Abstract
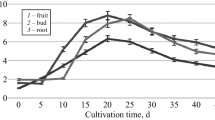
In cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus a rapid accumulation of secondary compounds (tryptamine, indole alkaloids, phenolics) was observed after transfer of the cells into special ‘induction’-media devoid of phosphate and other essential growth factors [11, 14]. The increase of product levels was suppressed in the presence of phosphate which was almost completely taken up from the medium and accumulated by the cells within 48 h after inoculation. The activities of tryptophan decarboxylase (TDC), the first enzyme in indole alkaloid biosynthesis, and of phenyl-alanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), the key enzyme of phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, were influenced differently by phosphate. Whereas the accumulation of phenolics and PAL activity were similarly inhibited by low concentration of phosphate, the medium-induced enhanced activity of TDC was not affected although the product pools were considerably reduced. Some consequences for the regulation of secondary metabolism will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAL:
-
phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- TDC:
-
tryptophan decarboxylase
References
Ames BR, Dubin DT (1960) The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage desoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 23:767–775
Berlin J, Widholm JM (1977) Correlation between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity and phenolic biosynthesis in p-fluorophenylalanine-sensitive and-resistant tobacco and carrot tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 59:550–553
Bieleski RL (1973) Phosphate pools, phosphate transport and phosphate availability. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 24:225–252
Courtois D, Guern J (1980) Temperature response of Catharanthus roseus cells cultivated in liquid medium. Plant Science Lett 17:473–482
Courtois D, Kurkdjian A, Guern J (1980) Tryptamine uptake and accumulation by Catharanthus roseus cells cultivated in liquid medium. Plant Science Lett 18:85–96
Delfel NE (1980) The effect of nutritional factors on alkaloid metabolism in Cephalotaxus harringtonia tissue cultures. Planta medica 39:168–179
Delfel NE, Smith LJ (1980) The importance of culture conditions and medium component interactions on the growth of Cephalotaxus harringtonia tissue cultures. Planta medica 40:237–244
Fujita Y, Hara Y, Suga C, Morimoto T (1981) Production of shikonin derivatives by cell suspension cultures of Lithospermum erythrorhizon. II. A new medium for the production of shikonin derivatives. Plant Cell Reports 1:61–63
Hahlbrock K, Knobloch KH, Kreuzaler F, Potts JRM, Wellmann E (1976) Coordinated induction and subsequent activity changes in two groups of metabolically interrelated enzymes. Light-induced synthesis of flavonoid glycosides in cell suspension cultures of Petroselinum hortense. Eur J Biochem 61:199–206
Knobloch KH (1982) Uptake of phosphate and its effect on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and cinnamoyl putrescines in cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Cell Reports 1:128–130
Knobloch KH, Berlin J (1980) Influence of medium composition on the formation of secondary compounds in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Z Naturforsch 35c:551–556
Knobloch KH, Berlin J (1981) Phosphate mediated regulation of cinnamoyl putrescine biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Planta med 42:167–172
Knobloch KH, Beutnagel G, Berlin J (1981b) Influence of accumulated phosphate on culture growth and formation of cinnamoyl putrescines in medium-induced cell suspension cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Planta 153:582–585
Knobloch KH, Hansen B, Berlin J (1981a) Medium-induced formation of indole alkaloids and concomitant changes of interrelated enzyme activities in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Z Naturforsch 36a:40–43
Knobloch KH, Bast G, Berlin J (1982) Medium-and light-induced formation of serpentine and anthocyanins in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Phytochemistry 21:591–594
Margna U (1977) Control at the level of substrate supply. An alternative in the regulation of phenylpropanoid accumulation in plant cells. Phytochemistry 16:419–426
Martin JF (1977) Control of antibiotic synthesis by phosphate. In: Adv. Biochem. Eng. Vol 6 pp 105–127, Ghose TK, Fiechter A, Blakebrough N, eds, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Tal B, Gressel J, Goldberg J (1982) The effect of medium constituents on growth and diosgenin production of Dioscorea deltoidea cells. Planta medica 44:111–115
Weinberg ED (1974) Secondary metabolism: Control by temperature and inorganic phosphate. Dev Ind Microbiol 15:70–81
Zenk MH, El-Shagi H, Arens H, Stoeckigt J, Weiler EW, Deus B (1977) Formation of the indole alkaloids serpentine and ajmalicine in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. In: Plant Tissue Culture and its Bio-technological Application pp 27–43, Barz W, Reinhard E, Zenk MH, eds, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knobloch, KH., Berlin, J. Influence of phosphate on the formation of the indole alkaloids and phenolic compounds in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus I. Comparison of enzyme activities and product accumulation. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 2, 333–340 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039880
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039880