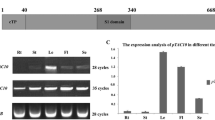
Abstract
Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RPI) catalyses the interconversion of ribose-5-phosphate and ribulose-5-phosphate in the reductive and oxidative pentose phosphate pathways in plants. RPI from spinach chloroplasts was purified and microsequenced. Via PCR with degenerate primers designed against microsequenced peptides, a hybridisation probe was obtained and used to isolate several cDNA clones which encode RPI. The nuclear-encoded 239 amino acid mature RPI subunit has a predicted size of 25.3 kDa and is translated as a cytosolic precursor possessing a 50 amino acid transit peptide. The processing site of the transit peptide was identified from protein sequence data. Spinach leaves possess only one type of homodimeric RPI enzyme which is localized in chloroplasts and is encoded by a single nuclear gene. Molecular characterization of RPI supports the view that a single amphibolic RPI enzyme functions in the oxidative and reductive pentose phosphate pathways of spinach plastids.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RPI:
-
ribose-5-phosphate isomerase
- OPPP:
-
oxidative pentose phosphate pathway
- CNBr:
-
cyanogen bromide
- R5P:
-
ribose-5-phosphate
- Ru5P:
-
ribulose-5-phosphate
References
Anderson LE: Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. III. Pea leaf ribose 5-phosphate isomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta 235: 507–512 (1971).
Anderson LE: Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase and ribulose-5-phosphate kinase show apparent specificity for a specific ribulose 5-phosphate species. FEBS Lett 212: 45–48 (1987).
Apel TW, Scherer A, Adachi T, Auch D, Ayane M, Reth M: The ribose-5-phosphate isomerase-encoding gene is located immediately downstream from that encoding murine immunoglobulin κ. Gene 156: 191–197 (1995).
Bernacchia G, Schwall G, Lottspeich F, Salamini F, Bartels D: The transketolase gene family of the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum: differential expression during the rehydration phase. EMBO J 14: 610–618 (1995).
Bowien B, Bednarski R, Kusian B, Windhövel U, Freter A, Schäferjohann J, Yoo J-G: Genetic regulation of CO2 assimilation in chemoautotrophs. In: Murrel JC, Kelley DP (eds) Microbial Growth on C1 Compounds, pp. 481–491. Intercept Scientific, Andover, UK (1993).
Brinkmann H, Martin W: Higher plant chloroplast and cytosolic 3-phosphoglycerate kinases: a case of endosymbiotic gene replacement. Plant Mol Biol 30: 65–75 (1996).
Chao S, Raines CA, Longstaff M, Sharp PJ, Gale MD, Dyer TA: Chromosomal location and copy number in wheat and some of its close relatives of genes for enzymes involved in photosynthesis. Mol Gen Genet 218: 423–430 (1989).
Chen J-H, Gibson JL, McCue LA, Tabita FR: Identification, expression, and deduced primary structure of transketolase and other enzymes encoded within the form II carbon dioxide fixation operon of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biol Chem 266: 20447–20452 (1991).
Coruzzi G, Broglie R, Edwards C, Chua NH: Tissue-specific and light-regulated expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. EMBO J 3: 1671–1679 (1984).
DeRocher EJ, Quigley F, Mache R, Bohnert HJ: The six genes of the Rubisco small subunit multigene family from Mesembryanthemum crystallinum, a facultative CAM plant. Mol Gen Genet 239: 450–462 (1993).
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O: A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1984).
Eckerskorn C, Lottspeich F: Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by gel electrophoresis after tryptic digestion in polyacrylamide matrix. Chromatographia 28: 92–94 (1989).
Edman P, Begg G: A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem 1: 80–91 (1967).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 137: 266–267 (1984).
Felsenstein J: PHYLIP: Phylogeny Inference Package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5: 164–166 (1989).
Geiger DR, Servaites JC: Diurnal regulation of photosynthetic carbon metabolism in C3 plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 45: 235–256 (1994).
Gibson JL, Falcone DL, Tabita FR: Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis and expression of genes endoded within the form I CO2 fixation operon of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Biol Chem 266: 14646–14653 (1991).
Gibson JL, Tabita FR: Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of CbbR, a positive regulator of the Calvin cycle operons of Rhodobacter sphaeroides: J Bact 175: 5778–5784.
Gontero B, Cardenas ML, Ricard J: A functional five-enzyme complex of chloroplasts involved in the Calvin cycle. Eur J Biochem 173: 437–443 (1988).
Graeve K, von Schaewen A, Scheibe R: Purification, characterization, and cDNA sequence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant J 5: 353–361 (1994).
Heber U, Hallier UW, Hudson MA: Untersuchungen zur intrazellulären Verteilung von Enzymen und Substraten in der Blattzelle. II. Lokalisation von Enzymen des reduktiven und dem oxidativen Pentosephosphat-Zyklus in den Chloroplasten und Permeabilität der Chloroplasten-Membran gegenüber Metaboliten. Z Naturforsch 22b: 1200–1215 (1967).
Henze K, Badr A, Wettern M, Cerff R, Martin W: A nuclear gene of eubacterial origin in Euglena gracilis reflects cryptic endosymbioses during protist evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 9122–9126 (1995).
Henze K, Schnarrenberger C, Kellermann J, Martin W: Chloroplast and cytosolic triosephosphate isomerase from spinach: purification, microsequencing and cDNA sequence of the chloroplast enzyme. Plant Mol Biol 26: 1961–1973 (1994).
Hove-Jensen B, Maigaard M: Escherichia coli rpiA gene encoding ribose phosphate isomerase A. J Bact 175: 5628–5635 (1993).
Jansson S, Meyer-Gauen G, Cerff R, Martin W: Nucleotide distribution in gymnosperm nuclear sequences suggest a model for GC-content change in land plant nuclear genomes. J Mol Evol 39: 34–46 (1994).
Jensen RA: The shikimate/arogenate pathway: Link between carbohydrate metabolism and secondary metabolism. Physiol Plant 66: 164–168 (1985).
Kumada Y, Benson DR, Hillemann D, Hosted TJ, Rochefort DA, Thompson CJ, Wohlleben W, Tateno Y: Evolution of the glutamin synthase gene, one of the oldest existing and functioning genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 3009–3013 (1993).
Latzko E, Gibbs M: Distribution and activity of enzymes of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle in spinach leaves and in chloroplasts isolated by different methods. Z Pflanzenphysiol 59: 184–194 (1968).
Longstaff M, Raines CA, McMorrow E, Bradbeer JW, Dyer TA: Wheat phosphoglycerate kinase: evidence for recombination between the chloroplastic and cytosolic enzymes. Nucl Acids Res 17: 6569–6580 (1989).
Martin W, Cerff R: Prokaryotic features of a nucleus encoded enzyme: cDNA sequences for chloroplast and cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases from mustard (Sinapis alba). Eur J Biochem 159: 323–331 (1986).
Milanez S, Mural RJ: Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding the mature form of phosphoribulokinase from spinach. Gene 66: 55–63 (1988).
Murray NE: Phage lambda and molecular cloning. In: Hendrix RW (ed) Lambda II, pp. 395–432. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1983).
Nowitzki U, Wyrich R, Westhoff P, Henze K, Schnarrenberger C, Martin W: Cloning of the amphibolic Calvin cycle/OPPP enzyme D-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase (E.C. 5.1.3.1) from spinach chloroplasts: functional and evolutionary aspects. Plant Mol Biol 29: 1279–1291 (1995).
Pelzer-Reith B, Penger A, Schnarrenberger C: Plant aldolase: cDNA and deduced amino-acid sequence of the chloroplast and cytosol enzyme from spinach. Plant Mol Biol 21: 331–340 (1993).
Raines CA, Lloyd JC, Willingham NM, Potts S, Dyer TA: cDNA and gene sequences of wheat chloroplast sedulose-1,7-bisphosphatase reveal homology with fructose-1,6-bisphosphatases. Eur J Biochem 205: 1053–1059 (1992).
Rutner AC: Spinach 5-phosphoribose isomerase. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry 9: 178–184 (1970).
Saines JK, Harris GC: The association of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase with phosphoriboisomerase and phosphoribulokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 139: 947–954 (1986).
Saitou N, Nei M: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4: 406–425 (1987).
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Schmidt M, Svendsen Ib, Feierabend J: Analysis of the primary structure of the chloroplast isozyme of triosephosphate isomerase from rye leaves by protein and cDNA sequencing indicates a eukaryotic origin of its gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1261: 257–264 (1995).
Schnarrenberger C, Flechner A, Martin W: Enzymatic evidence indicating a complete oxidative pentose phosphate in the chloroplasts and an incomplete pathway in the cytosol of spinach leaves. Plant Physiol 108: 609–614 (1995).
Sharkey TD, Socias X, Loreto F: CO2 effects on photosynthetic and product synthesis and feedback. In: Alscher GC, Wellburn AR (eds) Plant Responses to the Gaseous Environment, pp. 55–78. Chapman and Hall, London (1994).
Skrukrud CL, Anderson LE: Chloroplast phosphoribulokinase associates with yeast phosphoriboisomerase in the presence of substrate. FEBS Lett 280: 259–261 (1991).
Süss K-H, Arkona C, Manteuffel R, Adler K: Calvin cycle multienzyme complexes are bound to chloroplast thylakoid membranes of higher plants in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5514–5518 (1993).
Tabita FR, Gibson JL, Falcone DL, Wang X, Li L-A, Read BA, Terlesky KC, Paoli GC: Current studies on the molecular biology and biochemistry of CO2 fixation in phototrophic bacteria. In: Murrel JC, Kelley DP (eds) Microbial Growth on C1 Compounds, pp. 469–479. Intercept Scientific, Andover, UK (1993).
Tumer NE, Clark WG, Tabor GJ, Hironaka CM, Fraley RT, Shah DM: The genes encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase are expressed differentially in petunia leaves. Nucl Acids Res 14: 3325–3342 (1986).
Wolter F, Fritz C, Willmitzer L, Schell J, Schreier P: rbcS genes in Solanum tuberosum: conservation of transit peptide and exon shuffling during evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 846–850 (1988).
Wood T: The Pentose Phosphate Pathway. Academic Pres, New York (1985).
Woodrow IE, Berry JA: Enzymatic regulation of photosynthetic CO2 fixation in C3 plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 39: 533–594 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, W., Henze, K., Kellermann, J. et al. Microsequecing and cDNA cloning of the Calvin cycle/OPPP enzyme ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.6) from spinach chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 30, 795–805 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019012