Abstract
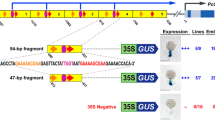
Bean nuclear extracts were used in gel retardation assays and DNase I footprinting experiments to identify a protein factor, designated SBF-1, that specifically interacts with regulatory sequences in the promoter of the bean defense gene CHS15, which encodes the flavonoid biosynthetic enzyme chalcone synthase. SBF-1 binds to three short sequences designated boxes 1, 2 and 3 in the region -326 to -173. This cis-element, which is involved in organ-specific expression in plant development, functions as a transcriptional silencer in electroporated protoplasts derived from undifferentiated suspension-cultured soybean cells. The silencer element activates in trans a co-electroporated CHS15-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene fusion, indicating that the factor acts as a repressor in these cells. SBF-1 binding in vitro is rapid, reversible and sensitive to prior heat or protease treatment. Competitive binding assays show that boxes 1, 2 and 3 interact cooperatively, but that each box can bind the factor independently, with box 3 showing the strongest binding and box 2 the weakest binding. GGTTAA(A/T)(A/T)(A/T), which forms a consensus sequence common to all three boxes, resembles the binding site for the GT-1 factor in light-responsive elements of the pea rbcS-3A gene, which encodes the small subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Binding to the CHS15 -326 to -173 element, and to boxes 1, 2 or 3 individually, is competed by the GT-1 binding sequence of rbcS-3A, but not by a functionally inactive form, and likewise the CHS sequences can compete with authentic GT-1 sites from the rbcS-3A promoter for binding. These data suggest that SBF-1 is identical to, or closely related to, GT-1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford M: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254 (1976).
Choudhary AD, Kessmann H, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Stress responses in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) IV. Expression of defense gene constructs in electroporated suspension cell protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 9: 42–46 (1990).
Cramer CL, Edwards K, Dron M, Liang X, Dildine SL, Bolwell GP, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ, Schuch W: Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene organization and structure. Plant Mol Biol 12: 367–383 (1989).
Dignam JD, Lebovitz RM, Roeder TG: Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucl Acids Res 11: 1475–1489 (1983).
Dron M, Clouse SD, Dixon RA, Lawton MA, Lamb CJ: Glutathione and fungal elicitor regulation of a plant defense gene promoter in electroporated protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6738–6742 (1988).
Garcia-Blanco MA, Clerc RG, Sharp PA: The DNA-binding homeo domain of the Oct-2 protein. Genes Dev 3: 739–745 (1989).
Green PJ, Kay SA, Chua N-H: Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J 9: 2543–2549 (1987).
Green PJ, Yong M-H, Cuozzo M, Kano-Murakami Y, Silverstein P, Chua N-H: Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J 7: 4035–4044 (1988).
Hahlbrock K, Scheel D: Physiology and molecular biology of phenylpropanoid metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40: 347–369 (1989).
Jacobs M, Rubery PH: Naturally occurring auxin transport regulators. Science 241: 346–349 (1988).
Kay SA, Keith B, Shinozaki K, Chye M-L, Chua N-H: The rice phytochrome gene: structure, autoregulated expression, and binding of GT-1 to a conserved site in the 5′ upstream region. Plant Cell 1: 351–360 (1989).
Kuhlemeier C, Cuozzo M, Green PJ, Goyvaerts E, Ward K, Chua N-H: Localization and conditional redundancy of regulatory elements in rbcS-3A, a pea gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 4662–4666 (1988).
Lam E, Chua N-H: GT-1 binding site confers light responsive expression in transgenic tobacco. Science 248: 471–474 (1990).
Lamb CJ, Lawton MA, Dron M, Dixon RA: Signals and transduction mechanisms for activation of plant defenses against microbial attack. Cell 56: 215–224 (1989).
Lawton MA, Lamb CJ: Transcriptional activation of plant defense genes by fungal elicitor, wounding, and infection. Mol Cell Biol 7: 335–341 (1987).
Lawton MA, Dixon RA, Hahlbrock K, Lamb CJ: Elicitor induction of mRNA activity: rapid effects of elicitor on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNA activities in bean cells. Eur J Biochem 130: 131–139 (1983).
Lawton MA, Clouse SD, Lamb CJ: Glutathione-elicited changes in chromatin structure within the promoter of the defense gene chalcone synthase. Plant Cell Rep 8: 561–564 (1990).
Liang X, Dron M, Schmid J, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ: Developmental and environmental regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-β-glucuronidase gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9284–9288 (1989).
Liang X, Dron M, Cramer CL, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ: Differential regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes during plant development and by environmental cues. J Biol Chem 264: 14486–14492 (1989).
Lipphardt S, Brettschneider R, Kreuzaler F, Schell J, Dangl JL: UV-inducible transient expression in parsley protoplasts identifies regulatory cis-elements of a chimeric Antirrhinum majus chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J 7: 4027–4033 (1988).
Long SR: Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell 56: 203–214 (1989).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd Edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Schmid J, Doerner PW, Clouse SD, Dixon RA, Lamb CJ: Developmental and environmental regulation of a bean chalcone synthase promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell 2: 619–631 (1990).
Schulze-Lefert P, Becker-André M, Schulz W, Hahlbrock K, Dangl JL: Functional architecture of the light-responsive chalcone synthase promoter from parsley. Plant Cell 1: 707–714 (1989).
Singh H, Sen R, Baltimore D, Sharp PA: A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature 319: 154–158 (1986).
Sorger PK, Pelham HRB: Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J 6: 3035–3041 (1987).
Stermer BA, Schmid J, Lamb CJ, Dixon RA: Infection and stress activation of bean chalcone synthase promoters in transgenic tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Int: in press (1990).
Strauss F, Varshavsky A: A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutal proximity by DNA folding at the nucleosome. Cell 37: 889–901 (1984).
Treisman R: Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J 6: 2711–2717 (1987).
Willmitzer L, Wagner KG: Isolation of nuclei from tissue-cultured plant cells. Exp Cell Res 135: 69–77 (1981).
Wingate VPM, Lawton MA, Lamb CJ: Glutathione causes a massive and selective induction of plant defense genes. Plant Physiol 87: 206–210 (1988).
Yousaf SI, Carroll AR, Clarke BE: A new and improved method for 3′-end labelling DNA using [α-32]ddATP. Gene 27: 309–313 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawton, M.A., Dean, S.M., Dron, M. et al. Silencer region of a chalcone synthase promoter contains multiple binding sites for a factor, SBF-1, closely related to GT-1. Plant Mol Biol 16, 235–249 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020555
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020555