Abstract
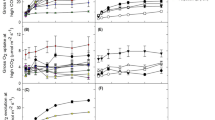
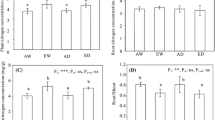
Responses of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPCase) to an elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration were determined along with net CO2 uptake rates for the Crassulacean acid metabolism species Opuntia ficus-indica growing in open-top chambers. During the spring 13 months after planting, total daily net CO2 uptake of basal and first-order daughter cladodes was 28% higher at 720 than at 360 μl CO2 l-1. The enhancement, caused mainly by higher CO2 assimilation during the early part of the night, was also observed during late summer (5 months after planting) and the following winter. The activities of Rubisco and PEPCase measured in vitro were both lower at the elevated CO2 concentration, particularly under the more favorable growth conditions in the spring and late summer. Enzyme activity in second-order daughter cladodes increased with cladode age, becoming maximal at 6 to 10 days. The effect ofelevated CO2 on Rubisco and PEPCase activity declined with decreasing irradiance, especially for Rubisco. Throughout the 13-month observation period, O. ficus-indica thus showed increased CO2 uptake when the atmospheric CO2 concentration was doubled despite lower activities of both carboxylating enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo E, Badilla I and Nobel PS (1983) Water relations, diurnal acidity changes, and productivity of a cultivated cactus, Opuntia ficus-indica. Plant Physiol 72: 775–780
AllenJr LH (1990) Plant responses to rising carbon dioxide and potential interactions with air pollutants. J Environ Quality 19: 15–34
Badger M (1992) Manipulating agricultural plants for a future high CO2 environment. Aust J Bot 40: 421–429
Beer S, Israel A, Drechsler Z and Cohen Y (1990) Photosynthesis in Ulva fasciata. V. evidence for an inorganic carbon concentrating system, and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase CO2 kinetics. Plant Physiol 94: 1542–1546
Besford RT and Hand DW (1989) The effects of CO2 enrichment and nitrogen oxides on some Calvin cycle enzymes and nitrite reductase in glasshouse lettuce. J Exp Bot 40: 329–336
Besford RT, Ludwig LJ and Withers AC (1990) The greenhouse effect: acclimation of tomato plants growing in high CO2, photosynthesis and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase protein. J Exp Bot 41: 925–931
Bowes G (1991) Growth at elevated CO2: photosynthetic responses mediated through Rubisco. Plant Cell Environ 14: 795–806
Bowes G (1993) Facing the inevitable: plants and increasing atmospheric CO2. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44: 309–332
Campbell WJ, AllenJr LH and Bowes G (1988) Effects of CO2 concentration on Rubisco activity, amount, and photosynthesis in soybean leaves. Plant Physiol 88: 1310–1316
Cui M, Miller PM and Nobel PS (1993) CO2 exchange and growth of the Crassulacean acid metabolism plant Opuntia ficus-indica under elevated CO2 in open-top chambers. Plant Physiol 103: 519–524
Cure JD and Acock B (1986) Crop response to carbon dioxide doubling: A literature survey. Agric Forest Meteorol 38: 127–145
Goldstein G, Ortega JKE, Nerd A and Nobel PS (1991) Diel patterns of water potential components for the crassulacean acid metabolism plant Opuntia ficus-indica when well-watered or droughted. Plant Physiol 95: 274–280
Huerta AJ and Ting IP (1988) Effects of various levels of CO2 on the induction of Crassulacean acid metabolism in Portulacaria afra (L) Jacq. Plant Physiol 88: 183–188
Idso SB, Kimball BA, Anderson MG and Szarek SR (1986) Growth response of a succulent plant, Agave vilmoriniana, to elevated CO2. Plant Physiol 80: 796–797
Keeling CD and Whorf TP (1990) Atmospheric CO2 concentrations, Mauna Loa. In: Boden TA, Kanciruk P and Farrel MP (eds) Trends '90: A Compendium of Data on Global Change, pp 8–9. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN
King AW, Emanuel WR and Post WM (1992) Projecting future concentrations of atmospheric CO2 with global carbon cycle models: the importance of simulating historical changes. Environ Management 16: 91–108
Lawlor DW and Mitchell RAC (1991) The effects of increasing CO2 on crop photosynthesis and productivity: A review of field studies. Plant Cell Environ 14: 807–818
Luo Y and Nobel PS (1993) Growth characteristics of newly initiated cladodes of Opuntia ficus-indica as affected by shading, drought and elevated CO2. Physiol Plant 87: 467–474
Nobel PS (1988) Environmental Biology of Agaves and Cacti. Cambridge University Press, New York
Nobel PS and Garcia de Cortázar V (1991) Growth and predicted productivity of Opuntia ficus-indica for current and elevated carbon dioxide. Agron J 83: 224–230
Nobel PS and hartsock TL (1983) Relationships between photosynthetically active radiation, nocturnal acid accumulation, and CO2 uptake for a Crassulacean acid metabolism plant, Opuntia ficus-indica. Physiol Plant 71: 71–75
Nobel PS and Hartsock TL (1986) Short-term and long-term responses of Crassulacean acid metabolism plants to elevated CO2. Plant Physiol 82: 604–606
Osmond CB and Björkman O (1975) Pathways of CO2 fixation in the CAM plant Kalanchoë daigremontiana. II. effects of O2 and CO2 concentration on light and dark CO2 fixation. Aust J Plant Physiol 2: 155–162
Potvin C and Strain BR (1985) Effects of CO2 enrichment and temperature on growth in two C4 weeds, Echinocloa crus-galli and Eleusine indica. Can J Bot 63: 1495–1499
Sage RF and Seemann JR (1993) Regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity in response to reduced light intensity in C4 plants. Plant Physiol 102: 21–28
Sage RF, Sharkey TD and Seemann JR (1989) Acclimation of photosynthesis to elevated CO2 in five C3 species. Plant Physiol 89: 590–596
Smith SD, Strain BR and Sharkey TD (1987) Effects of CO2 enrichment on four Great Basin grasses. Funct Ecol 1: 139–143
Spencer W and Bowes G (1986) Photosynthesis and growth of water hyacinth under CO2 enrichment. Plant Physiol 82: 528–533
Szarek SR, Holthe PA and Ting IP (1987) Minor physiological response to elevated CO2 by the CAM plant Agave vilmoriniana. Plant Physiol 83: 938–940
Ting IP (1985) Crassulacean acid metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 36: 595–622
Van TK, Haller WT and Bowes G (1976) Comparison of the photosynthetic characteristics of three submerged aquatic plants. Plant Physiol 58: 761–768
Von Caemmerer S and Farquhar GD (1984) Effects of partial defoliation, changes of irradiance during growth, short-term water stress and growth at enhanced p(CO2) on the photosynthetic capacity of leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Planta 160: 320–329
Yelle S, BeesonJr RC, Trudel MJ and Gosselin A (1989) Acclimation of two tomato species to high atmospheric CO2. II. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Physiol 90: 1473–1477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Israel, A.A., Nobel, P.S. Activities of carboxylating enzymes in the CAM species Opuntia ficus-indica grown under current and elevated CO2 concentrations. Photosynth Res 40, 223–229 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034772
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034772