Abstract
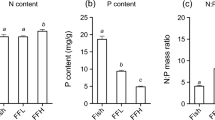
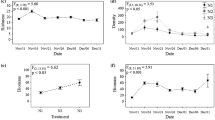
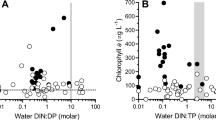
The hypotheses that larval fish density may potentially affect phytoplankton abundance through regulating zooplankton community structure, and that fish effect may also depend on nutrient levels were tested experimentally in ponds with three densities of larval walleye, Stizostedion vitreum (0, 25, and 50 fish m−3), and two fertilizer types (inorganic vs organic fertilizer). A significant negative relationship between larval fish density and large zooplankton abundance was observed despite fertilizer types. Larval walleye significantly reduced the abundances of Daphnia, Bosmina, and Diaptomus but enhanced the abundance of various rotifer species (Brachionus, Polyarthra, and Keratella). When fish predation was excluded, Daphnia became dominant, but Daphnia grazing did not significantly suppress blue-green algae. Clearly, larval fish can be an important regulator for zooplankton community. Algal composition and abundance were affected more by fertilizer type than by fish density. Inorganic fertilizer with a high N:P ratio (20:1) enhanced blue-green algal blooms, while organic fertilizer with a lower N:P ratio (10:1) suppressed the abundance of blue-green algae. This result may be attributed to the high density of blue-green algae at the beginning of the experiment and the fertilizer type. Our data suggest that continuous release of nutrients from suspended organic fertilizer at a low rate may discourage the development of blue-green algae. Nutrient inputs at a low N:P ratio do not necessarily result in the dominance of blue-green algae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, 1989. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC., 1550 pp.
Barica, J., H. Kling & J. Gibson, 1980. Experimental manipulation of algal bloom composition by nitrogen addition. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 1175–1183.
Benndorf, J., H. Schultz, A. Benndorf, R. Unger, E. Penz, H. Kneschke, K. Kossatz, R. Dumke, U. Horning, R. Krupse & S. Reichel, 1988. Food-web manipulation by enhancement of piscivorous fish stocks: long-term effects in the hypertrophic Bautzen Reservoir. Limnologica 19: 97–110.
Benndorf, J., 1990. Conditions for effective biomanipulation: conclusions derived from whole-lake experiments in Europe. Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 187–203.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Carpenter, S. R., J. F. Kitchell & J. R. Hodgson, 1985. Cascading trophic interactions and lake productivity. BioScience 35: 634–639.
Culver, D. A., 1991. Effects of the N:P ratio in fertilizer for fish hatchery ponds. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 1503–1507.
Cushing, D. H., 1983. Are fish larvae too dilute to affect the density of their food organism?. J. Plankton Res. 5: 847–854.
Darley, W. M., 1982. Algal biology: A physiological approach. Blackwell Scientific Publication, Oxford, 168 pp.
Dawidowicz, P., Z. M. Gliwicz & R. D. Gulati, 1988. Can Daphnia prevent a blue-green algal bloom in hypertrophic lakes? A laboratory test. Limnologica 19: 21–26.
Dettmers, J. M. & R. A. Stein, 1992. Food consumption by larval gizzard shad: zooplankton effects and its implications for reservoir communities. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 121: 494–507.
DeVries, D. R. & R. A. Stein, 1992. Complex interactions between fish and zooplankton: quantifying the role of an open-water planktivore. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 49: 1216–1227.
Fulton III, R. S., 1988. Grazing on filamentous algae by herbivorous zooplankton. Freshwat. Biol. 20: 263–271.
Gliwicz, Z. M., 1980. Filtering rates, food size selection and feeding rates in cladocerans. In W. C. Kerfoot (ed.), Evolution and ecology of zooplankton communities. The University Press of New England, Hanover (N.H.); Lond.: 282–291.
Gliwicz, Z. M., 1990. Why do cladocerans fail to control algal blooms? Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 83–97.
Gliwicz, Z. M. & W. Lampert, 1990. Food thresholds in Daphnia species in the absence and presence of blue-green filaments. Ecology 71: 691–702.
Gliwicz, Z. M. & E. Siedlar, 1980. Food size limitation and algae interfering with food collection in Daphnia. Arch. Hydrobiologia 88: 155–177.
Gulati, R. D., 1990. Structural and grazing responses of zooplankton community to biomanipulation of some Dutch water bodies. Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 99–118.
Gulati, R. D. & van Donk, 1989. Biomanipulation in The Netherlands: applications in freshwater ecosystems and estuaries water — an introduction. Hydrobiol. Bull. 23: 1–4.
Helal, H. & D. A. Culver, 1991. N:P ratio and plankton production in fish ponds. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 1508–1511.
Henrikson, L., H. G. Nyman, H. G. Oscarson & J. A. E. Stenson, 1980. Trophic changes without change in external nutrient loading. Hydrobiologia 68: 257–263.
Hrbáček, J., M. Dvořáková, V. Korinek & L. Procházková, 1961. Demonstration effect of fish stock on the species composition of zooplankton and the intensity of metabolism of the whole plankton assemblage. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 14: 162–195.
Jensen, J. P., E. Jeppesen, K. Olrik & P. Kristensen, 1994. Impact of nutrients and physical factors on the shift from cyanobacterial to chlorophyte dominance in shallow Danish lakes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 51: 1692–1699.
Lazzaro, X., 1987. A review of planktivorous fishes: their evolution, feeding behaviors, selectivities, and impacts. Hydrobiologia 146: 97–167.
McQueen, D. W., J. R. Post & E. L. Mills, 1986. Trophic relationship in freshwater pelagic ecosystems. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 43: 1571–1581.
Northcote, T. G., 1988. Fish in the structure and function of freshwater ecosystems: a ‘top-down’ view. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 45: 361–379.
Porter, K. G. & R. McDonough, 1984. The energetic cost of response to blue-green algal filaments by cladocerans. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 365–369.
Qin, J. & D. A. Culver, 1992. The survival and growth of larval walleye, Stizostedion vitreum, and trophic dynamics in fertilized ponds. Aquaculture 108: 257–276.
Qin, J. & D. A. Culver, 1995. Effect of young-of-the-year walleye (Percideae: Stizostedion vitreum) on plankton dynamics and water quality in ponds. Hydrobiologia 297: 217–227.
Qin, J. & S. T. Threlkeld, 1990. Experimental comparison of the effects of benthivorous fish and planktivorous fish on plankton communities. Arch. Hydrobiol. 119: 121–141.
Qin, J., D. A. Culver & N. Yu, 1994. Comparative growth of larval walleye and saugeye, and their impact on zooplankton in experimental ponds. Prog. Fish-Cult. 56: 91–99.
Raisanen, G. A. & R. L. Applegate, 1983. Prey selection of walleye fry in an experimental system. Prog. Fish-Cult. 45: 209–214.
Richardson, W. B. & S. T. Threlkeld, 1992. Complex interactions of multiple aquatic consumers: an experimental mesocosm manipulation. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 50: 29–42.
Sarnelle, O., 1992. Nutrient enrichment and grazer effects on phytoplankton in lakes. Ecology 73: 551–560.
SAS, 1988. SAS User's Guide: Statistics, version 6.03. Cary, NC., 1028 pp.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Shahady, T. D., 1993. Impact of larval Dorosoma predation on Daphnia parvula dynamics. Freshwat. Biol. 30: 279–287.
Shapiro, J. & D. I. Wright, 1984. Lake restoration by manipulation, Round Lake, Minnesota — the first two years. Freshwat. Biol. 14: 371–383.
Smith, V. H., 1983. Low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios favor dominance by blue-green in lake algae phytoplankton. Science 221: 669–671.
Smith, V. H., 1990. Phytoplankton responses to eutrophication in inland waters. In I. Akatsuka (ed.), Introduction to applied phycology. Academic Publishing bv. The Hague, The Netherlands: 231–249.
Sommer, U., 1985. Comparison between steady state and non-steady state competition: experiments with natural phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30: 335–346.
Tátrai, I., G. Tóth, J. E. Ponyi, J. Zlinskzky & V. Istvánovics, 1990. Bottom-up effects of bream (Abramis brama L.) in lake Balaton. Hydrobiologia 200/201 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 61): 167–175.
Tilman, D., R. Kiesling, R. Sterner, S. S. Kilham & F. A. Johnson, 1986. Green, bluegreen and diatom algae: taxonomic differences in competitive ability for phosphorus, silicon and nitrogen. Arch. Hydrobiol. 106: 473–485.
Trimbee, A. M. & E. E. Prepas, 1987. Evaluation of total phosphorus as a predictor of the relative biomass of blue-green algae with emphasis on Alberta lakes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 44: 1337–1342.
Vaga, R. M., 1986. Experimental studies on trophic interactions in the plankton. Ph.D. dissertation. The Ohio State University, Columbus, 256 pp.
Vanni, M. J., C. Luecke, J. F. Kitchell, Y. Allen, J. Temte & J. J. Magnuson, 1991. Effects on lower trophic levels of massive fish mortality. Nature 344: 333–335.
Wetzel, G. R. & G. E. Likens, 1991. Limnological analyses. Springer Verlag, New York, 391 pp.
Winer, B. J., 1991. Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1057 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., Culver, D.A. Effect of larval fish and nutrient enrichment on plankton dynamics in experimental ponds. Hydrobiologia 321, 109–118 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023168
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023168