Abstract
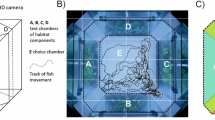
The effects of a submerged macrophyte (Potamogeton pectinatus), turbidity (produced by 50 mg l−1 kaolin), and their combination on the feeding rate of young razor fish (Pelecus cultratus (L.)) were studied in the laboratory. Young razor fish showed preference for Copepoda in most of the simulated habitats. Razor fish fed more efficiently in the absence of any environmental structure, but the more structured habitats, 3 g wet wt l−1 of simulated submerged macrophyte and turbidity combined with vegetation, had a negative impact on food consumption rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, O., 1984. Optimal foraging by largemouth bass in the structured environments. Ecology 65: 851–861.
Berg, L. & T. G. Northcote, 1985. Changes in territorial, gill-flaring, and feeding behavior in juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) following short term pulses of suspended sediment. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 42: 1410–1417.
Boehlert, G. W. & J. B. Morgan, 1985. Turbidity enhances feeding abilities of larval Pacific herring, Clupeus harengus pallasi. Hydrobiologia 123: 161–170.
Breitburg, D. L., 1988. Effects of turbidity on prey consumption by stripped bass larvae. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 117: 72–77.
Carvalho, M. L., 1984. Influence of predation by fish and water turbidity on a Daphnia gessneri population in an Amazonian floodplain lake, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 113: 243–247.
Crowder, L. B. & W. E. Cooper, 1979. Structural complexity and fish-prey interactions in ponds: a point of view. In D. L. Johnson & R. F. Carline (eds), Response of Fish to Habitat Structure in Standing Water, North Central Division, American Fisheries Society, Special Publication 6: 1–10.
Diehl, S., 1988. Foraging efficiency of three freshwater fishes: effects of structural complexity and light. Oikos 53: 207–214.
Herzig, A., 1979. The zooplankton of the open lake. In: H. Löffler (ed. ), Neusiedlersee: The Limnology of a Shallow Lake in Central Europe. Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 281–335.
Herzig, A., 1980. Effects of food and competition in the plankton community of a shallow lake (Neusiedlersee, Austria). In M. Dokulil, H. Metz & D. Jewson (eds), Dev. Hydrobiol. 3, Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague: 45–51.
Herzig, A., 1984. Temperature and life cycle strategies of Diaphanosoma brachyurum: an experimental study on development, growth, and survival. Arch. Hydrobiol. 101: 143–178.
Herzig, A., 1987. The analysis of planktonic rotifer populations: A plea for long-term investigations. Hydrobiologia 147: 163–180.
Kotrschal, K., R. Brandstatter, A. Gomahr, H. Junger, M. Palzenberger & M. Zaunreiter, 1991. Brain and sensory systems. In I. J. Winfield & J. S. Nelson (eds), Cyprinid fishes, Chapman & Hall: 284–329.
Matthews, W. J., 1984. Influence of turbid inflows on vertical distribution of larval shad and freshwater drum. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 113: 192–198.
Montgomery, I. C. & I. A. MacDonald, 1987. Sensory tuning of lateral line receptors in Antarctic fish to the movement of planktonic prey. Science, 235: 195–196.
Newcombe, C. P. & D. D. MacDonald, 1991. Effects of suspended sediments on aquatic ecosystems. North am. J. Fish. Mgmt 11: 72–82.
O'Brien, W. J., 1987. Planktivory by freshwater fish: thrust and parry in the pelagia. In W. C. Kerfoot & A. Sih (eds), Predation. Univ. Press of New England, Hanover: 3–16.
Russo, A. R., 1987. Role of habitat complexity in mediating predation by the gray damselfish Abudefduf sordidus on epyphytal amphipods. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 36: 101–107.
Savino, J. F. & R. A. Stein, 1982. Predator-prey interaction between largemouth bass and bluegills as influenced by simulated, submerged vegetation. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 111: 255–266.
Scholtz, S., M. T. Seaman & J. H. Pieterse, 1988. Effects of turbidity on life history parameters of two species of Daphnia. Freshwat. Biol. 2: 177–184.
Townsend, C. R. & I. J. Winfield, 1985. The application of optimal foraging theory to feeding behaviour in fish. In P. Tytler & P. Calow (eds), Fish Energetics: New Perspectives, Croom Helm, London: 67–98.
Werner, E. E., J. F. Gilliam, D. J. Hall & G. G. Mittelbach, 1983. An experimental test of the effects of predation risk on habitat use in fish. Ecology 64: 1540–1548.
Winfield, I. J., 1986. The influence of simulated aquatic macrophytes on the zooplankton consumption rate of juvenile roach, Rutilus rutilus, rudd, Scardinius erythrophthalmus, and perch, Perca fiuviatilis. J. Fish Biol. 29: 37–48.
Wright, D.I. & J. O'Brien, 1984. Model analysis of the feeding ecology of a freshwater planktivorous fish. Am. Ass. Advancement Sci. Sel. Symp. 85: 243–267.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tátrai, I., Herzig, A. Effect of habitat structure on the feeding efficiency of young stages of razor fish (Pelecus cultratus (L.)): an experimental approach. Hydrobiologia 299, 75–81 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016887
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016887