Abstract
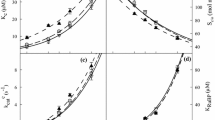
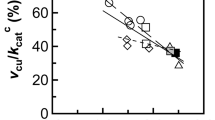
Modulation of the activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) in low light and darkness was measured in A) 25 genotypes from the four cultivated species of Phaseolus (P. vulgaris, P. acutifolius, P. lunatus and P. coccineus), B) 8 non-cultivated Phaseolus species, and C) the related species Macroptileum atropurpureum. The activity ratio of Rubisco (the ratio of initial and total Rubisco activities, which reflects Rubisco carbamylation), and the molar activity of fully-activated Rubisco (which primarily reflects the inhibition of Rubisco activity by carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate, CA1P) were assayed in leaves from the cultivated species sampled at midday in full sunlight, in low light at dusk (60 to 100 μmol photons m-2s-1), and after at least 4 h in darkness. Dark inhibition of Rubisco molar activity was compared in both cultivated and non-cultivated species. In all cultivated genotypes, a significant reduction of the activity ratio of Rubisco was measured in leaves sampled at low light; however, the molar activity of fully activated Rubisco was not greatly reduced in these low light samples. In darkened leaves, molar activities substantially declined in most Phaseolus species with 11 of 13 exhibiting greater than 60% reduction. In P. vulgaris, the reduction of molar activity was extensive (greater than 69%) in all genotypes studied, which included wild progenitors as well as ancient and advanced cultivars. These results indicate that at low light late in the day, modulation of Rubisco activity is primarily through changes in carbamylation state, with CA1P playing a more limited role. By contrast in the dark, binding of CA1P dominates the modulation of Rubisco activity in Phaseolus in a pattern that appears to be conserved within a species, but can vary significantly between species within a genus. The degree of CA1P inhibition in Phaseolus was associated with phylogenetic affinities within the genus, as the species with extensive dark-inhibition of Rubisco activity tended to be more closely related to each other than to species with reduced inhibition of Rubisco activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA1P:
-
carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate
- CABP:
-
carboxyarabinitol bisphosphate
- PFD:
-
photon flux density between 400 and 700 nm
- Rubisco:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
References
Bowes G, Rowland-Bamford A and AllenJr LH (1990) Regulation of Rubisco activity by carboxyarabinitol phosphate and elevated atmospheric CO2 in rice and soybean cultivars. In: Baltscheffsky M (ed) Current Research in Photosynthesis, Vol 3, pp 399–402. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Butz ND and Sharkey TD (1989) Activity ratios of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase accurately reflect carbamylation ratios. Plant Physiol 89: 735–739
Collatz GJ, Badger MR, Smith C and Berry JA (1979) A radioimmune assay for RuP2 carboxylase protein. Carnegie Inst Washington Yrbk 78: 171–175
Debouck DG (1988) Phaseolus germplasm exploration. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic Resources of Phaseolus Beans, pp 3–29. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Delgado-Salinas AO (1985) Systematics of the genus Phaseolus (Leguminosae) in north and central america. PhD Thesis, University of Texas, Austin
Delgado-Salinas A, Brauneau N and Doyle JA (1993) Chloroplast phylogenetic studies of new world Phaseolineae (Leguminosae: Papilionoideae: Phaseoleae). Syst Bot 18 (in press)
Edmondson DL, Kane HJ and Andrews TJ (1990) Substrate isomerization inhibits ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase during catalysis. FEBS Lett 260: 62–66
Evans AM (1976) Beans. In: Simmonds NW (ed) Evolution of Crop Plants, pp 168–172. Longman, London
Evans JR (1986) The relationship between carbon-dioxide limited photosynthetic rate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase content in two nuclear-cytoplasm substitution lines of wheat, and the coordination of ribulose-bisphosphate-carboxylation and electron transport capacities. Planta 167: 351–358
Evans JR and Seemann JR (1984) Differences between wheat genotypes in specific activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the relationship to photosynthesis. Plant Physiol 74: 759–765
Hidalgo R (1988) The Phaseolus world collection. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic Resources of Phaseolus Beans, pp 67–90. Kluwer Academic Publishers, dordrecht, The Netherlands
Holbrook GP, Turner JA and Polans NO (1992) Dark inhibition of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in legumes: A biosystematic study. Photosynth Res 32: 37–44
Kobza J and Seemann JR (1988) Mechanism of light regulation of ribulose-1,5-carboxylase activity and photosynthesis in intact leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3815–3819
Marechal R, Mascherpa J and Stainier F (1978) Etude taxonomique d'un groupe complexe d'especies des genres Phaseolus et Vigna (Papilionaceae) sur la base de donées morphologiques et polliniques, traitées par l'analyse informatique. Biossiera 28: 1–273
Moore BD, Kobza J and Seemann JR (1991) Measurement of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate in plant leaves by isotope dilution. Plant Physiol 96: 208–213
Sage RF, Sharkey TD and Seemann JR (1990) Regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/Oxygenase activity in response to light intensity and CO2 in the C3 annuals Chenopodium album L. and Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol 94: 1735–1742
Salvucci ME (1989) Regulation of Rubisco activity in vivo. Physiol Plant 77: 164–171
Seemann JR, Berry JA, Freas SM and Krump MA (1985) Regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in vivo by a light modulated inhibitor of catalysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 8024–8028
Seemann JR, Kobza J and Moore BD (1990) Metabolism of 2-carboxyarabinitol 1-phosphate and regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity. Photosynthe Res 23: 119–130
Servaites JC, Torisky RS and Chao SF (1984) Diurnal changes in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity and activation state in leaves of field-grown soybeans. Plant Sci Lett 35: 115–121
Servaites JC, Parry MA, Gutteridge S and Keys AJ (1986) Species variation in the predawn inhibition of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Plant Physiol 82: 1161–1163
Servaites JC, Shieh W and Geiger DR (1991) Regulation of photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle by ribulose bisphosphate and phosphoglyceric acid. Plant Physiol 97: 1115–1121
Sharkey TD, Seemann JR and Berry JA (1986) Regulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase activity in response to changing partial pressures of O2 and light in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Physiol 81: 788–791
Smartt J (1988) Morphological, physiological and biochemical changes in Phaseolus beans under domestication. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic Resources of Phaseolus Beans, pp 143–161. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Vu JCV, Allen LH and Bowes G (1984) Dark/light modulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase activity in plants from different photosynthetic categories. Plant Physiol 76: 834–845
White JW, Castillo JA and Ehleringer J (1990) Associations between productivity, root growth and carbon isotope discrimination in Phaseolus vulgaris under water deficit. Aust J Plant Physiol 17: 189–198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sage, R.F. Light-dependent modulation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activity in the genus Phaseolus . Photosynth Res 35, 219–226 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016553
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016553