Summary
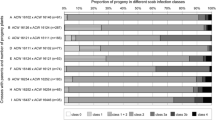
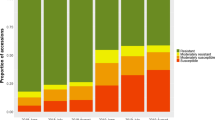
Eight scab-resistant cultivars and selections along with eight commercial apple cultivars were evaluated for powdery mildew resistance in greenhouse and nursery tests. ‘Dayton’, ‘Liberty’, Delicious’ and ‘Tolman Sweet’ were rated moderately resistant to infection in both greenhouse and nursery tests. Segregation of seedlings among 14 progenies for mildew reaction indicated that mildew resistance is polygenically controlled in this material with additive gene effects. Recovery of mildew resistant seedlings from crosses involving a scab-resistant parent(s) suggested that this material can be useful in developing scab- and mildew-resistant apple cultivars. Histological investigations were conducted to describe mildew symptoms of infected leaves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alston, F.H., J.W. Bates, B.C. Hamilton & K. Corkhill, 1978. Transfer of mildew resistance from wild Malus species. Annu. Rpt. E. Malling Res. Sta. for 1988. p. 126.
Alston, F.H. & J.W. Bates, 1979. Glasshouse selection for mildew resistance. Annu. Rpt. E. Malling Res. Sta. for 1978. pp. 135–136.
Anderson, H.W., 1956. Diseases of fruit crops. McCraw Hill, New York. pp. 139–143.
Dayton, D.F., 1977. Genetic immunity to apple mildew incited by Podosphaera leucotricha. Hort. Science 12: 225–226.
de Wald, S.G., 1982. Studies on the feasibility of greenhouse screening as a technique for the early identification of powdery mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha) resistant apple seedlings (Malus domestica) and determining a rating system to evaluate apple selections for field resistance to powdery mildew. M.S. Thesis. Purdue Univ. Indiana.
Gallott, J.C., R.C., Lamb & H.S., Aldwinckle, 1985. Resistance to powdery mildew from some small-fruited Malus cultivars. Hort. Science 20: 1085–1087.
Kirkham, D.S., R.C., Hignett & P.J., Ormerod, 1974. Effects of interrupted light on plant disease. Nature 247: 158–160.
Knight, R.L. & F.H., Alston, 1968. Sources of field immunity to mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha) in apple. Can. J. Gen. and Cytol. 10: 294–298.
Knight, R.L. & F.H. Alston, 1972. Progress at East Malling in breeding for resistance to apple mildew, Podosphaera leucotricha. Annu. Rpt. E. Malling Res. Sta. for 1971. pp. 317–324.
Korban, S.S. & D.F., Dayton, 1983. Evaluation of Malus germplasm for resistance to powdery mildew. Hort. Science 18: 219–220.
Lalancette, N. & K.D., Hickey, 1985. Apple powdery mildew disease progress on sections of shoot growth: an analysis of leaf maturation and fungicide effects. Phytopathol. 75: 130–134.
Misic, P.D., 1969. An investigation of the inheritance of resistance to apple powdery mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha) (Ell. & Ev.). Salm. Hort. Res. 9: 85–92.
Visser, T. & J.J. Verhaegh, 1979. Resistance to powdery mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha) of apple seedlings growing under glasshouse and nursery conditions. Proc. Eucarpia Fruit Breed. Symp., Angers. pp. 111–120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korban, S.S., Riemer, S.E. Genetics and histology of powdery mildew resistance in apple. Euphytica 48, 261–267 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023659
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023659