Abstract
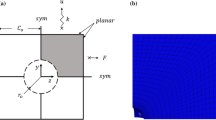
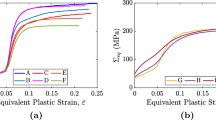
The influence of void nucleation occurring during the deformation history on shear localization is investigated by employing a constitutive model of a rate independent porous plastic solid. Both plastic strain controlled and stress controlled nucleation processes are simulated. Two deformation histories are considered, one corresponding to uniaxial tension and the other to plane strain tension. The enhanced triaxiality at the center of a neck is simulated by application of Bridgman's solution for the stress and deformation state at the minimum section of a necked bar. The destabilizing effect that arises when void nucleation is stress controlled and nucleation occurs over a narrow range of stress is illustrated. Results are also presented employing parameter values representative of spheroidized carbon steels employed in a recent experimental study carried out by Fisher [23] and the predictions of the model are discussed in light of the experimental observations.
Résumé
On étudie l'influence de la nucléation de lacunes qui survient au cours de la déformation dans les zones où se produit un cisaillement, en recourant à un modèle constitutif représentant un solide plastique poreux dont les caractéristiques sont indépendantes de la vitesse. On simule à la fois les processus de nucléation sous déformation plastique contrôlée et sous contrainte contrôlée. On considère deux histoires de déformations, l'une correspondant à une contrainte uniaxiale et l'autre à une contrainte appliquée en état plan de déformation. La triaxialité créée au centre d'un rétrécissement est simulée par l'application d'une solution de Bridgman pour déterminer la contrainte et l'état de déformation à la section minimum d'une barre rétrécie. On illustre l'effet déstabilisant qui se produit lorsque la nucléation de lacunes se trouve contrôlée par la tension et qu'elle survient sur une bande étroite de contraintes. Les résultats sont également présentés en recourant à des valeurs paramétriques représentatives pour les aciers au carbone utilisés dans une étude expérimentale récente effectuée par Fisher (23), et l'on discute les prédictions du modèle à la lumière des observations expérimentales.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Rice, in Proceedings of the 14th International Congress on Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Delft, North-Holland, editor W.T. Koiter, Vol. 1 (1976) 207–220.
A. Needleman and J.R. Rice, in Mechanics of Sheet Metal Forming, editors D.P. Koistinen and N.-M. Wang, Plenum Publishing Co. (1978) 237–265.
C.A. Berg, in Inelastic Behavior of Solids, editors M.F. Kanninen et al., McGraw-Hill, New York (1970) 171–209.
A.L. Gurson, Plastic Flow and Fracture Behavior of Ductile Materials Incorporating Void Nucleation, Growth and Interaction, Ph.D. Thesis, Brown University (1975).
A.L. Gurson, Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, Transactions of theASME 99 (1977) 2–15.
J. Hadamard, Lecons sur la Propagation des Ondes et les Equations de L'Hydrodynamique, Paris (1903).
R. Hill, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 10 (1962) 1–16.
T.Y. Thomas, Plastic Flow and Fracture in Solids, Academic Press (1961).
J. Mandel, in Rheology and Soil Mechanics, editors J. Kravtchenko and P.M. Sirieys, Springer-Verlag (1966) 58–68.
H. Yamamoto, International Journal of Fracture 11 (1978) 347–365.
P.W. Bridgman, Studies in Large Plastic Flow and Fracture, McGraw-Hill (1952).
J. Gurland, Acta Metallurgica 20 (1972) 735–741.
S.H. Goods and L.M. Brown, Acta Metallurgica 27 (1979) 1–15.
A.S. Argon, J. Im and A. Needleman, Metallurgical Transactions, 6A (1975) 815–824.
A.S. Argon, J. Im and R. Safoglu, Metallurgical Transactions, 6A (1975) 825–838.
A.S. Argon and J. Im, Metallurgical Transactions, 6A (1975) 839–851.
C.C. Chu and A. Needleman, Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology 102 (1980) 249–256.
V. Tvergaard, International Journal of Fracture 17 (1981) 389–407.
V. Tvergaard, On Localization in Ductile Materials Containing Spherical Voids, The Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, DCAMM Report 181 (1980).
J.F.W. Bishop and R. Hill, Philosophical Magazine 42 (1951) 414–427.
A.R. Rosenfield, Metallurgical Reviews 13 (1968) 29–40.
G.H. LeRoy, Large Scale Plastic Deformation and Fracture for Multiaxial Stress States, Ph.D. Thesis, McMaster University (1978).
J.R. Fisher, Void Nucleation in Spheroidized Steels during Tensile Deformation, Ph.D. Thesis, Brown University (1980).
J.W. Rudnicki and J.R. Rice, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 23 (1975) 371–394.
J.R. Rice and J.W. Rudnicki, International Journal of Solids and Structures 16 (1980) 597–605.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saje, M., Pan, J. & Needleman, A. Void nucleation effects on shear localization in porous plastic solids. Int J Fract 19, 163–182 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017128
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017128