Summary
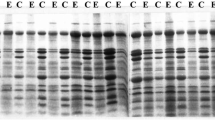
Seed protein profiles of 19 accessions representing seven sections of the genus Arachis were studied using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The general profile showed appreciable homology between these taxa, supporting their classification based on morphology and cross-compatibility relationships. The accessions of section Arachis expressed a high variation confirming inferences from earlier studies. Variation between accessions of a species is limited. Accessions of the section Ambinervosae and Caulorhizae formed one cluster and accessions of sect. Erectoides and Procumbensae formed another. Whereas the representative accessions of sect. Triseminalae and Extranervosae formed two independent clusters. Using the percentage of dissimilarity in electrophoretic bands as a statistical genetic distance between accessions, sect. Arachis (containing the cultivated groundnut, A. hypogaea) is phylogenetically closest to sect. Erectoides followed by Procumbensae, Ambinervosae, Caulorhizae, Triseminalae and Extranervosae, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bianchi-Hall, C.M., R.D. Keys, H.T. Stalker & J.P. Murphy, 1993. Diversity of seed storage protein patterns in wild peanut (Arachis, Fabaceae) species. Pl. Syst. Evol. 186: 1–15.
Cherry, J.P., 1975. Comparative studies of seed proteins and enzymes of species and collections of Arachis by gel electrophoresis. Peanut Sci. 2: 57–65.
Cherry, J.P., 1990. Peanut protein and product functionality. JACOS 67: 293–301.
Crawford, D.J., 1990. Plant Molecular Systematics. pp. 30–50 New York, Wiley.
Gregory, W.C., A. Krapovickas & M.P. Gregory, 1980. Structure, variation, evolution and classification in Arachis. In: R.J. Summerfield & A.H. Bunting (Eds), Advances in Legume Sciences, pp. 469–481. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, England.
Halward, T.M., H.T. Stalker, E.A. La Rue & G. Kochert, 1991. Genetic variation detectable with molecular markers among unadapted germplasm resources of cultivated peanut and related wild species. Genome 34: 1013–1020.
Halward, T.M., H.T. Stalker, E.A. La Rue & G. Kocher, 1992. Use of single primer DNA amplifications in genetic studies of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Pl. Molec. Biol. 18: 315–320.
Klozova, E., J. Svachulova, J. Smartt, E. Hadac, V. Turkova & V. Hadacova, 1983a. The comparison of seed protein pattern within the genus Arachis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biol. Plant 25: 266–273.
Klozova, L., V. Turkova, J. Smartt, K. Pitterova & J. Svachulova, 1983b. Immunochemical characterization of seed protein of some species of the genus Arachis L. Biol. Plant 25: 201–208.
Kochert, G.D., T.M. Halward, W.D. Branch & C.E. Simpson, 1991. RFLP variability in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars and wild species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 81: 565–570.
Krapovickas, A., 1990. Classification of Arachis. In: IBPGR 1990 International Crop Network Series. 2. Report of workshop on genetic resources of wild Arachis species, held at CIAT, IBPGR, FAO, Rome, Italy.
Ladizinsky, G. & T. Hymowitz, 1979. Seed protein electrophoresis in taxonomic and evolutionary studies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 54: 145–151.
Neucere, N.J. & J.P. Cherry, 1975. An immunochemical survey of protein in species of Arachis. Peanut Sci. 2: 66–72.
Rao, C.R., 1952. Advanced statistical methods in biometric research. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Singh, A.K. & J.P. Moss, 1982. Utilization of wild relatives in genetic improvement of Arachis hypogaea L. 2. Chromosome complements of species of section Arachis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 61: 305–314.
Singh, A.K. & J.P. Moss, 1984. Utilization of wild relatives in genetic improvement of Arachis hypogaea L. 5. Genome analysis in section Arachis and its implications in gene transfer. Theor. Appl. Genet. 68: 355–364.
Singh, A.K., S. Sivaramakrishnan, M.H. Mengesha & C.D. Ramaiah, 1991. Phylogenetic relation in section Arachis based on seed protein profile. Theor. Appl. Genet. 82: 593–597.
Stalker, H.T., T.M. Jones & J.P. Murphy, 1990. Isozyme variability among Arachis species. Amer. Peanut Res. Educ. Soc. 22: 50 (abstr.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Submitted as Journal Article No. 1485 by the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) Patancheru, A.P. 502 324, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, A.K., Gurtu, S. & Jambunathan, R. Phylogenetic relationships in the genus Arachis based on seed protein profiles. Euphytica 74, 219–225 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040404
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040404