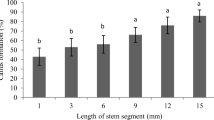
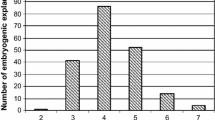
Abstract
An improved procedure for the induction, proliferation and regeneration of embryogenic callus from coffee leaf explants has been developed. The optimal culture conditions for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis yielded so-called “high frequency” embryogenic callus ofCoffea canephora P. ex Fr., Arabusta and Congusta, more rapidly and abundantly than other published procedures.Coffea arabica L. genotypes, however, were less responsive to the procedure. The highest multiplication rate of embryogenic callus in liquid culture, which avoided the differentiation of embryos, was obtained by culture at an inoculum density of 10 g callus 1-1 in a modified MS medium containing 4.5 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, under 3 μmol m-2 s-1 illumination, and subcultured every 7–10 days. The best long-term maintenance of embryogenic potential was obtained by culture of aggregates (250–1000 μm in diameter) at an inoculum density of 5 g 1-1, with medium renewed every 3–4 weeks. Under these conditions, embryogenic potential ofC. canephora callus was maintained for over 2 years. Analysis of nutrients absorbed by the callus cultures demonstrated that half strength MS macro- and micro-salts were not depleted during at least 3 weeks of sustained culture. The highest regeneration of embryogenic callus required the omission of 2,4-D and a reduced culture density of 1 g 1-1. Under these conditions of culture, 1 g ofC. canephora or Arabusta callus produced 1.2 and 0.9×105 somatic embryos, respectively, after 8–10 weeks in liquid regeneration medium. This was an overall reduction of 4–6 months from explant to regenerant, when compared with other procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
N6-benzyladenine
- HFSE:
-
high frequency somatic embryogenesis
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
indole-3-butyric acid
- rpm:
-
rotations per minute
- LFSE:
-
low frequency somatic embryogenesis
- MS:
-
Murashige & Skoog medium
- PPF:
-
photosynthetic photon flux
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 2-iP:
-
2-isopentenyladenine
References
Alvard D, Cote F & Teisson C (1993) Comparison of methods of liquid medium culture for banana propagation. Effects of temporary immersion of explants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 32: 55–60
Anonymous (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th ed (pp 3.9–3.15). Amer. Public Health Assoc., Amer. Water Works Assoc., Water & Environment Federation, Washington
Bieysse D, Gofflot A & Michaux-Ferrière N (1993) Effect of experimental conditions and genotypic variability on somatic embryogenesis inCoffea arabica. Can. J. Bot. 71: 1496–1502
Bliss C (1967) Statistics in Biology, Vol. 1 (pp 253–257). McGraw-Hill, New York
Chee P & Cantliffe D (1989) Composition of embryogenic suspension cultures ofIpomoea batatas Poir. and production of individualized embryos, Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 17: 39–52
Dublin P (1981) Embryogenèse somatique directe sur fragments de feuilles de caféier Arabusta. Café Cacao Thé 25: 237–242
Dublin P (1984) Techniques de reproduction végétativein vitro et amélioration génétique chez les caféiers cultivés. Café Cacao Thé 28: 231–244
Ducos JP, Zamarripa A, Eskes A & Pétiard V (1993) Production of somatic embryos of coffee in a bioreactor. In: 15ème Colloq. Sci. Int. Café, Montpellier, 6–11 June (pp 89–96). ASIC, Paris
Gray D & Mortensen J (1987) Initiation and maintenance of long term somatic embryogenesis from anthers and ovaries ofVitis longii Microsperma. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 9: 73–80
Hatanaka T, Arakawa O, Yasuda T, Uchida N & Yamaguchi T (1991) Effect of plant growth regulators on somatic embryogenesis in leaf cultures ofCoffea canephora. Plant Cell Rep. 10: 179–182
Michaux-Ferrière N & Schwendiman J (1992) Histology of somatic embryogenesis. In: Dattée Y, Dumas C & Gallais A (eds) Reproductive Biology and Plant Breeding, 13th Eucarpia Congress, Angers, 6–11 July (pp 247–259). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Michaux-Ferrière N, Bieysse D, Alvard D & Dublin P (1989) Etude histologique de l'embryogenèse somatique chezCoffea arabica induite par culture sur milieux uniques de fragments foliaires de génotypes différents. Café Cacao Thé 33: 207–217
Monaco L, Söndahl M, Carvalho A, Crocomo O & Sharp W (1977) Applications of tissue culture in the improvement of coffee. In: Reinert J & Bajaj Y (eds) Applied and Fundamental Aspects of Plant Cell, Tissue, and Organ Culture (pp 109–129). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Muralidharan E, Gupta P & Mascarenhas A (1989) Plantlet production through high frequency somatic embryogenesis in long term cultures ofEucalyptus citriodora. Plant Cell Rep. 8: 41–43
Nadel B, Altman A & Ziv M (1989) Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in celery cell suspensions. 1. Promoting effects of mannitol on somatic embryo development. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 18: 181–189
Neuenschwander B & Baumann T (1992) A novel type of somatic embryogenesis inCoffea arabica. Plant Cell Rep. 10: 608–612
Noriega C & Söndahl M (1993) Arabica coffee micropropagation through somatic embryogenesis via bioreactors. In: 15ème Colloq. Sci. Int. Café, Montpellier, 6–11 June (pp 73–81). ASIC, Paris
Söndahl M & Sharp W (1977) High frequency induction of somatic embryos in cultured leaf explants ofCoffea arabica L. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 81: 395–408
Söndahl M, Spahlinger D & Sharp W (1979) A histological study of high frequency and low frequency induction of somatic embryos in cultured leaf explants ofCoffea arabica L.. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 94: 101–108
Söndahl M, Monaco L & Sharp W (1981)In vitro methods applied to coffee. In: Thorpe T (ed) Tissue Culture and Its Application in Agriculture (pp 325–347). Academic Press, New York
Söndahl M, Nakamura T & Sharp W (1985) Propagation of coffee. In: Henke RR, Hughes KW, Constantin M & Hollaender A (eds) Tissue Culture in Forestry and Agriculture (pp 215–232). Plenum Press, New York
Staritsky G (1970) Embryoid formation in callus tissues of coffee. Acta Bot. Neerl. 19: 509–514
Staritsky G & van Hasselt G (1980) The synchronised mass propagation ofCoffea canephora in vitro. In: 9ème Colloq. Sci. Int. Café, London, 16–20 June (pp 597–602). ASIC Paris
Vasil V & Vasil I (1986) Plant regeneration from friable embryogenic callus and cell suspension cultures ofZea mays L.. J. Plant Physiol. 127: 399–408
Vogel A (1961) Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, 3rd ed (pp 256–257). Longmans, London
Yasuda T, Fujii Y & Yamaguchi T (1985) Embryogenic callus induction fromCoffea arabica leaf explants by benzyladenine. Plant Cell Physiol. 26: 595–597
Zamarripa A (1993) Etude et développement de l'embryogenèse somatique en milieu liquide du caféier (Coffea canephora P.,Coffea arabica L. et l'hybride Arabusta). Thèse de doctorat, Ecole Nationale Supérieure Agronomique, Rennes, France, 191 p.
Zamarripa A, Ducos JP, Tessereau H, Bollon H, Eskes A & Pétiard V (1991) Développement d'un procédé de multiplication en masse du caféier par embryogenèse somatique en milieu liquide. In: 14ème Colloq. Sci. Int. Café, San Francisco, 14–19 July (pp 392–402). ASIC, Paris
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Boxtel, J., Berthouly, M. High frequency somatic embryogenesis from coffee leaves. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 44, 7–17 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00045907
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00045907