Abstract
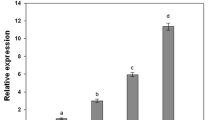
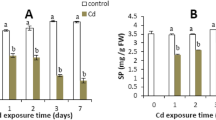
The effects of NaCl on changes in ammonium level and enzyme activities of ammonium assimilation in roots growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings were investigated. NaCl was effective in inhibiting root growth and stimulated the accumulation of ammonium in roots. Accumulation of ammonium in roots preceded inhibition of root growth caused by NaCl. Both effects caused by NaCl are reversible. Exogenous ammonium chloride and methionine sulfoximine (MSO), which caused ammonium accumulation in roots, inhibited root growth of rice seedlings. NaCl decreased glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthase activities in roots, but increased glutamate dehydrogenase activity. The growth inhibition of roots by NaCl or MSO could be reversed by the addition of L-glutamic acid or L-glutamine. The current results suggest that disturbance of ammonium assimilation in roots may be involved in regulating root growth reduction caused by NaCl.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GDH:
-
glutamate dehydrogenase
- GOGAT:
-
glutamate synthase
- GS:
-
glutamine synthetase
- MSO:
-
methionine sulfoximine
References
Cao Y, Glass ADM and Crawford NM (1993) Ammonium inhibition of Arabidopsis root growth can be reversed by potassium and by auxin resistance mutation aux 1, axr1, and axr2. Plant Physiol 102: 983–989
Haynes RJ (1986) Uptake and assimilation of mineral nitrogen by plants. In: Haynes RJ (eds) Mineral Nitrogen in the Plant-Soil System, pp 303–378 San Diego: Academic Press
Joshi G, Dolan T, Gee R and Saltman P (1962) Sodium chloride effect on dark fixation of CO2 by marine and terrestrial plants. Plant Physiol 37: 446–449
Kanamori T, Konishi S and Takahashi E (1972) Inducible formation of glutamate dehydrogenase in rice plant roots by the addition of ammonia to the media. Physiol Plant 26: 1–6
Marschner H (1986) Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. San Diego: Academic Press
Miflin BJ and Lea PJ (1976) The pathway of nitrogen assimilation in plants. Phytochemistry 15: 873–885
Miflin BJ and Lea PJ (1977) Amino acid metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 28: 199–329
Misra N and Dwivedi UN (1990) Nitrogen assimilation in germinating Phaseolus aurens seeds under saline stress. J Plant Physiol 135: 719–724
Oaks A, Stulen J, Jones K, Winspear MJ and Boosel IL (1980) Enzymes of nitrogen assimilation in maize roots. Planta 148: 477–484
Pulich WM (1986) Variation in leaf soluble amino acids and ammonium content in subtropical seagrasses related to salinity. Plant Physiol 80: 283–286
Singh RD and Srivastava HS (1986) Increase in glutamate synthase (NADH) activity in maize seedlings in response to nitrate and ammonium nitrogen. Physiol Plant 66: 413–416
Stewart GR and Rhodes D (1978) Nitrogen metabolism of halophytes III. Enzymes of ammonia assimilation. New Phytol 80: 307–316
Weatherburn MW (1967) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39: 971–974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C.C., Kao, C.H. Disturbed ammonium assimilation is associated with growth inhibition of roots in rice seedlings caused by NaCl. Plant Growth Regul 18, 233–238 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024387
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024387