Abstract
In this paper we compared the pigment composition, photochemical activity, chloroplast ultrastructure, thylakoid membrane polypeptide composition and ribosomal content of wild-type and seven light-sensitive mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii.
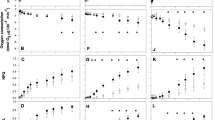
All the mutants had low chlorophyll and carotenoid content compared to wild-type. Mutants lts-30 and lts-135 were also characterized by a complete absence of visible carotenoids, while mutant lts-19 was fully deficient in chlorophylls.
In most mutants, the chloroplast fragment could not carry out any DCIP photoreduction and O2 evolution was also blocked. The PSI/P700/activity was decreased in most cases.
The mutant strains contained mostly single lamellae in their plastids, that is the stacking capacity of the thylakoid membranes was very decreased or fully absent. In most cases the number of lamellae was also very low.
The relative amounts of 70 S ribosomes were decreased in all of the mutants. The thylakoid membranes showed anomalies in the region of 24 000–30 000 dalton polypeptides. The common characteristic for them was the relatively higher amount of the 30 000 dalton polypeptide and considerably decreased level of the 27 000 and 24 000 dalton polypeptides relative to the wild-type. These polypeptides were probably constituents of the chlorophyll-protein complex II which has been suggested to be the light harvesting pigment complex for PSII. The polypeptide of 30 000 daltons is the precursor for the LHCP apoprotein (24 000 dalton protein). It may be that the lighstimulated conversion of this precursor into LHCP apoprotein was blocked in our pigment-deficient mutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPI:
-
Chlorophyll-protein complex I
- PSI:
-
Photosystem I
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- LHCP:
-
Light-harvesting pigment complex
- DCIP:
-
2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol
- RuDPC-ase:
-
Ribulose-1,5-biphosphate-carboxylase
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- LIDS:
-
Lithium dodecyl sulfate
- PAG:
-
Polyacrylamide gel
- TKM buffer:
-
25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.S; 25 mM KCl; 25 mM Mg acetate
References
AndersonJM and LevineRP (1974) Membrane polypeptides of some higher plant chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 333: 378–387.
ApelK and KloppstechK (1978) The plastid membranes of barley Hordeum vulgare light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J biochem 85:581–588.
AvronM (1960) Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 40:257–272.
BennounP, GirardJ and ChuaNH (1977) A uniparental mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii deficient in the chlorophyll-protein complex CPI. Mol Gen Genet 153:343–348.
Bush ET and Hansen DL (1965) Improvement of liquid scintillator composition. Relative efficiencies for three new fluors. In Radioisotope. Sample Measurement Techniques in Medicine and Biology, pp 395–408. Vienna.
ChuaNH and BennounP (1975) Thylakoid membrane polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardii: Wild-type and mutant strains deficient in photosystem II reaction center. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:2175–2179.
ChuaNH, MatlinK and BennounP (1975) A chlorophyll protein complex in lacking photosystem I mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Cell Biol 67:361–377.
DemeterS and KeB (1977) Electrochemical and spectrokinetic evidence for an intermediate electron acceptor in photosystem I. Biochim Biophys Acta 462:770–774.
EytonG and OhadI (1970) Biogenesis of chloroplast membranes VI. Cooperation between cytoplasmic and chloroplast ribosomes in the synthesis of photosynthetic lamella proteins during the greening process in a mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii y-1. J Biol Chem 245:4297–4307.
FairbanksG, StockTL and WallachDFH (1971) Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocytes membrane. Biochemistry 10: 2606–2617.
GirardJ, ChuaNH, BennounP, SchmidtG and DelosmeM (1980) Studies on mutants deficient in the photosystem I reaction centers in Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Current Genetics 2:215–221.
GyurjánI, ErdösG, KeresztesÁ, SchóthBA and SzigetiZ (1980) Photosynthetic functions and structure in pigment-deficient mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Photosynthetica 14:12–16.
Gyurján I, Nagy AH, Popova MA, Erdös G, Paless Gy, Keresztes Á, Szigeti Z and Kovács P (1982) The major polypeptides of chloroplast membranes in non-mendellan yellow mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii (in preparation).
HermannF (1971) Genetic control of pigment-protein complexes I and Ia of the plastid mutant en: alba-1 of Antirrhinum majus. FEBS Lett 19:267–269.
HermannF (1971) Chloroplast lamellar proteins of the plastid mutant en:viridis-1 of Antirrhinum majus having impaired photosystem II. Exp Cell Res 70:452–453.
HooberJK (1970) Sites of synthesis of chloroplast membrane polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardii y-1. J Biol Chem 245:4327–4334.
KanKS and ThornberJP (1976) The light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-protein complex of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant Physiol 57:47–52.
LaemmliVK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–682.
LevineRP and DurhamHA (1973) The polypeptides of stacked and unstacked Chlamydomonas reinhardii ehloroplast membranes and their relation to photosystem II activity. Biochim Biophys Act 325:565–572.
MargulisKG and Kendrick (1968) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem 25:347–362.
NevilleDM (1971) Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem 246:6328–6334.
SagerR and GranickS (1953) Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Ann New York Acad Sci 56:831.
SpreitzerRJ and MetsL (1981) Photosynthesis-deficient mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii with associated light-sensitive phenotypes. Plant Physiol 67:565–569.
StolbovaAV (1975) Genetic analysis of light-sensitive mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. In: Genetic Aspects of Photosynthesis (ed. YuSNasyrov and ZSestak) Dr W Junk, The Hague, 1975, pp 217–223.
ThornberJP and HighkinHR (1974) Composition of the photosynthetic apparatus of normal barley leaves and a mutant lacking chlorophyll b. Eur J Biochem 41: 109–116.
VernonLP and ShowER (1969) Oxidation of 1,5-diphenyl-crabazide as a measure of photosystem 2 activity in subchloroplast fragments. Biochim Biophys Res Commum 36:878–884.
WettsteinDvon (1957) Chlorophyll Totale und der submikroskopische Formwechsel der Plastiden. Exp Cell Res 12:427–506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyurján, I., Nagy, A.H., Frdős, G. et al. Photosynthetic functions and thylakoid membrane polypeptide composition in light-sensitive mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii . Photosynth Res 3, 255–271 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032261
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032261