the hypolimnion of ionically enriched Onondaga Lake, NY, USA. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 39: 59–74.
Effler, S. W., M. G. Perkins & C. Brooks, 1986. The oxygen resources of the hypolimnion of ionically enriched Onondaga Lake, NY, USA. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 29: 93–108.
Effler, S. W., C. M. Brooks, J. M. Addess, S. M. Doerr, M. L. Storey & B. A. Wagner, 1991. Pollutant loadings from Solvay Waste beds to lower Ninemile Creek, New York. Wat. Air Soil Pollut. 55: 427–444.
Einsele, W., 1936. Über die Beziehungen des Eisenkreislaufs Zum Phosphatkreislauf im eutrophen See. Arch. Hydrobiol. 29: 664–686.
Field, S. D., 1980. Nutrient-saturated algal growth in hypereutrophic Onondaga Lake, Syracuse, New York. Thesis. Syracuse University. Syracuse, NY.
Gächter, R., 1987. Lake restoration. Why oxygenation and artificial mixing cannot substitute for a decrease in the external phosphorus loading. Z. Hydrobiol. 49: 170–185.
Heaney, S. I. & W. Davison, 1977. The determination of ferrous iron in natural waters with 2,2′ bipyridyl. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 753–759.
Honstein, R. L., 1981. An assessment of mechanisms by which phosphorus may be regulated within the sediments of Onondaga Lake, New York. Thesis, Syracuse University Syracuse, NY.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1973. Eutrophication. The scientific background of a contemporary practical problem. Am. Sci. 61: 269–279.
Johnson, D. L., J. Jiao, S. G. DosSantos & S. W. Effler, 1991. Individual particle analysis of suspended materials in Onondaga Lake, New York. Envir. Sci. Technol. 25: 736–744.
Larsen, D. P., D. W. Schultz & K. W. Malereg, 1981. Summer internal phosphorus supplies in Shagawa Lake, Minnesota. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26: 740–753.
Mortimer, C. J., 1941. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes (Parts I and II). J. Ecol. 29: 280–329.
Mortimer, C. H., 1942. The exchange of dissolved substances between mud and water in lakes (Parts III and IV). J. Ecol. 30: 147–201.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Staudinger, B., S. Peiffer, Y. Avnimelech & T. Berman, 1990. Phosphorus mobility in interstitial waters of sediments in Lake Kinneret, Israel. Hydrobiologia 207: 167–177.
Stauffer, R. E., 1985. Relationships between phosphorus loading and trophic state in calcareous lakes of southeast Wisconsin. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 123–145.
Stumm, W. & J. O. Leckie, 1971. Phosphate exchange with sediments: its role in the productivity of surface waters. Adv. Wat. Pollut. Res. 5; 1970, III-26: 1–16.
Stumm, W. & J. J. Morgan, 1981. Aquatic chemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley Interscience, New York.
Uttormark, F. D., 1978. General concepts of lake degradation and lake restoration. Environmental Protection Agency. EPA-740/5-79-001, pp. 65–70.
Vollenweider, R. A., 1975. Input-output models, with special reference to the phosphorus loading concept in limnology. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 37: 53–84.
Welch, E. B., D. E. Spyridakis, J. I. Shuster & R. R. Horner, 1986. Declining lake sediment phosphorus release and oxygen deficit following wastewater diversion. J. Wat. Pollut. Contr. Fed. 58: 92–96.
Westall, J. C., J. L. Zachary & F. M. M. Morel, 1976. Technical note 18, R. M. Parsons Laboratory for Water Resources and Hydrodynamics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge.
Williams, J. D., J. M. Jaquet & R. L. Thomas, 1976. Forms of phosphorus in the surficial sediments of Lake Erie. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 33: 413–429.
Wodka, M. C., S. W. Effler & C. T. Driscoll, 1985. Phosphorus desposition from the epilimnion of Onondaga Lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 833–843.
Yin, C. & D. L. Johnson, 1984. An individual particle analysis and budget study of Onondaga Lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 1193–1201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Driscoll, C.T., Effler, S.W., Auer, M.T. et al. Supply of phosphorus to the water column of a productive hardwater lake: controlling mechanisms and management considerations. Hydrobiologia 253, 61–72 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00050722
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00050722