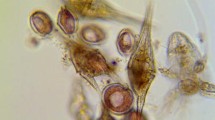
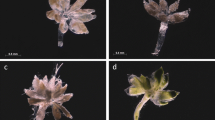
Abstract
Polysiphonia breviarticulata, a species previously known only from the Adriatic, the Mediterranean, and the Canary Islands, is reported for the first time from the Western Atlantic in Dominica and North Carolina. In the latter region it has grown in bloom quantities as drifting, planktonic plants that are a nuisance on beaches and a serious impediment to fishermen whose nets become fouled with the plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arasaki, S., H. Tokuda & K. Fujima, 1955. The reproduction and morphologeny in Codium fragile. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 69: 39–45.
Aysel, O., 1980. Some species of Polysiphonia Grev. (Rhodophyta, Rhodomelaceae) from the Aegean Coasts, Turkey. TÜBITAK VII. Bilim Kongresi Biyoloji Seksiyonu: 841–855.
Bouck, G. B. & E. Morgan, 1957. The occurrence of Codium in Long Island waters. Bull. Torrey bot. Club 84: 384–387.
Borden, C. A. & J. R. Stein, 1969. Reproduction and early development in Codium fragile (Suringar) Hariot: Chlorophyceae. Phycologia 8: 91–99.
Børgesen, F., 1930. The marine algae of Canary Islands especially from Teneriffe and Gran Canaria. III. Rhodophyceac. Part III, Ceramiales. Biol. Meddr. 9 (1): 1–159.
Critchley, A. T., W. F. Farnham & S. L. Morrell, 1983. A chronology of new European sites of attachment for the invasive brown alga, Sargassum muticum, 1973–1981. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 63: 799–811.
Dixon, P. S. & L. M. Irvine, 1977. Seaweeds of the British Isles. Part I. Introduction, Nemaliales, Gigartinales. British Museum (Natural History), London, 252 pp.
Farlow, W. G., 1881. The Marine Algae of New England. Rep. U.S. Comm. Fish and Fisheries for 1879, Appendix A-1: 1–210.
Fralick, R. A. & A. C. Mathieson, 1973. Ecological studies of Codium fragile in New England, U.S.A. Mar. Biol. 19: 127–132.
Hock, C. van den, 1982. The distribution of benthic marine algae in relation to the temperature regulation of their life histories. Biol. J. linn. Soc. 18: 81–114.
Hoek, C. van den, 1987. The possible significance of longrange dispersal for the biogeography of seaweeds. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 41: 261–272.
Hollenberg, G. J., 1961. Marine red algae of Pacific Mexico. Part 5. The genus Polysiphonia. Pac. Nat. 2: 345–375.
Hollenberg, G. J., 1968. An account of the species of Polysiphonia of the central and western tropical Pacific Oceans. I. Oligosiphonia. Pac. Sci. 22: 56–98.
Kapraun, D. F., 1977. The genus Polysiphonia in North Carolina, U.S.A. Bot. mar. 20: 313–331.
Kapraun, D. F., 1978a. Field and culture studies on selected North Carolina Polysiphonia species. Bot. mar. 21: 143–153.
Kapraun, D. F., 1978b. Field and culture studies on growth and reproduction of Callihamnion byssoides (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) in North Carolina. J. Phycol. 14: 21–24.
Kapraun, D. F., 1979. The genus Polysiphonia (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) in the vicinity of Port Aransas, Texas. Cont. mar. Sci. 22: 105–120.
Kapraun, D. F., 1980. Floristic affinities of inshore benthic marine algae in North Carolina. Phycologia 19: 245–252.
Kapraun, D. F., 1984. An illustrated guide to the marine algae of coastal North Carolina. II. Chlorophyta and Phaeophyta. Bibliotheca Phycologia 85: 1–173.
Kapraun, D. F. & D. J. Martin, 1987. Karyological studies of three species of Codium (Codiales, Chlorophyta) from coastal North Carolina. Phycologia 26: 228–234.
Kapraun, D. F. & J. R. Norris, 1982. The genus Polysiphonia (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) in the vicinity of Carrie Bow Cay, Belize. Smithson. Cont. mar. Sci. 12: 225–238.
Kapraun, D. F., A. J. Lemus & G. Bula-Meyer, 1983. The genus Polysiphonia (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) in the tropical western atlantic I. Colombia and Venezuela. Bull. mar. Sci. 33: 881–898.
Lauret, M., 1967. Morphologie, phénologie, répartition des Polysiphonia marines du littoral languedocien. I. Section Oligosiphonia. Naturalia monspel. Ser. bot. 18: 347–373.
Lewis, I. F. & W. R. Taylor, 1928. Notes from the Woods Hole Laboratory, 1928. Rhodora 30: 193–198.
Norton, T. A., 1985. Provisional atlas of the marine algae of Britain & Ireland. Institute of Terestrial Ecology, Huntington, 159 pp.
Preda, A., 1908. Flora Italica Cryptogama. Pars. II. Algae. Florideae, 1 (2). Rocca S. Casciano, Italy, 358 pp.
Ramus, J., 1971. Codium: the invader. Discovery, New Haven, U.S.A. 6: 59–68.
Rueness, J., 1989. Sargassum muticum and other introduced Japanese macroalgae: biological pollution of European coasts. Mar. Poll. Bull. 20: 173–176.
Searles, R. B., M. H. Hommersand & C. D. Amsler, 1984. The occurrence of Codium fragile subsp. tomentosoides and C. taylori (Chlorophyta) in North Carolina. Bot. mar. 27: 185–187.
Silva, P. C., 1955. The dichotomous species of Codium in Britain. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 34: 565–577.
Silva, P. C. & H. B. S. Womersley, 1956. The genus Codium (Chlorophyta) in southern Australia. Aust. J. Bot. 4: 261–289.
South, G. R., 1984. A checklist of marine algae of eastern Canada, second revision. Can. J. Bot. 62: 680–704.
Taylor, W. R., 1957. Marine algae of the northeastern coast of North America. 2nd ed. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, 509 pp.
Wilce, R. T., C. W. Schneider, A. V. Quinlan & K. van den Bosch, 1982. The life history and morphology of free-living Pilayella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. (Ectocarpaceae, Ectocarpales) in Nahant Bay, Massachusetts. Phycologia 21: 336–354.
Wollaston, E. M., 1968. Morphology and taxonomy of southern Australian genera of the Crouanieae Schmitz (Ceramiaceae, Rhodophyta). Aust. J. Bot. 16: 217–417.
Womersley, H. B. S., 1979. Southern. Australian species of Polysiphonia Greville (Rhodophyta). Aust. J. Bot. 27: 459–528.
Womersley, H. B. S. & R. E. Norris, 1959. A free-floating marine alga. Nature, Lond. 184: 828.
Wynne, M. J., 1986. A checklist of benthic marine algae of the tropical and subtropical western Atlantic. Can. J. Bot. 64: 2239–2281.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapraun, D.F., Searles, R.B. Planktonic bloom of an introduced species of Polysiphonia (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta) along the coast of North Carolina, USA. Hydrobiologia 204, 269–274 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040244
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040244