Abstract
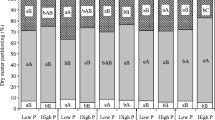
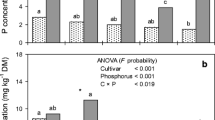
A promising approach for overcoming poor crop yields in phosphorus (P)-deficient soils is to exploit the genetic variation among plants to grow under low P conditions. We examined the P requirements of three mungbean cultivars, T-77, MI-5 and E-72, using four P rates, 0, 30, 60 and 90 mg P kg-1 soil (designated P0, P1, P2 and P3, respectively). Nodulation was highest in T-77, and unlike the other cultivars, nodule numbers were not increased by P application. Similarly, growth of T-77 was the highest, and was not influenced by P rates. In contrast shoot yields of MI-5 and E-72 at P0 were only 76 and 65%, respectively, of the maximum obtained under P application. Nodule dry weight and the amount of N fixed (Ndfa) in each cultivar was enhanced by P application, with T-77 generally giving the lowest response, and accumulating the highest Ndfa. The data suggest a higher P requirement for N2 fixation (especially for T-77) than for growth. All plants increased their P uptake as P rates increased, with T-77 accumulating the highest amount of P at each P level. Differences in the physiological P use efficiency, PPUE (g shoot mg-1 P) among genotypes were generally not significant, neither were there any consistent trends as P rates changed. The ability to absorb P therefore appeared to be more important than PPUE in enhancing growth. We conclude from our data that it is possible by selection to obtain plants capable of good growth and high N2 fixation in soils of low P; cultivar T-77 is a good example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar S M, Afridi M M R K and Khon M M A 1982 Effect of basal nitrogen and phosphorus on yield characteristics of summer moon (Vigna radiata var. T-44). Ind. J. Plant Physiol. 25, 27–31.
Andrew C S 1977 Nutritional restraints on legume symbiosis. In Exploiting the Legume-Rhizobium Symbiosis in Tropical Agriculture. Ed. J MVincent. pp 253–274. University of Hawaii, College of Tropical Agriculture. Hawaii.
Barton C J 1948 Photometric analysis of phosphate rocks. Anal. Chem. 20, 1068–1073.
Bonetti R, Montanheiro M N S and Saito S M T, 1984 The effects of phosphate and soil moisture on the nodulation and growth of Phaseolus vulgaris. J. Agric. Sci. Camb. 103, 95–102.
Chisholm R H and Blair G J 1988 Phosphorus efficiency in pasture species. I. Measures based on total dry weight and P content. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 39, 807–816.
Collins M, Lang D J and Kelling K A 1986 Effects of phosphorus, potassium and sulfur on alfalfa nitrogen fixation under field conditions. Agron. J. 78, 959–963.
Davis M R 1991 The comparative phosphorus requirements of some temperate perennial legumes. Plant and Soil 133, 17–30.
Fiedler R and Proksch G 1975 The determination of nitrogen-15 by emission and mass spectrometry in biochemical analysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 78, 1–62.
Föhse D, Claassen N and Jungk A 1988 Phosphorus efficiency of plants. Plant and Soil 110, 101–109.
Fried M and Middleboe V 1977 Measurement of amount of nitrogen fixed by a legume crop. Plant and Soil 47, 713–715.
Gill M A, Ali N and Nayyar M M 1985 Relative effect of phosphorus combined with potash and Rhizobium phaseoli on the yield of Vigna aureus (mung). J. Agric. Res. 23, 279–282.
Herath H M G and Suraweera D E F 1987 Socio-economic aspects of food legume production in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings: Improved Production and Utilization of Food Legumes in Sri Lanka. Ed. H P MGunasena and H M GHerath. Faculty of Agriculture, University of Peradeniya, Sri Lanka.
Hernandez B S and Focht D D 1985 Effects of phosphorus, calcium and Hup- and Hup+ rhizobia on pigeon pea yields in an infertile tropical soil. Agron. J. 77, 867–871.
Israel D W 1987 Investigation of the role of phosphorus in symbiotic dinitrogen fixation. Plant Physiol. 84, 835–840.
Israel D W and Rufty T W 1988 Influence of phosphorus nutrition on phosphorus and nitrogen utilization efficiencies and associated physiological responses in soybean. Crop Sci. 28, 954–960.
Jakobsen I 1985 The role of phosphorus in nitrogen fixation by young pea plants (Pisum sativum). Physiol. Plant. 64, 190–196.
Mushtaq M, Shah P, Jan S and Sattar A 1986 Effect of different levels of phosphorus and potash on the emergence, plant height and straw yield of mungbean (Vigna radiata (L) Welzcek) Sarhad J. Agric. 2, 467–472.
Ogata S, Adu-Gyamfi J and Fujita K 1988 Effect of phosphorus and pH on dry matter production, dinitrogen fixation and critical phosphorus concentration in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (L) Millsp.), Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 34, 55–64.
Olofintoye J A 1986 Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp) response to different levels of phosphorus and nitrogen in the Guinea savanna of Nigeria. Phil. Agric. 69, 411–418.
Pereira P A A and Bliss F A 1987 Nitrogen fixation and plant growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at different levels of phosphorus availability. Plant and Soil 104, 79–84.
Rennie R J and Kemp G A 1984 15N-determined time course for N2 fixation in two cultivars of field bean. Agron. J. 76, 146–154.
Sanginga N, Danso S K A and Bowen G D 1989 Nodulation and growth response of Allocasuarina and Casuarina species to phosphorus fertilization. Plant and Soil 118, 125–132.
Sanginga N, Bowen G D and Danso S K A 1991 Intraspecific variation in growth and P accumulation of Leucaena leucocephala and Gliricidia sepium as influenced by soil phosphate status Plant and Soil 133, 201–208.
Tewari G P 1965 Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on nodulation in cowpea. Expt. Agric. 1, 257–259.
Thind S S, Rishi A K and Goswami N N 1990 Utilization of applied phosphorus by green gram (Vigna radiata L Wilczek), Bengal gram (Cicer arietinum L.) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) in soils of Delhi. J. Nucl. Agric. Biol. 19, 152–156.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunawardena, S.F.B.N., Danso, S.K.A. & Zapata, F. Phosphorus requirements and nitrogen accumulation by three mungbean (Vigna radiata (L) Welzek) cultivars. Plant Soil 147, 267–274 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029078
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029078