Abstract
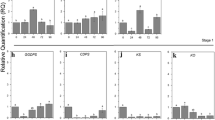
Nuclear transcript run-on analysis was used to investigate the relative transcription rates of genes encoding enzymes of isoflavonoid phytoalexin biosynthesis and related pathways in elicitor-treated alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cell suspension cultures. Genes encoding L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), chalcone synthase (CHS) and chalcone reductase (CHR) were most rapidly activated, with increases in transcription measurable within 10–20 min after elicitation. Cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase (C4H), chalcone isomerase (CHI), isoflavone reductase (IFR) and caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase (COMT) genes were also rapidly activated, but at a slower initial rate. Transcription of chalcone 2′-O-methyltransferase (CHOMT), and 1,3-β-D-glucanase genes was less rapid, with lag periods of 60 and 30 min post-elicitation, respectively. Treatment of cells with the PAL inhibitor L-α-aminooxy-β-phenylpropionic acid (AOPP) resulted in increased transcription of PAL, CHS and CHR, but reduced transcription of CHOMT, indicating a role for phenylpropanoid products as both negative and positive regulators of gene expression within the phenylpropanoid pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballance GM, Dixon RA: Medicago sativa cDNAs encoding chalcone reductase. Plant Physiol 107: 1027–1028 (1995).
Bolwell GP, Mavandad M, Millar DJ, Edwards KJ, Schuch W, Dixon RA: Inhibition of mRNA levels and activities by trans-cinnamic acid in elicitor-induced bean cells. Phytochemistry 27: 2109–2117 (1988).
Cramer CL, Ryder TB, Bell JN, Lamb CJ: Rapid switching of plant gene expression induced by fungal elicitor. Science 227: 1240–1243 (1985).
da Costa e Silva O, Klein L, Schmelzer E, Trezzini GF, Hahlbrock K: BPF-1, a pathogen-induced DNA-binding protein involved in the plant defense response. Plant J 4: 125–135 (1993).
Dalkin K, Edwards R, Edington B, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) I. Induction of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis and hydrolytic enzymes in elicitor-treated cell suspension cultures. Plant Physiol 92: 440–446 (1990).
Dangl JL, In: Boller T, Meins F, (eds) Plant Gene Research: Regulatory Elements Controlling Developmental and Stress-Induced Expression of Phenylpropanoid Genes, pp. 303–326. Springer-Verlag, New York (1992).
DeLisle AL, Crouch ML: Seed storage protein transcription and mRNA levels in Brassica napus during development and in response to exogenous abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 91: 617–623 (1989).
Desjardins AE, Hohn TM, McCormick SP: Tricothecene synthesis in Fusarium species: chemistry, genetics and significance. Microbiol Rev 57: 595–604 (1993).
Dixon RA, Harrison MJ: Activation, structure, and organization of genes involved in microbial defense in plants. Adv Genet 28: 165–234 (1990).
Dixon RA, Harrison MJ, Paiva NL: The isoflavonoid phytoalexin pathway: From enzymes to genes to transcription factors. Physiol Plant 93: 385–392 (1995).
Fahrendorf T, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XVIII. Molecular cloning and expression of the elicitor-inducible cinnamic acid 4-hydroxylase cytochrome P450. Arch Biochem Biophys 305: 509–515 (1993).
Fahrendorf T, Ni W, Shorrosh BS, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XIX. Transcriptional activation of oxidative pentose phosphate pathway genes at the onset of the isoflavonoid phytoalexin response. Plant Mol Biol 28: 885–900 (1995).
Görlach J, Raesecke HR, Rentsch D, Regenass M, Roy P, Zala M, Keel C, Boller T, Amrhein N, Schmid J: Temporally distinct accumulation of transcripts encoding enzymes of the prechorismate pathway in elicitor-treated cultured tomato cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3166–3170 (1995).
Gowri G, Bugos RC, Campbell WH, Maxwell CA, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). X. Molecular cloning and expression of S-adenosyl-L-methionine: caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase, a key enzyme of lignin biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 97: 7–14 (1991).
Gowri G, Paiva NL, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). 12. Sequence analysis of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) cDNA clones and appearance of PAL transcripts in elicitor-treated cell cultures and developing fruits. Plant Mol Biol 17: 415–429 (1991).
Hahlbrock K, Scheel D, Logemann E, Nurnberger T, Parniske M, Reinhold S, Sacks WR, Schmelzer E: Oligopeptide elicitor-mediated defense gene activation in cultured parsley cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 4150–4157 (1995).
Harris N, Taylor JE, Roberts JA: Isolation of a mRNA encoding nucleoside diphosphate kinase from tomato that is up-regulated by wounding. Plant Mol Biol 25: 739–742 (1994).
Junghans H, Dalkin K, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). 15. Characterization and expression patterns of members of a subset of the chalcone synthase multigene family. Plant Mol Biol 22: 239–253 (1993).
Kodrzycki R, Boston RS, Larkins BA: The opaque-2 mutation of maize differentially reduces zein gene transcription. Plant Cell 1: 105–114 (1989).
Lamb CJ: Trans-cinnamic acid as a mediator of the light-stimulated increase in hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA: quinate hydroxycinnamoyl transferase. FEBS Lett 75: 37–39 (1977).
Lawton MA, Lamb CJ: Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitor, wounding, and infection. Mol Cell Biol 7: 335–341 (1987).
Loake GJ, Choudhary AD, Harrison MJ, Mavandad M, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Phenylpropanoid pathway intermediates regulate transient expression of a chalcone synthase gene promoter. Plant Cell 3: 829–840 (1991).
Loake GJ, Faktor O, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Combination of H-box [CCTACC(N)7CT] and G-box (CACGTG) cis elements is necessary for feed-forward stimulation of a chalcone synthase promoter by the phenylpropanoid-pathway intermediate p-coumaric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 9230–9234 (1992).
Maher EA, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XII. Identification of multiple hydrolases and molecular characterization of an acidic glucanase. Physiol Mol Plant Path 43: 329–342 (1993).
Maxwell CA, Harrison MJ, Dixon RA: Molecular characterization and expression of alfalfa isoliquiritigene 2′-O-methyltransferase, an enzyme specifically involved in the biosynthesis of an inducer of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Plant J 4: 971–981 (1993).
Oommen A, Dixon R.A, Paiva NL: The elicitor-inducible alfalfa isoflavone reductase promoter confers different patterns of developmental expression in homologous and heterologous transgenic plants. Plant Cell 6: 1789–1803 (1994).
Orr JD, Edwards R, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XIV. Changes in the levels of phenylpropanoid pathway intermediates in relation to regulation of L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in elicitor-treated cell-suspension cultures. Plant Physiol 101: 847–856 (1993).
Paiva NL, Edwards R, Sun Y, Hrazdina G, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). 11. Molecular cloning and expression of alfalfa isoflavone reductase, a key enzyme of isoflavonoid phytoalexin biosynthesis. Plant Mol Biol 17: 653–667 (1991).
Plater R, Strohl WR: Polyketide biosynthesis: Antibiotics in Streptomyces. In: Ellis BE, Kuroki GW, Stafford HA (eds) Genetic Engineering of Plant Secondary Metabolism, pp. 61–91. Plenum Press, New York (1994).
Raventos D, Jensen AB, Rask MB, Casacuberta JM, Mundy J, Segundo BS: A 20 bp cis-acting element is both necessary and sufficient to mediate elicitor response of a maize PRms gene. Plant J 7: 147–155 (1995).
Schuller HJ, Hahn A, Troster F, Schutz A, Schweizer E: coordinate genetic control of yeast fatty acid synthase genes FAS1 and FAS2 by an upstream activation site common to genes involved in membrane lipid biosynthesis. EMBO J 11: 107–114 (1992).
Schumacher HM, Gundlach H, Fiedler F, Zenk MH: Elicitation of benzophenanthridine alkaloid synthesis in Escholtzia cell cultures. Plant Cell Rep 6: 410–413 (1987).
Shorrosh BS, Dixon RA: Molecular cloning of a putative plant endomembrane protein resembling protein disulfide isomerase and a phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C from vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10941–10945 (1991).
Somssich IE, Bollmann J, Hahlbrock K, Kombrink E, Schulz W: Differential early activation of defense-related genes in elicitor-treated parsley cells. Plant Mol Biol 12: 227–234 (1989).
Sze JY, Woontner M, Jaehning JA, Kohlhaw GB: In vitro transcriptional activation by a metabolic intermediate: activation by Leu3 depends on α-isopropylmalate. Science 258: 1143–1145 (1992).
Welle R, Schröder J: Expression cloning in Escherichia coli and preparative isolation of the reductase co-acting with chalcone synthase during the key step in the biosynthesis of soybean phytoalexins. Arch Biochem Biophys 293: 377–381 (1992).
Yu LM, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Purification and biochemical characterization of proteins which bind to the H-box cis-element implicated in transcriptional activation of plant defense genes. Plant J 3: 805–816 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, W., Fahrendorf, T., Ballance, G.M. et al. Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). XX. Transcriptional activation of phenylpropanoid pathway genes in elicitor-induced cell suspension cultures. Plant Mol Biol 30, 427–438 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00049322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00049322