Abstract
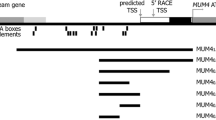
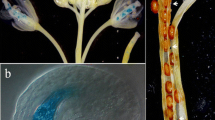
The Brassica napus cDNA clone A9 and the corresponding Arabidopsis thaliana gene have been sequenced. The B. napus cDNA and the A. thaliana gene encode proteins that are 73% identical and are predicted to be 10.3 kDa and 11.6 kDa in size respectively. Fusions of an RNase gene and the reporter gene β-glucuronidase to the A. thaliana A9 promoter demonstrated that in tobacco the A9 promoter is active solely in tapetal cells. Promoter activity is first detectable in anthers prior to sporogenous cell meiosis and ceases during microspore premitotic interphase.
The deduced A9 protein sequence has a pattern of cysteine residues that is present in a superfamily of seed plant proteins which contains seed storage proteins and several protease and α-amylase inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altenbach SB, Pearson KW, Leung FW, Sun SSM: Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding a Brazil nut protein exceptionally rich in methionine. Plant Mol Biol 8: 239–250 (1987).
Bevan MW: Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucl Acids Res 12: 8711–8721 (1984).
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilising the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 (1976).
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O: A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1983).
Draper J, Scott RJ, Armitage P, Walden R: Plant Genetic Transformation and Gene Expression: A Laboratory Manual. Blackwell, Oxford (1988).
Ericson ML, Roedin J, Lenman M, Glimelius K, Josefsson LG, Rask L: Structure of the rapeseed 1.7S storage protein, napin, and its precursor. J Biol Chem 261: 14576–14581 (1986).
Garcia-Maroto F, Marana C, Mena M, Garcia-Olmedo F, Carbonero P: Cloning of cDNA and chromosomal location of genes encoding the three types of subunits of the wheat tetrameric inhibitor of insect α-amylase. Plant Mol Biol 14: 845–853 (1990).
Gayler KR, Kolivas S, Macfarlane AJ, Lilley GG, Baldi M, Blagrove J, Johnson ED: Biosynthesis, cDNA and amino acid sequences of a precursor of conglutin δ, a sulphur-rich protein from Lupinus angustifolius. Plant Mol Biol 15: 879–893 (1990).
Grant I, Beversdorf WD, Peterson RL: A comparative light and electron microscopic study of microspore and tapetal development in male fertile and cytoplasmic male sterile oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Can J Bot 64: 1055–1068 (1986).
Guerineau JF, Woolston S, Brooks L, Mullineaux P: An expression cassette for targeting foreign proteins into chloroplasts. Nucl Acids Res 16: 11380 (1988).
Hartley RW: Barnase and barstar, expression of its cloned inhibitor permits expression of a cloned ribonuclease. J Mol Biol 202: 913–915 (1988).
Higgins DG, Sharp PM: CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Gene 73: 237–244 (1989).
Horovitz A, Serrano L, Avron B, Bycroft M, Fersht AR: Strength and co-operativity of contributions of surface salt bridges to protein stability. J Mol Biol 216: 1031–1044 (1990).
Izhar S, Frankel R: Mechanism of male sterility in Petunia: the relationship between pH, callase activity in the anthers, and the breakdown of the microsporogenesis. Theor Appl Genet 41: 104–108 (1971).
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW: GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6: 3901–3907 (1987).
Joshi CP: An inspection of the domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucl Acids Res 15: 6643–6653 (1987).
Joshi CP: Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucl Acids Res 15: 9627–9640 (1987).
Kamalay JC, Goldberg RB: Organ-specific nuclear RNAs in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 2801–2805 (1984).
Kashlan N, Richardson M: The complete amino acid sequence of a major wheat protein inhibitor of α-amylase. Phytochemistry 20: 1781–1784 (1981).
Koltunow AM, Truettner J, Cox KH, Wallroth M, Goldberg RB: Different temporal and spatial gene expression patterns occur during anther development. Plant Cell 2: 1201–1224 (1990).
Kreis M, Forde BG, Rahman S, Miflin BJ, Shewry PR: Molecular evolution of the seed storage proteins of barley, rye and wheat. J Mol Biol 183: 499–502 (1985).
Lazaro A, Rodriguez-Palenzuela P, Marana C, Carbonero P, Garcia-Olmedo F: Signal peptide homology between the sweet protein thaumatin II and unrelated cereal α-amylase/trypsin inhibitors. FEBS Lett 239: 147–150 (1988).
Lilley GG, Inglis A: Amino acid sequence of conglutin δ, a sulphur-rich seed protein of Lupinus angustifolius L. FEBS Lett 195: 235–241 (1986).
Maeda K, Wakabayashi S, Matsubara H: Disulphide bridges in an α-amylase inhibitor from wheat kernel. J Biochem 94: 865–870 (1983).
Maeda K, Wakabayashi S, Matsubara H: Complete amino acid sequence of an α-amylase inhibitor in wheat kernel (0.19-inhibitor). Biochim Biophys Acta 828: 213–221 (1985).
Mascarenhas JP: The male gametophyte of flowering plants. Plant Cell 1: 657–664 (1989).
Mariani C, DeBeuckeleer M, Truettner J, Leemans J, Goldberg RB. Induction of male sterility in plants by a chimaeric ribonuclease gene. Nature 347: 737–741 (1990).
Mepham RH, Lane GR: Formation and development of the tapetal periplasmodium in Tradescantia bracteata. Protoplasma 68: 175–192 (1969).
Nacken WKF, Huijser P, Saedler H, Sommer H: Molecular analysis of tap2, an anther-specific gene from Antirrhinum majus. FEBS Lett 280: 155–158 (1991).
Odani S, Koide T, Ono T, Ohnishi K: Structural relationship between barley (Hordeum vulgare) trypsin inhibitor and castor-bean (Ricinus communis) storage protein. Biochem J 213: 543–545 (1983).
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ: Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2444–2448 (1988).
Richardson M: The protease inhibitors of plants and micro-organisms. Phytochemistry 16: 159–169 (1977).
Scott R, Dagless E, Hodge R, Paul W, Soufleri I, Draper J: Patterns of gene expression in developing anthers of Brassica napus. Plant Mol Biol 17: 195–207 (1991).
Seurinck J, Truettner J, Goldberg RB: The nucleotide sequence of an anther-specific gene. Nucl Acids Res 18: 3403 (1990).
Sharief FS, Li SS-L: Amino acid sequence of small and large subunits of seed storage protein from Ricinus communis. J Biol Chem 257: 14753–14759 (1982).
Smith AG, Gasser CS, Budelier KA, Fraley RT: Identification and characterisation of stamen- and tapetum-specific genes from tomato. Mol Gen Genet 222: 9–16 (1990).
Vasil IK: Physiology and cytology of anther development. Biol Rev 42: 327–373 (1967).
vonHeijne G: Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur J Biochem 133: 17–21 (1983).
vonHeijne G: Signal sequences, the limits of variation. J Mol Biol 184: 99–105 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, W., Hodge, R., Smartt, S. et al. The isolation and characterisation of the tapetum-specific Arabidopsis thaliana A9 gene. Plant Mol Biol 19, 611–622 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026787
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026787