Abstract
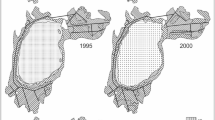
Colonization of submerged macrophytes and changes in species composition were studied in shallow Lake Væng during the first five years (1987–91) following fish manipulation in 1986–1988 and a resultant significant improvement in lake water transparency. No submerged macrophytes were present in the lake from 1981–1986, during which time the summer mean Secchi depth ranged from 0.6 and 0.8 m. From 1987 to 1990, Secchi depth increased from 0.9 m to 1.8 m and macrophyte coverage consequently increased (1 % of the lake area in 1987, 2% in 1988, 50% in 1989, 80% in 1990 and 90% in 1991). At the same time, the macrophytes became taller, and the weedbeds more dense. The macrophytes colonized from the exposed and deeper part of the lake towards the sheltered and more shallow part of the lake, a colonization pattern that was confirmed by transplantation experiments. The delay in colonization of the shallow parts may be caused by waterfowl grazing. The vegetation was initially dominated by Potamogeton crispus L., but there was a gradual change during 1988–1989 and Elodea canadensis Michx became exclusively dominant in 1990–1991.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barko, J. W. & R. M. Smart, 1986. Sediment related mechanisms and growth limitations in submersed macrophytes. Ecology 67: 1328–1340.
Chambers, P. A. & J. Kalff, 1985. Depth distribution and biomass of submersed aquatic macrophyte communities in relation to secchi depth. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 42: 701–709.
Chambers, P. A. & E. E. Prepas, 1988. Underwater spectral attenuation and its effect on the maximum depth of angiosperm colonization. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 45: 1010–1016.
Chambers, P. A., D. H. N. Spence & D. C. Weeks, 1985. Photocontrol of turion formation by P. crispus in the laboratory and natural water. New. Phytologist 99: 183–194.
Danell, K. & K. Sjøberg, 1982. Successional patterns of plants, invertebrates and ducks in a man-made lake. J. appl. Ecol. 19: 395–409.
Dobrev, P. K. & H. Kocev, 1983. Higher water vegetation formation in water basins originating post extraction of inert materials along the river Iskar, Sofia district. Fitologiya 23: 45–62.
Duarte, C. M. & J. Kalff, 1990. Biomass density and the relationship between submerged macrophyte biomass and growth form. Hydrobiologia 196: 17–23.
Ekzertzen, V., 1979. Life in the shore-zones of the Volga reservoirs. Higher aquatic vegetation. In Mordukhai-Boltovskoi, P. (ed.), The river Volga and its life, Hague-Boston-London: 271–294.
Hongve, D., 1973. Vasspest (Elodea canadensis Michx) i Jevnaker. Blyttia 31: 17–18.
Hunt, G. & R. W. Lutz, 1959. Seed production by curlyleaved pondweed and its significance to waterfowl. J. Wildl. Mgmt 23: 405–408.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen, P. Kristensen, B. Riemann, H. J. Jensen, J. P. Muller, O. Sortkjær, J. P. Jensen, K. Christoffersen, S. Bosselmann & E. Dall, 1990. Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic temperate lakes 1: cross analysis of three Danish case studies. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 205–218.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1991. Recovery resilience following a reduction in phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: Duration, governing factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 48: 127–148.
Johnstone, I. M. & P. W. Robinson, 1987. Light level variation in Lake Tutira (New Zealand) after transient sediment inflow and its effect on the submerged macrophytes. New Zealand J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 21: 47–54.
Keddy, P. A., 1983. Shoreline vegetation in Axe Lake, Ontario: effect of exposure. Ecology 64: 331–344.
Krahulec, F., J. Lepsl & O. Rauch, 1987. Vegetation succession on a new lowland reservoir. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 27: 83–93.
Krzyzanek, E., H. Kasza, W. Krzanowski, T. Kuflikowski & G. Pajak, 1986. Succession of communities in the Goczalkowice Dam Reservoir in the period 1955–1982. Arch. Hydrobiol. 106: 21–43.
Kuflikowski, T., 1986. Development and structure of the Goczalkowice Reservoir ecosystem X. Macrophytes. Ekol. Pol. 34: 429–445.
Kunii, H., 1982. Lifecycle and growth of P. crispus in a shallow pond Ojaga-ike. Botanic Magazine Tokyo 95: 109–124.
Lauridsen, T. L., E. Jeppesen, F. Ø. Andersen, submitted. Colonization of submerged macrophytes in shallow fish-manipulated Lake Væng: Impact of sediment composition and waterfowl grazing. Aquat. Bot.
Lillie, R. A., 1990. A quantitative survey of the submersed macrophytes in Devil's Lake, Sauk County, with a historical review of the Eurasian Watermilfoil, Myriophyllum spicatum L. Trans. Wis. Acad. Sci. Arts. Lett. 78: 1–20.
Malicky, G., 1984. Long term and short term vegetation changes in the northeast bay of the Lunzer Untersee. Hydrobiologia 101: 221–230.
McAtee, W. L., 1939. Wildfowl food plants, their value, propagation, and management. Collegiate press, Inc. Ames, Iowa, 141 pp.
Meijer, M. L., M. W. deHaan, A. W. Breukelaar & H. Beuiteveld, 1990. Is reduction of the benthivorous fish an important cause of high transparency following biomanipulation in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 303–315.
Meijer, M. L., E. Jeppesen, E. van Donk, B. Moss, M. Scheffer, E. Lammens, E. van Nes, J. A. van Berkum, G. J. de Jong, B. A. Eaafeng & J. P. Jensen, 1994. Long-term responses to fish-stock reduction in small shallow lakes: interpretation of five-year results of four biomanipulation cases in The Netherlands and Denmark. Hydrobiologia 275–276/Dev. Hydrobiol. 94: 457–466.
Moss, B., 1990. Engineering and biological approaches to the restoration from eutrophication of shallow lakes in which aquatic plant communities are important components. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 367–377.
Moss, B., H. Balls, K. Irvine * J. Stansfield, 1986. Restoration of two lowland lakes by isolation of nutrient-rich water sources with and without removal of sediment. J. appl. Ecol. 23: 391–414.
Nichols, S. A. & B. H. Shaw, 1986. Ecological life histories of the three aquatic nuisance plants, Myriophyllum spicatum, Potamogeton crispus and Elodea canadensis. Hydrobiologia 131: 3–21.
Olofsson, L., 1991. Retablering af undervandsvegetation i Stigsholm Sø. M.Sc.-thesis from National Environmental Research Institute, and Botanical Institute, University of Aarhus, (in Danish) 85 pp.
Ozimek, T., R. D. Gulati & E. van Donk, 1990. Can macrophytes be useful in biomanipulation of lakes? The Lake Zwemlust example. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 399–407.
Prejs, A., 1984. Herbivory by temperate freshwater fishes and its consequences. Envir. Biol. Fish 10: 281–296.
Rogers, R. H. & C. M. Breen, 1980. Growth and reproduction of P. crispus in a South African lake. J. Ecol. 68: 561–571.
Rørslett, B., 1977. Spredning av Vasspest (Elodea canadensis Michx) på Østlandet fram til 1977. Blyttia 35: 61–66.
Rørslett, B., D. Berge & S. W. Johansen, 1985. Mass invasion of Elodea canadensis in a mesotrophic, South Norwegian lake — impact on water quality. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2920–2926.
Rørslett, B. & B. Berge, 1986. Elodea canadensis in Norway in the 1980. Blyttia 44: 119–125.
Sastroutomo, S. S., I. Ikusima, M. Numata & S. Ilzumi, 1979. The importance of turions in the propagation of pondweed. Ecol. Revue 19: 2.
Scheffer, M., 1989. Alternative stable states eutrophic shallow freshwater systems: a minimal model. Hydrobiol. Bull. 23: 73–89.
Scheffer, M., 1990. Multiplicity of stable states in freshwater systems. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 475–486.
Sculthorpe, C. D., 1985. The biology of aquatic vascular plants. Edward Arnold (Publishers) Ltd. London, 610 pp.
Spence, D. H. N., 1982. The zonation of plants in freshwater lakes. Adv. ecol. Res. 12: 37–125.
Søndergaard, M., E. Jeppesen, E. Mortensen, E. Dall, P. Kristensen & O. Sortkjær, 1990. Phytoplankton biomass reduction after planktivorous fish reduction in a shallow eutrophic lake: a combined effect of reduced internal P-loading and increased zooplankton grazing. Hydrobiologia 200–201/Dev. Hydrobiol. 61: 229–240.
von Büsser, P. & P.-A. Tschumi, 1987. Nahrungsökologie der Rotaugen (Ritulus rutilus) im Litoral und and Pelagial des Bielersees. Schweiz. Z. Hydrol. 49: 62–74.
Ward, J. C., J. M. Talbot & I. D. Stewart, 1987. Aboveground biomass and productivity of submerged macrophytes in Lake Alexandrina, New Zealand. N. Zeal. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 21: 215–222.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lauridsen, T.L., Jeppesen, E. & Søndergaard, M. Colonization and succession of submerged macrophytes in shallow Lake Væng during the first five years following fish manipulation. Hydrobiologia 275, 233–242 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026714
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026714