Abstract
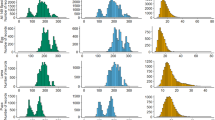
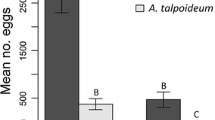
Life history and population dynamics were examined for an annual halophyte, Atriplex triangularis Willd., in an inland salt marsh at Rittman, Ohio. The effect of salinity and precipitation on survival, growth, and reproduction of Atriplex triangularis under field conditions was determined. Early germination enhanced the possibility of survival and reproduction of this species. No distinct ecotypes were found, but various populations demonstrated different degrees of phenotypic plasticity in response to salinity, indicating that genetic selection for plasticity in growth response is taking place along the salinity gradient. Most seeds fell directly below the parent plant, but a small number was found in traps up to 0.5 meter from fruiting individuals. High temperature, salinity, and darkness individually, and in combination, inhibited the germination of small seeds more than large seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeftink, W. G., Daane, M. C., De, Munk, W. & Nieuwenhuize, J., 1978. Aspects of population dynamics in Halimione portulacoides communities. Vegetatio 36: 31–43.
Chepil, W. S., 1946. Germination of weed seeds. I. Longevity, periodicity of germination and vitality of seeds in cultivated soils. Sci. Agric. 26: 307–346.
Cook, R. E., 1979. Pattern of juvenile mortality and recruitment in plants. In: O. T., Solbrig, S., Jain, G. B., Johnson & P. H., Raven (eds.), Topics in plant population biology. Columbia University Press, New York, pp. 207–231.
Gallagher, J. L., Reimold, R. J., Linthurst, R. A. & Pfeiffer, W. J., 1980. Aerial production, mortality, and mineral accumulation-export dynamics in Spartina alterniflora and Juncus roemerianus plant stands in a Georgia saline marsh. Ecology 61: 303–312.
Gray, A. J. & Scott, R., 1980. A genecological study of Puccinellia maritima Huds. (Parl.) I. Variation estimated from single-plant samples from British populations. New Phytol. 85: 89–107.
Harper, J. L., 1977. Population biology of plants. Academic Press, New York, 892 pp.
Harper, J. L. & White, J., 1974. The demography of plants. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 5: 419–463.
Hulme, B. A., 1957. Studies on some British species of Atriplex L. Ph.D. thesis, University of Edinburgh.
Jefferies, R. L., 1977. The vegetation of salt marshes at some coastal sites in arctic North America. J. Ecol. 65: 661–672.
Jefferies, R. L. & Gottlieb, L. D., 1982. Genetic differentiation of the microspecies Salicornia europaea L. (Sensu stricto) and S. ramosissima, J. Woods. New Phytol. 92: 123–129.
Jefferies, R. L. & Gottlieb, L. D., 1983. Genetic variation within and between populations of the asexual plant Puccinellia x phryganodes. Can. J. Bot. 61: 774–779.
Jefferies, R. L., Davy, A. J. & Rudmik, T., 1979. The growth strategies of coastal halophytes. In: R. L., Jefferies & A. J., Davy (eds), Ecological processes in coastal environments. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. pp. 243–268.
Jefferies, R. L., Davy, A. J. & Rudmik, T., 1981. Population biology of the salt marsh annual Salicornia europaea agg. J. Ecol. 69: 1–15.
Jefferies, R. L., Jensen, A. & Bazely, D., 1983. The biology of annual Salicornia europaea agg. at the limits of its range in Hudson Bay. Can. J. Bot. 61: 762–763.
Karimi, S. H., 1984. Ecophysiological responses of Atriplex triangularis Willd. to environmental stress. Ph. D. Dissertation, Ohio University.
Khan, M. A. & Ungar, I. A., 1984. Seed polymorphism and germination responses to salinity stress in Atriplex triangularis Willd. Bot. Gaz. 145: 487–494.
McGraw, D. C. & Ungar, I. A., 1981. Growth and survival of halophyte Salicornia europaea L. under saline conditions. Ohio J. Sci. 81: 109–113.
McMahon, K. A. & Ungar, I. A., 1978. Phenology, distribution and survival of Atriplex triangularis Willd. in an Ohio salt pan. Am. Mid. Nat. 100: 1–14.
Mendelssohn, I. A. & Seneca, E. D., 1980. The influence of soil drainage on the growth of salt marsh cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora) in North Carolina. Estuarine Coast Mar. Sci. 11: 27–40.
Osmond, C. B., Björkman, O. & Anderson, D. J., 1980. Physiological processes in plant ecology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 468 pp.
Philipupillai, J. & Ungar, I. A., 1984. The effect of seed dimorphism on the germination and survival of Salicornia europaea L. populations. Am. J. Bot. 71: 542–549.
Pomeroy, L. R. & Imberger, J., 1981. The physical and chemical development. In: L. R., Pomeroy & R. G., Wiegert, (eds). The ecology of a saline marsh. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 21–36.
Rabinowitz, D. & Rapp, J., 1980. Seed rain in a North American tall grass prairie. J. Appl. Ecol. 17: 793–802.
Riehl, T. E. & Ungar, I. A., 1982. Growth and ion accumulation in Salicornia europaea under saline field conditions. Oecologia 54: 193–199.
Riehl, T. E. & Ungar, I. A., 1983. Growth, water potential and ion accumulation in the inland halophyte Atriplex triangularis under saline field conditions. Oecol. Plant. 4: 27–39.
Roberts, H. A. & Neilson, J. E., 1980. Seed survival and periodicity of seedling emergence in some species of Atriplex, Chenopodium, Polygonum, and Rumex. Ann. Appl. Biol. 94: 111–120.
Rozema, J., 1978. Population dynamics and ecophysiological adaptations of some coastal members of the Juncaceae and Gramineae. In: R. L., Jefferies & A. J., Davy (eds), Ecological processes in coastal environments. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. pp. 229–241.
Thompson, K. & Grime, J. P., 1979. Seasonal variation in the seed banks of herbaceous species in ten contrasting habitats. J. Ecol. 67: 893–921.
Ungar, I. A., 1968. Species-soil relationships on the Great Salt Plains of northern Oklahoma. Am. Midl. Nat. 80: 392–406.
Ungar, I. A., 1972. The vegetation of inland saline marshes of North America, north of Mexico. In: R., Tüxen (ed.), frundfragen und Methoden in der Pflanzensoziologie. Junk, The Hague, pp. 397–411.
Ungar, I. A., 1974a. Inland halophytes of the United States. In: R., Reimold & W., Queen, (eds), Ecology of halophytes. Academic Press, New York. pp. 235–305.
Ungar, I. A., 1974b. Population dynamics of inland halophytic communities. Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 121: 287–292.
Ungar, I. A., 1983. Autecological studies with Atriplex triangularis Willdenow. In: A. R., Tiedemann, E. D., McArthur, H. C., Stutz, R., Stevens, & K. L., Johnson, compilers. Proc. symposium on the biology of Atriplex and related chenopods; 1983 May 2–6; Provo UT. Gen. Techn. Rep. INT-172. Ogden, UT: U.S. Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station; 1984. 309 pp.
Ungar, I. A., Benner, D. K. & McGraw, D. C., 1979. The distribution and growth of Salicornia europaea on an inland salt pan. Ecology 60: 329–336.
Weaver, J. E., 1918. The quadrat methods in teaching ecology. The plant world. 21: 267–283.
Wiegert, R. G., Chalmer, A. G. & Anderson, P. F., 1983. Productivity gradients in saline marshes: the response of Spartina alterniflora to experimentally manipulated soil water movement. Oikos 41: 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We acknowledge the thoughtful comments made by Dr. Warren A. Wistendahl and Brian C. McCarthy on an earlier draft of the manuscript. Thanks are also due to Morton Salt Company, Rittman, Ohio, for permission to conduct research on their property. This research was supported by the National Science Foundation Grant DEB-79-27236.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.A., Ungar, I.A. Life history and population dynamics of Atriplex triangularis . Vegetatio 66, 17–25 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00044079
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00044079