Abstract
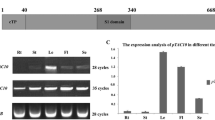
Five chloroplast RNA-binding proteins with consensus sequence-type RNA-binding domains have been isolated from tobacco chloroplasts. Here we report three nuclear genes for similar chloroplast RNA-binding proteins (cp29, cp31 and cp33) from Arabidopsis thaliana. Each of the three genes consists of four exons and three introns and their exon/intron junctions were determined by sequencing respective cDNAs. In vitro import assays showed that all three proteins are located in chloroplasts. The three genes are singly-copy each and the transcription start sites were determined to be 80/82 bp (cp29) and 76/88 bp (cp31) upstream from the translational initiation codons. Northern blot analysis revealed that the three genes are transcribed both in leaves and roots, but the transcript level in leaves is higher than in roots. Phylogenetic analysis of chloroplast RNA-binding proteins so far identified shows that these proteins can be classified into three groups. Tobacco and Arabidopsis have these three types of proteins and structural features of each group are conserved between the two plants, suggesting that they are important for chloroplast functions. Interestingly, cp31 (238 amino acids) shares the identical amino acid sequence from the 30th to the last (238th) residues (including two RNA-binding domains) with the Arabidopsis nucleolin-like ribonucleoprotein, FMV3bp [11]. FMV3bp lacks a transit-peptide and must be located in the nucleus or the cytoplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam SA, Nakagawa T, Swanson MS, Woodruff TK, Dreyfuss G: mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol 6: 2932–2943 (1986).
Barkan A, Miles D, Taylor WC: Chloroplast gene expression in nuclear, photosynthetic mutants of maize. EMBO J 5: 1421–1427 (1986).
Bar-Zvi D, Shagan T, Schindler U, Cashmore AR: RNP-T, a ribonucleoprotein from Arabidopsis thaliana, contains two RNP-80 motifs and a novel acidic repeat arranged in an α-helix conformation. Plant Mol Biol 20: 833–838 (1992).
Brown JWS: A catalogue of splice junction and putative branch point sequences from plant introns. Nucl Acids Res 14: 9549–9559 (1986).
Burd CG, Swanson MS, Görlach M, Dreyfuss G: Primary structures of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, B1, and C2 proteins: a diversity of RNA-binding proteins is generated by small peptide inserts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9788–9792 (1989).
Castresana C, Staneloni R, Malik VS, Cashmore AR: Molecular characterization of two clusters of genes encoding the type I CAB polypeptides of PSII in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Plant Mol Biol 10: 117–126 (1987).
Chang C, Meyerowitz EM: Molecular cloning and DNA sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 1408–1412 (1986).
Cook WB, Walker JC: Identification of a maize nucleic acid-binding protein (NBP) belonging to a family of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins. Nucl Acids Res 20: 359–364 (1992).
Deng XW, Gruissem W: Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell 49: 379–387 (1987).
de Vries S, Hoge H, Bisseling T: Isolation of total and polysomal RNA from plant tissues. In: Gelvin SB, Schilperoort (eds) Plant Molecular Biology Manual B6: pp. 1–13. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1988).
Didier DK, Klee HJ: Identification of an Arabidopsis DNA-binding protein with homology to nucleolin. Plant Mol Biol 18: 977–979 (1992).
Dreyfuss G, Matunis MJ, Piñol-Roma S, Burd CG: hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem 62: 289–321 (1993).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1983).
Fu XD, Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science 256: 535–538 (1992).
Gamble PE, Mullet JE: Blue light regulates the accumulation of two psbD-psbC transcripts in barley chloroplasts. EMBO J 8: 2785–2794 (1989).
Ge H, Zuo P, Manley JL: Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell 66: 373–382 (1991).
Hiratsuka J, Shimada H, Whittier R, Ishibashi T, Sakamoto M, Mori M, Kondo C, Honji Y, Sun CR, Meng BY, Li Y, Kanno A, Nishizawa Y, Hirai A, Shinozaki K, Sugiura M: The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular re-combination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet 217: 185–194 (1989).
Keegstra K, Olsen LJ, Theg SM: Chloroplastic precursors and their transport across the envelope membranes. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40: 471–501 (1989).
Kenan DJ, Query CC, Keene JD: RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci 16: 214–220 (1991).
Klee HJ, Muskopf YM, Gasser CS: Cloning of an Arabidopsis thaliana gene encoding 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase: sequence analysis and manipulation to obtain glyphosate-tolerant plants. Mol Gen Genet 210: 437–442 (1987).
Krainer AR, Mayeda A, Kozak D, Binns G: Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell 66: 383–394 (1991).
Kuchka MR, Goldschmidt-Clermont M, van Dillewijn J, Rochaix JD: Mutation at the Chlamydomonas nuclear NAC2 locus specifically affects stability of the chloroplast psbD transcript encoding polypeptide D2 of PS II. Cell 58: 869–876 (1989).
Li Y, Sugiura M: Three distinct ribonucleoproteins from tobacco chloroplasts: each contains a unique amino terminal acidic domain and two ribonucleoprotein consensus motifs. EMBO J 9: 3059–3066 (1990).
Li Y, Sugiura M: Nucleic acid-binding specificities of tobacco chloroplast ribonucleoproteins. Nucl Acids Res 19: 2893–2896 (1991).
Li Y, Ye L, Sugita M, Sugiura M: Tobacco nuclear gene for the 31 kd chloroplast ribonucleoprotein: genomic organization, sequence analysis and expression. Nucl Acids Res 19: 2987–2991 (1991).
Li Y, Nagayoshi S, Sugita M, Sugiura M: Structure and expression of the tobacco nuclear gene encoding the 33 kDa chloroplast ribonucleoprotein. Mol Gen Genet 239: 304–309 (1993).
Margilus: Symbiosis in Cell Evolution: Life and its Environment in the Early Earth. Freeman, San Francisco (1981).
Mieszczak M, Klahre U, Levy JH, Goodall GJ, Filipowicz W: Multiple plant RNA-binding proteins identified by PCR: expression of cDNAs encoding RNA-binding proteins targeted to chloroplasts in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Mol Gen Genet 234: 390–400 (1992).
Mullet JE, Klein RR: Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J 6: 1571–1579 (1987).
Murray MG, Thompson WF: Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8: 4321–4325 (1980).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York (1989).
Schuster G, Gruissem W: Chloroplast mRNA 3′ end processing requires a nuclear-encoded RNA-binding protein. EMBO J 10: 1493–1502 (1991).
Sieburth LE, Berry-Lowe S, Schmidt GW: Chloroplast RNA stability in Chlamydomonas: rapid degradation of psbB and psbC transcripts in two nuclear mutants. Plant Cell 3: 175–189 (1991).
Sugiura M: Transcript processing in plastid: trimming, cutting, splicing. In: Bogorad L, Vasil IK (eds) The Molecular Biology of Plastids, pp. 125–137. Academic Press, San Diego (1991).
Von Heijne G, Steppuhn J, Herrmann RG: Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem 180: 535–545 (1989).
Ye L, Li Y, Fukami-Kobayashi K, Go M, Konishi T, Watanabe A, Sugiura M: Diversity of a ribonucleoprotein family in tobacco chloroplasts: two new chloroplast ribonucleoproteins and a phylogenetic tree of ten chloroplast RNA-binding domains. Nucl Acids Res 19: 6485–6490 (1991).
Zamore PD, Patton JG, Green MR: Cloning and domain structure of the mammalian splicing factor U2AF. Nature 355: 609–614 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohta, M., Sugita, M. & Sugiura, M. Three types of nuclear genes encoding chloroplast RNA-binding proteins (cp29, cp31 and cp33) are present in Arabidopsis thaliana: presence of cp31 in chloroplasts and its homologue in nuclei/cytoplasms. Plant Mol Biol 27, 529–539 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019319
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019319